Abstract
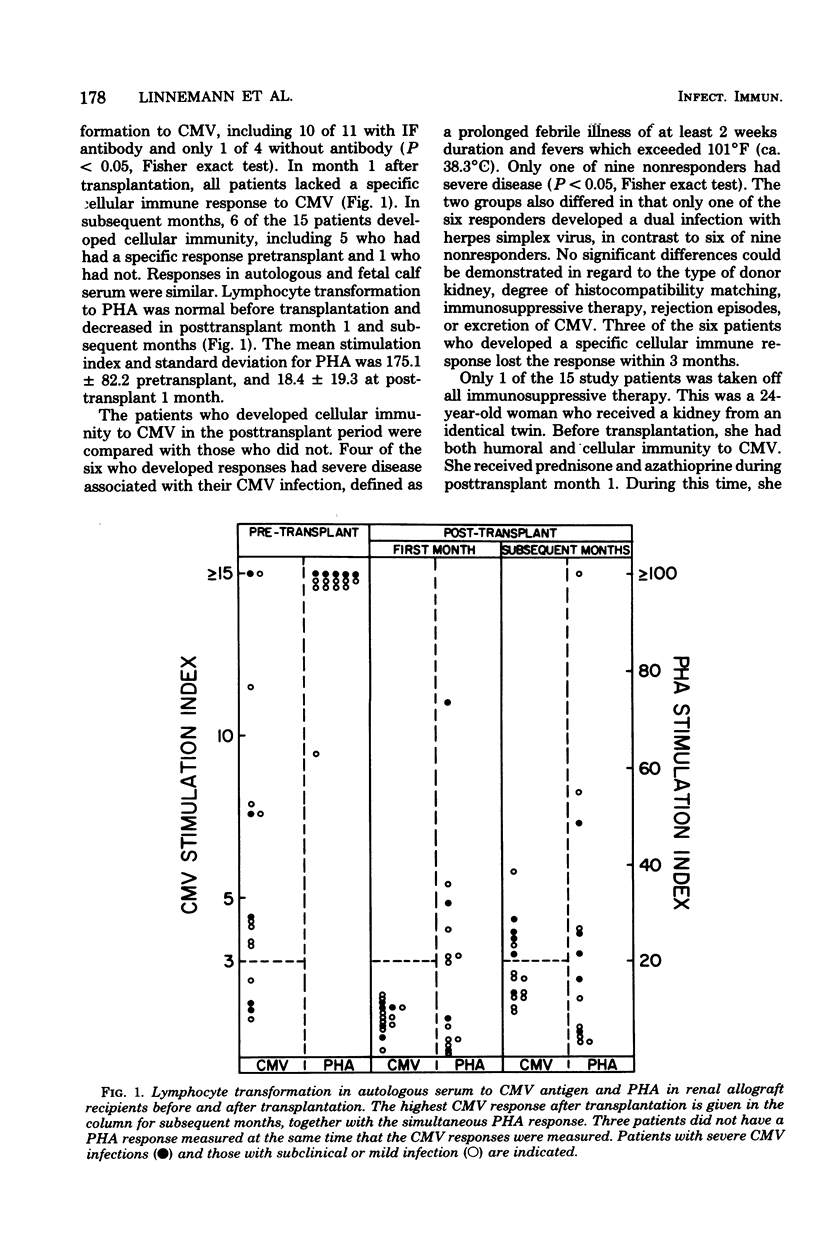
A prospective study of 15 patients who received renal transplants defined the effect of renal transplantation on the cellular immune response to cytomegalovirus infection. Of 15 patients, 14 developed cytomegalovirus infection, usually in the first 2 months after transplantation, and all infections were accompanied by a normal humoral immune response. After the initiation of immunosuppressive therapy and transplantation, there was a general depression of lymphocyte transformation, as reflected in the response to phytohemagglutinin, accompanied by a specific defect in cellular immunity, as indicated by lymphocyte transformation to cytomegalovirus antigen. Eleven patients had cellular immunity to cytomegalovirus before transplantation, and all of these became negative in the first month after transplantation. In subsequent months, only 6 of the 14 study patients with cytomegalovirus infection developed specific cellular immune responses to cytomegalovirus. This occurred most often in patients who had severe febrile illnesses in association with infection. The specific cellular immune response which developed in the posttransplant period did not persist in three of the patients. This study demonstrates the dissociation of the humoral and cellular immune response to cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant patients and indicates the importance of the loss of cellular immunity in the appearance of infection. Previously infected patients lost their cell-mediated immunity and had reactivation infections despite the presence of serum antibody.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betts R. F., Freeman R. B., Douglas R. G., Jr, Talley T. E. Clinical manifestations of renal allograft derived primary cytomegalovirus infection. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Jul;131(7):759–763. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120200041010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betts R. F., George S. D., Rundell R. B., Freeman R. B., Douglas R. G., Jr Comparative activity of immunofluorescent antibody and complement-fixing antibody in cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):151–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.151-156.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrz R. C., Marker S. C., Knorr S. O., Kalis J. M., Balfour H. H., Jr Specific cell-mediated immune defect in active cytomegalovirus infection of young children and their mothers. Lancet. 1977 Oct 22;2(8043):844–847. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman C. A., Phair J. P., Linnemann C. C., Jr, Schiff G. M. Cell-mediated immunity in humans during viral infection. I. Effect of rubella on dermal hypersensitivity, phytohemagglutinin response, and T lymphocyte numbers. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):212–215. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.212-215.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard R. B., Rand K. H., Arvin A. M., Merigan T. C. Cell-mediated immunity of cytomegalovirus infection in normal subjects and cardiac transplant patients. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):541–549. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Frenkel L. D., Fuccillo D. A., Hensen S. A., Vincent M. M., Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Bellanti J. A. Specific impairment of cell-mediated immunity in mothers of infants with congenital infection due to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):386–391. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Aaberg T. M., Dee T. H., Heim L. H. Therapy of cytomegalovirus retinitis with transfer factor. Cell Immunol. 1975 Sep;19(1):8–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Aguilar-Torres F. G., Balay J., Heim L. R. Assessment of the status of cell-mediated immunity in cytomegalovirus-infected renal allograft recipients. Cell Immunol. 1978 Apr;37(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Balay J. Cytomegalovirus infection and immunity in renal allograft recipients: assessment of the competence of humoral immunity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1633–1637. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1633-1637.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Kauffman H. M. Clinical efficacy of adenine arabinoside in therapy of cytomegalovirus infections in renal allograft recipients. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):202–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E. S. Clinical aspects of cytomegalovirus infection in kidney-graft recipients. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(4):315–323. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-4.04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas I. T., Soothill J. F., Hawkins G. T., Marshall W. C. Transfer-factor treatment in congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Lancet. 1977 Nov 19;2(8047):1056–1057. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91887-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman G. B., Ahmed A., Strong D. M., Knudsen R. C., Grace W. R., Sell K. W. Lymphocyte activation in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus and cytomegalovirus infections. In vitro stimulation in response to viral-infected cell lines. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):839–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


