Abstract
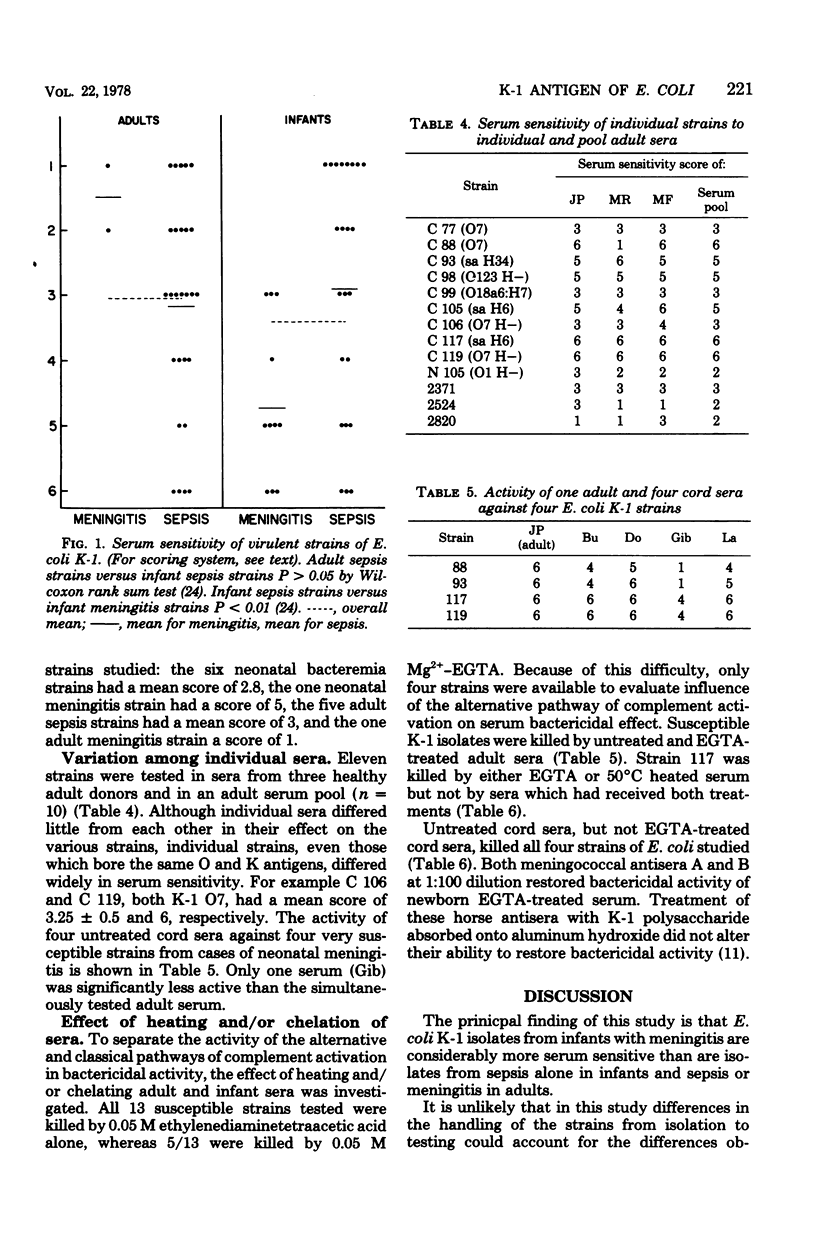
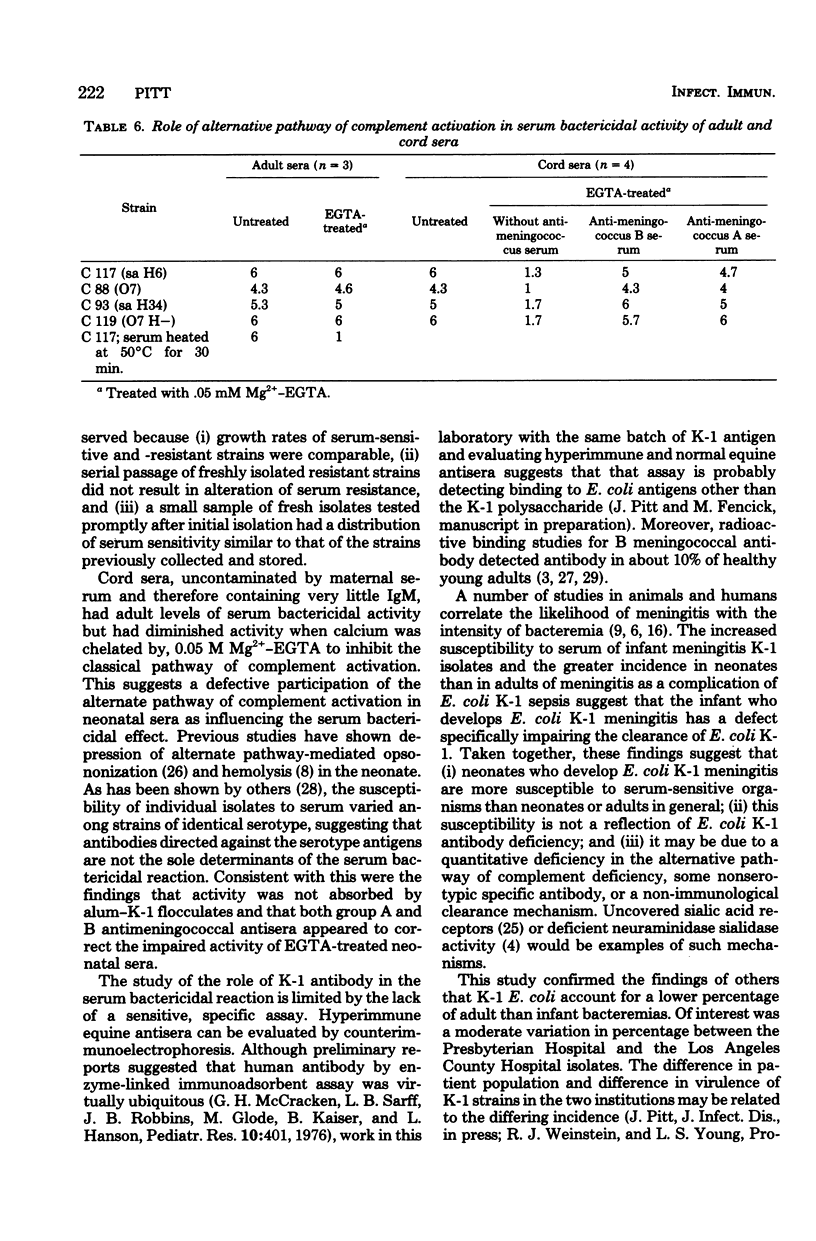
K-1 Escherichia coli are far more frequent in neonatal sepsis (36% of E. coli sepsis) and meningitis (80% of E. coli meningitis) than would be expected by the frequency of K-1 E. coli colonization in neonates (11 to 25%). There is no apparent parallel in cases of sepsis in adults. To study further this apparent age-related difference in virulence, E. coli K-1 clinical isolates were tested for their sensitivity to sera. Strains isolated from cases of neonatal meningitis were more sensitive to serum bactericidal activity than those from cases of neonatal or adult sepsis or adult meningitis (P < 0.01). Serum sensitivity did not appear to be determined by K or O antigens. Four isolates sensitive to serum bactericidal activity obtained from neonatal cerebrospinal fluid were killed by adult serum chelated with 0.05 M Mg2+ ethyleneglycol-bis (β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N-tetraacetic acid (EGTA), suggesting that the alternative pathway was activated. Although untreated neonatal sera killed these strains as well as adult sera did, EGTA-treated neonatal sera were less effective than EGTA-treated adult sera. This suggests that the alternative pathway function was not activated in neonatal sera. The bactericidal defect of neonatal EGTA-treated serum was partially corrected by addition of either A or B hyperimmune equine meningococcal antiserum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRY G. T., GOEBEL W. F. Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature. 1957 Jan 26;179(4552):206–206. doi: 10.1038/179206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt B. L., Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S. A radioactive antigen-binding assay for Neisseria meningitidis polysaccharide antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):913–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzman D. E., Fischer G. W., Schoenknecht F. D. Neonatal Escherichia coli septicemia--bacterial counts in blood. J Pediatr. 1974 Jul;85(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein P. A., Kaplan S. R. The alternative pathway of complement activation in the neonate. Pediatr Res. 1975 Oct;9(10):803–806. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197510000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode M. P., Sutton A., Moxon E. R., Robbins J. B. Pathogenesis of neonatal Escherichia coli meningitis: induction of bacteremia and meningitis in infant rats fed E. coli K1. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.75-80.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E. Human heat labile opsonins: evidence for their mediation via the alternate pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):26–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Winkelhake J. L., Zollinger W. D., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Immunochemical similarity between polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli 07: K1(L):NM and group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. E., Rosse W., Frank M. M. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Alternate-complement-pathway-mediated lysis induced by magnesium. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 4;289(14):705–709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310042891401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Serum complement levels in bacteremia due to gram-negative organisms. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):21–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Jann B., Jann K. Immunoelectrophoretic patterns of extracts from all Escherichia coli O and K antigen test strains: correlation with pathogenicity. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):142–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozsoylu S., Hosain F., McIntyre P. A. Functional development of phagocytic activity of the spleen. J Pediatr. 1977 Apr;90(4):560–562. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen B. H., Graham J. A., Brooks G. F. Human deficiency of the eighth component of complement. The requirement of C8 for serum Neisseria gonorrhoeae bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):283–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI108279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Smith A. L., Anderson P., Smith D. H. The paradox of Hemophilus infuenzae type B bacteremia in the presence of serum bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1172/JCI108525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddart R. W., Widdowson E. M. Changes in the organs of pigs in response to feeding for the first 24 h after birth. III. Fluorescence histochemistry of the carbohydrates of the intestine. Biol Neonate. 1976;29(1-2):18–27. doi: 10.1159/000240844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Opsonic activity in the newborn: role of properdin. Pediatrics. 1973 Jul;52(1):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Artenstein M. S. Latex agglutination test for measurement of antibodies to meningococcal polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):346–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.346-351.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Randall E. Sensitivity of serologically classified strains of escherichia coli of human origin to the serum bactericidal system. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Feb;259(2):114–119. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197002000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


