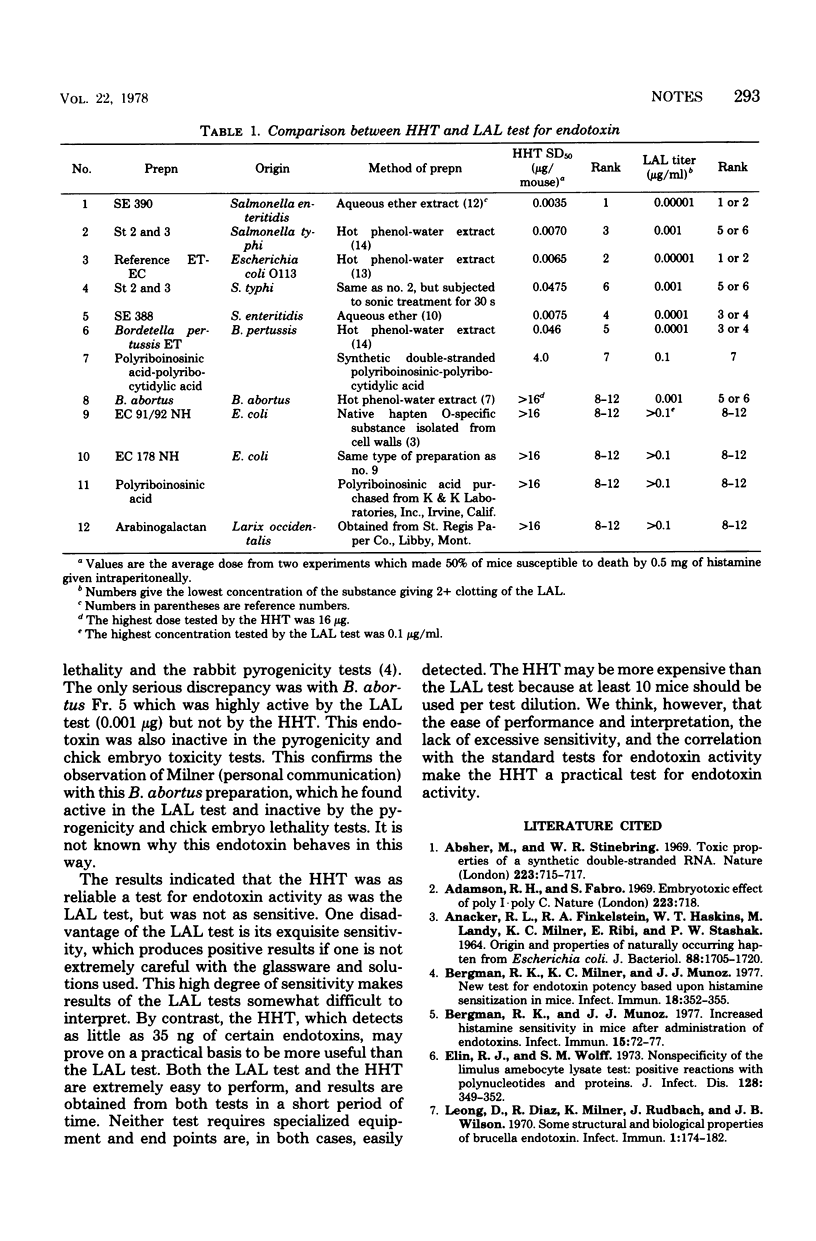
Abstract
The histamine hypersensitivity test and the Limulus amoebocyte lysate test were compared for their effectiveness to quantitate endotoxin activity. The two tests compared favorably in all the trials, except with a sample of endotoxin from Brucella abortus that gave a positive Limulus amoebocyte lysate test at a concentration of 0.001 microgram, while failing to sensitize mice to histamine at a dose of 16 microgram per mouse. The Limulus amoebocyte lysate test was more sensitive than the histamine hypersensitivity test.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., FINKELSTEIN R. A., HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E., STASHAK P. W. ORIGIN AND PROPERTIES OF NATURALLY OCCURRING HAPTEN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1705–1720. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1705-1720.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absher M., Stinebring W. R. Toxic properties of a synthetic double-stranded RNA. Endotoxin-like properties of poly I. poly C, an interferon stimulator. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):715–717. doi: 10.1038/223715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson R. H., Fabro S. Embryotoxic effect of poly I. poly C. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):718–718. doi: 10.1038/223718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. K., Milner K. C., Munoz J. J. New test for endotoxin potency based upon histamine sensitization in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):352–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.352-355.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. K., Munoz J. J. Increased histamine sensitivity in mice after administration of endotoxins. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.72-77.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Nonspecificity of the limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):349–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN IN THE EXTRACELLULAR COAGULATION OF LIMULUS BLOOD. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Sep;115:265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Diaz R., Milner K., Rudbach J., Wilson J. B. Some structural and biological properties of Brucella endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):174–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.174-182.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay H. L., Trown P. W., Brandt J., Forbes M. Pyrogenicity of poly I. poly C in rabbits. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):717–718. doi: 10.1038/223717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. I. Metabolism of galactose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., MILNER K. C., PERRINE T. D. Endotoxic and antigenic fractions from the cell wall of Salmonella enteritidis; methods for separation and some biologic activities. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold R. B., Fine J. A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):334–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A., Akiya F. I., Elin R. J., Hochstein H. D., Luoma M. K., Milner E. C., Milner K. C., Thomas K. R. Preparation and properties of a national reference endotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.21-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



