Abstract
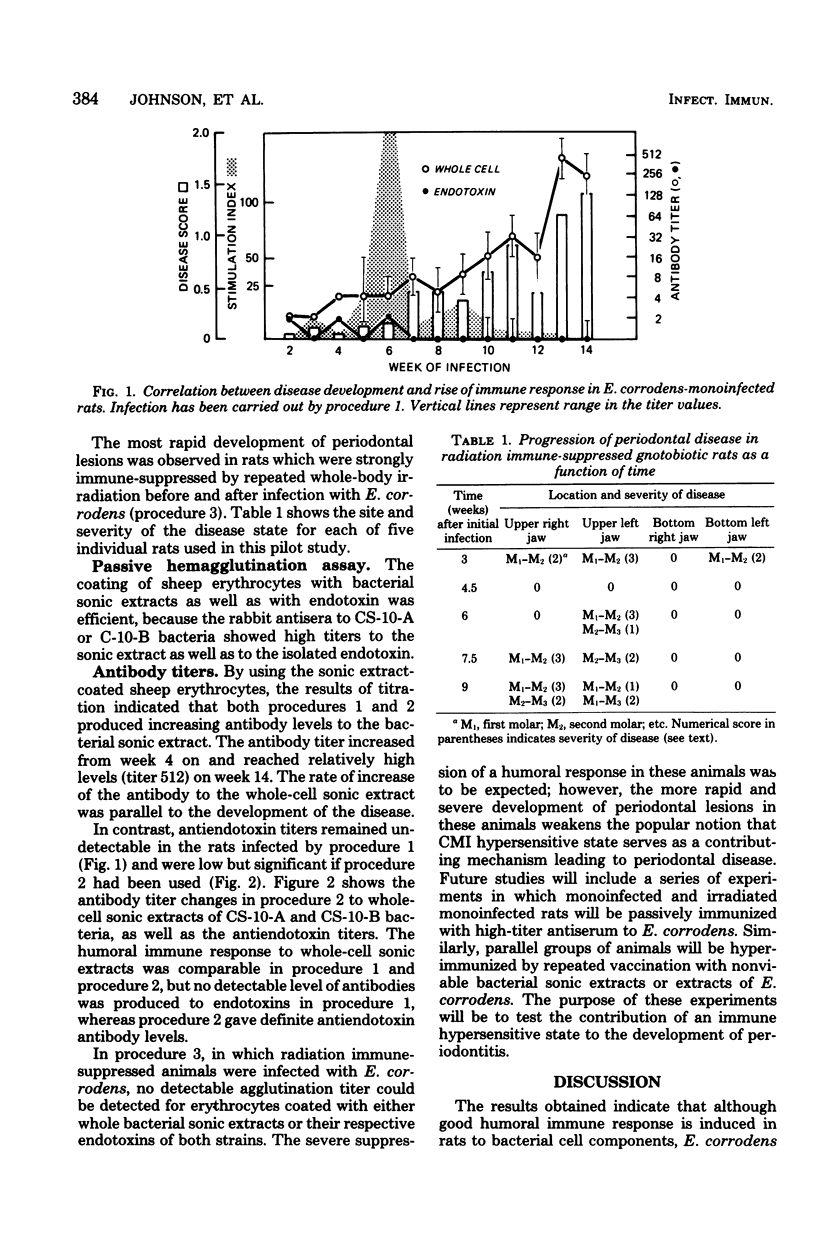
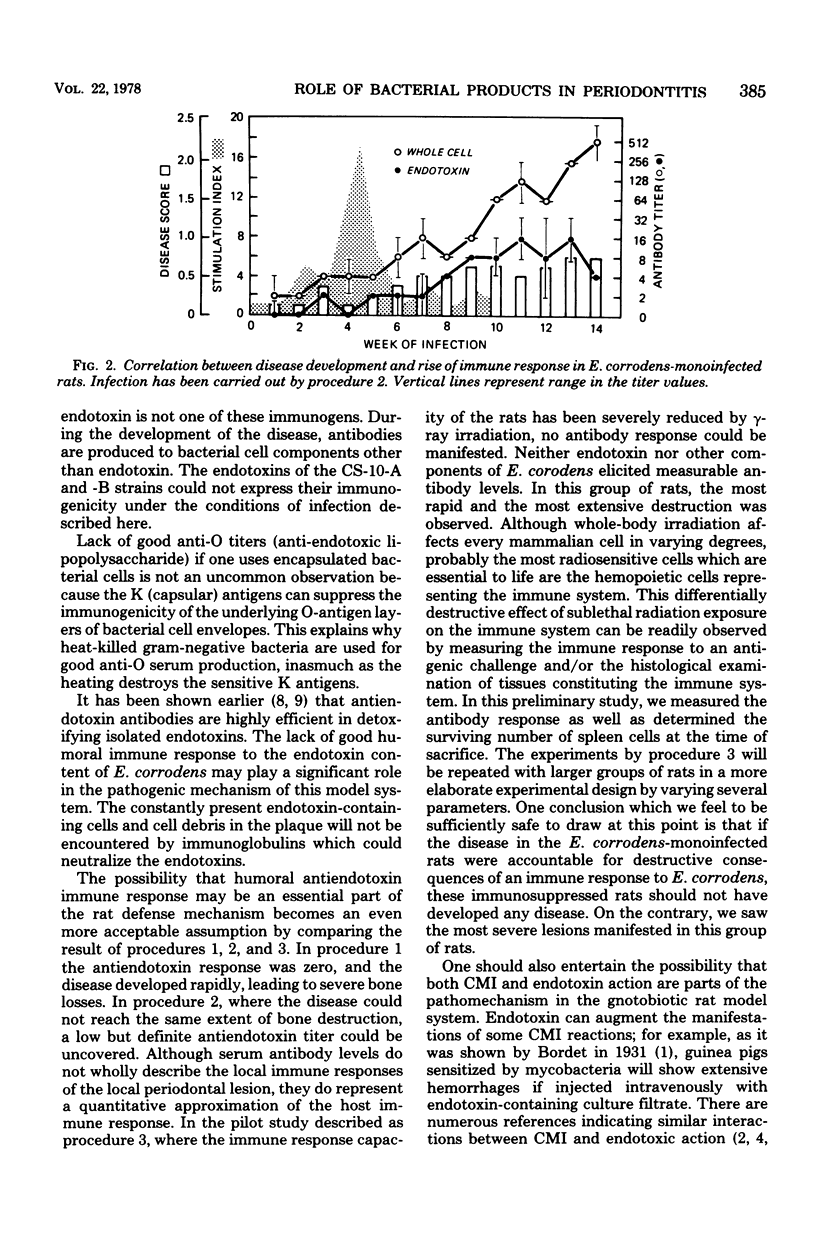
Eikenella corrodens can induce periodontitis-like disease in gnotobiotic rats. Some components of this bacterial cell elicit measurable humoral immune response during the development of the disease, but in this system endotoxin is not among the efficient immunogens. Because no humoral immune response could be seen to the endotoxin of Eikenella corrodens it is assumed that this endotoxin can act uncontrolled in monoinfected rats. Accordingly, the lack of protective humoral immune response to pathogenic components of Eikenella corrodens may be the major factor permitting the development of the disease described here. The possibility that both cell-mediated immunity and uncontrolled endotoxic action are parts of the pathomechanism of the disease is supported by our observations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson D. A., Behling U. H., Lai C. H., Listgarten M., Socransky S., Nowotny A. Role of bacterial products in periodontitis: immune response in gnotobiotic rats monoinfected with Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):246–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.246-253.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Mackaness G. B. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the induction and expression of cell-mediated immunity. II. Stimulation of the efferent arc. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Johnson D., Nowotny A., Tanner A. C., Socransky S. S. Histopathology of periodontal disease in gnotobiotic rats monoinfected with Eikenella corrodens. J Periodontal Res. 1978 Mar;13(2):134–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1978.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., BERTRAM L. F., ARBESMAN C. E. Demonstration of Escherichia coli 055 and 0111 antigens by means of hemagglutination test. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Feb;79(2):255–257. doi: 10.3181/00379727-79-19343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Radvany R., Neale N. E. Neutralization of toxic bacterial O-antigens with O-antibodies while maintaining their stimulus on non-specific resistance. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(10):1107–1114. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radvany R., Neale N. L., Nowotny A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. VI. Neutralization of endotoxic O-antigens by homologous O-antibody. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):763–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E., ULLMAN G. E., HOFFMAN R. G. Sensitivity of mice to endotoxin after vaccination with BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Oct;99(1):167–169. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAKATELLIS A., STINEBRING W. R., AXELROD A. E. Hyperreactivity to endotoxin in BCG-treated guinea pigs and its relationship to delayed hypersensitivity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Feb;112:349–352. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


