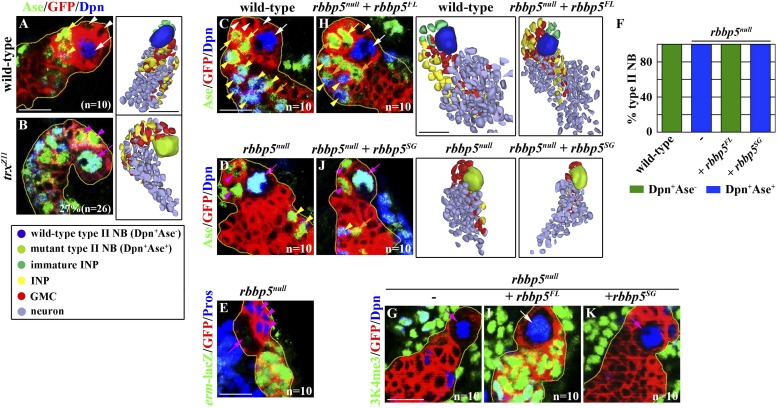
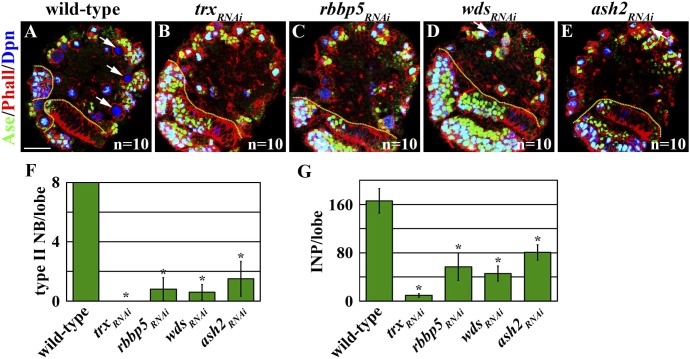
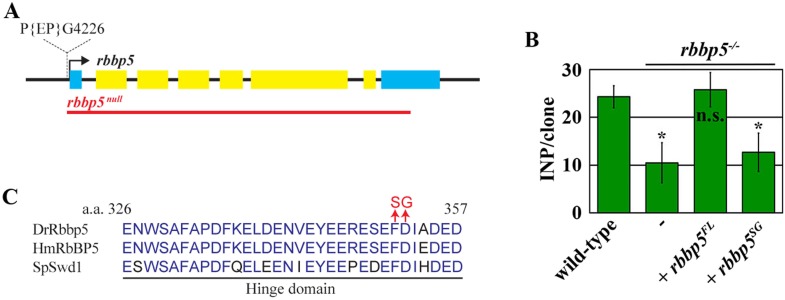
Figure 3. Trx and the core components of the SET/MLL complex maintain a type II neurobalst functional identity dependently on their catalytic activity for H3K4 methylaiton.
(A–B) The function of trx for the H3K4 methylation is required for the maintenance of a type II neuroblast functional identity. (A–B) In the 72-hr clones, a trxZ11 mutant type II neuroblast displays a type I neuroblast marker expression profile and directly generates GMCs. Scale bar, 10 μm. Three-dimensionally reconstructed images of the clones are shown to the right. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C–K) The function of rbbp5 for the H3K4 methylation is required for the maintenance of a type II neuroblast functional identity. (C–E, H, J) In the 96-hr clones, rbbp5null type II neuroblasts display a type I neuroblast marker expression profile and directly generate GMCs. Over-expression of rbbp5FL but not rbbp5SG restores a type II neuroblast functional identity in rbbp5null type II neuroblasts. Three-dimensionally reconstructed images of the clones are shown to the right. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) The frequency of type II neuroblasts of the indicated genotypes displaying the type I or type II marker expression profiles. (G, I, K) rbbp5 function is essential for the H3K4 methylation in fly larval brains. Scale bar, 10 μm.