Abstract
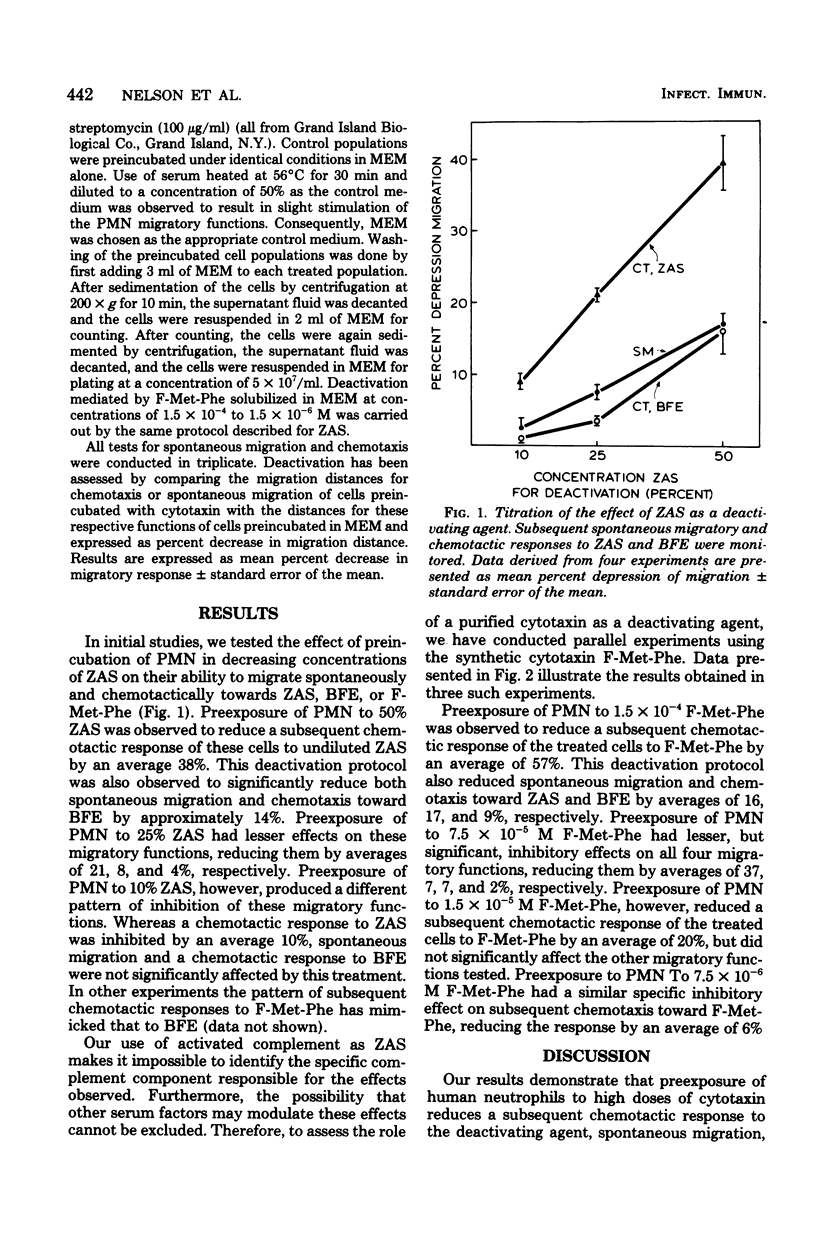
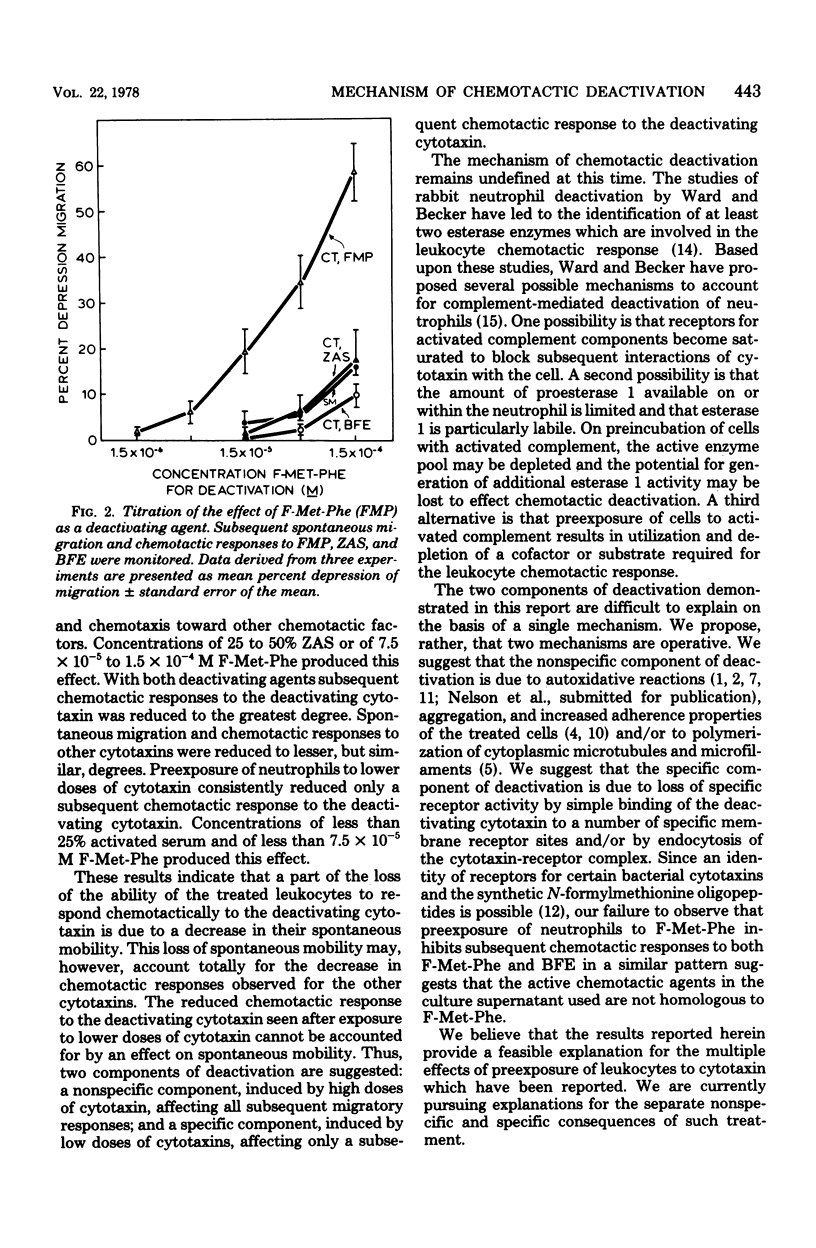
Human polymorphonuclear neutrophils have been preexposed to activated complement as zymosan-activated serum (ZAS) or to the chemotactic oligopeptide N-formyl methionylphenylalanine (F-Met-Phe). Spontaneous migration and chemotactic responses toward the deactivating and other cytotaxins were monitored after washing and resuspension of cells in cytotaxin-free medium. Two patterns of deactivation were observed. Preexposure of the leukocytes to high doses of ZAS or F-Met-Phe decreased all subsequent migratory responses. Preexposure of the leukocytes to lower doses of ZAS or F-Met-Phe decreased only a subsequent chemotactic response to the deactivating cytotaxin. These results suggest two mechanisms, or components, of chemotactic deactivation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A., Allen J. M., Davis J. Autooxidation as a basis for altered function by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Aug;50(2):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase--H2O2--halide system: cytotoxic effect on human blood leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Jacob H. S. Complement-mediated granulocyte dysfunction in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1976 Jun;47(6):931–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Jacob H. S. In vitro granulocyte adherence and in vivo margination: two associated complement-dependent functions. Studies based on the acute neutropenia of filtration leukophoresis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):641–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Rosenthal A. S. The regulatory role of divalent cations in human granulocyte chemotaxis. Evidence for an association between calcium exchanges and microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):594–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Biggar W. D. Influence of serum-derived chemotactic factors and bacterial products on human neutrophil chemotaxis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):212–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.212-220.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock J. C., Stossel T. P. Detection, pathogenesis, and prevention of damage to human granulocytes caused by interaction with nylon wool fiber. Implications for filtration leukapheresis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1183–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI108871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E. Chemotaxis and random mobility. Clinical and biologic differentiation. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1974;19:338–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factor influences on the aggregation, swelling, and foreign surface adhesiveness of human leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1978 Mar;90(3):537–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation. Protection of phagocytosine leukocytes by superoxide dismutase. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1319–1323. doi: 10.1172/JCI108208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Mechanisms of the inhibition of chemotaxis by phosphonate esters. J Exp Med. 1967 Jun 1;125(6):1001–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.6.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Whitmer D., Geotzl E. J., Austen K. F. Chemotactic deactivation of human eosinophils by the eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (38527). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jan;148(1):301–306. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



