Abstract
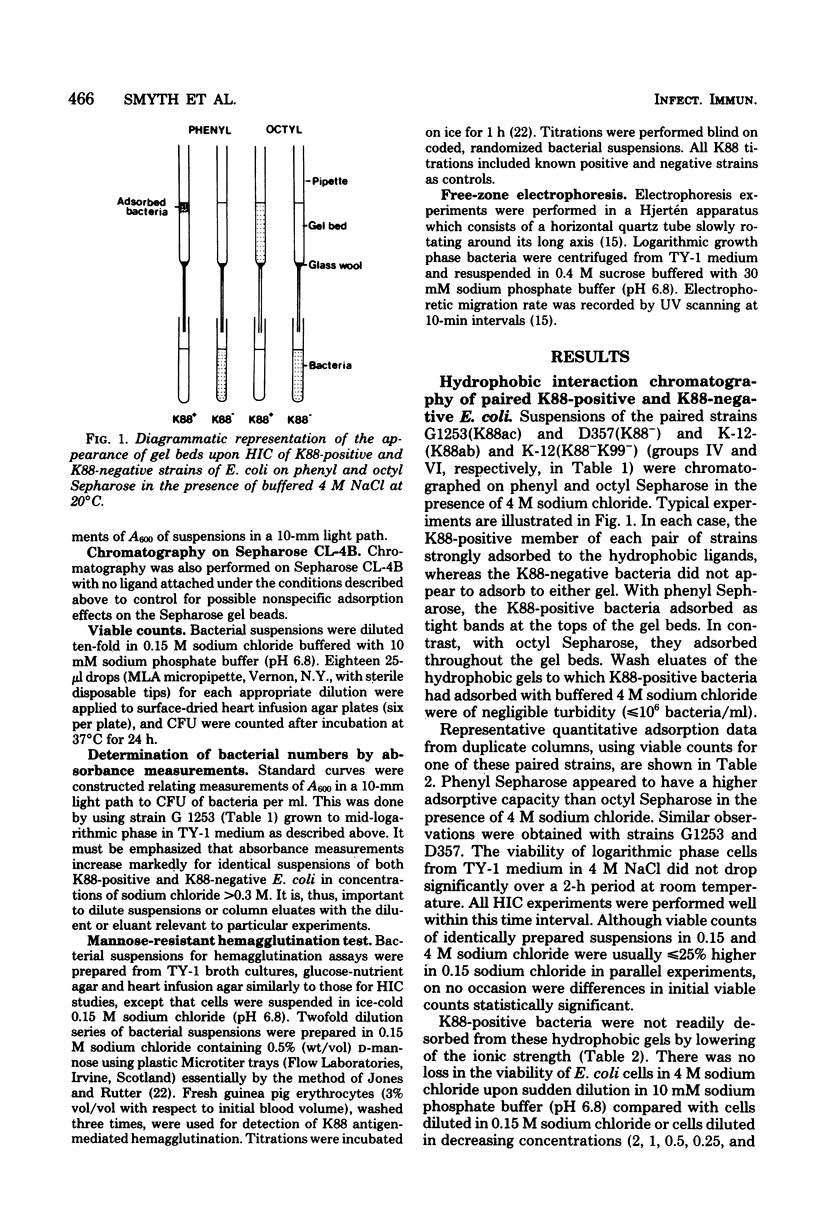
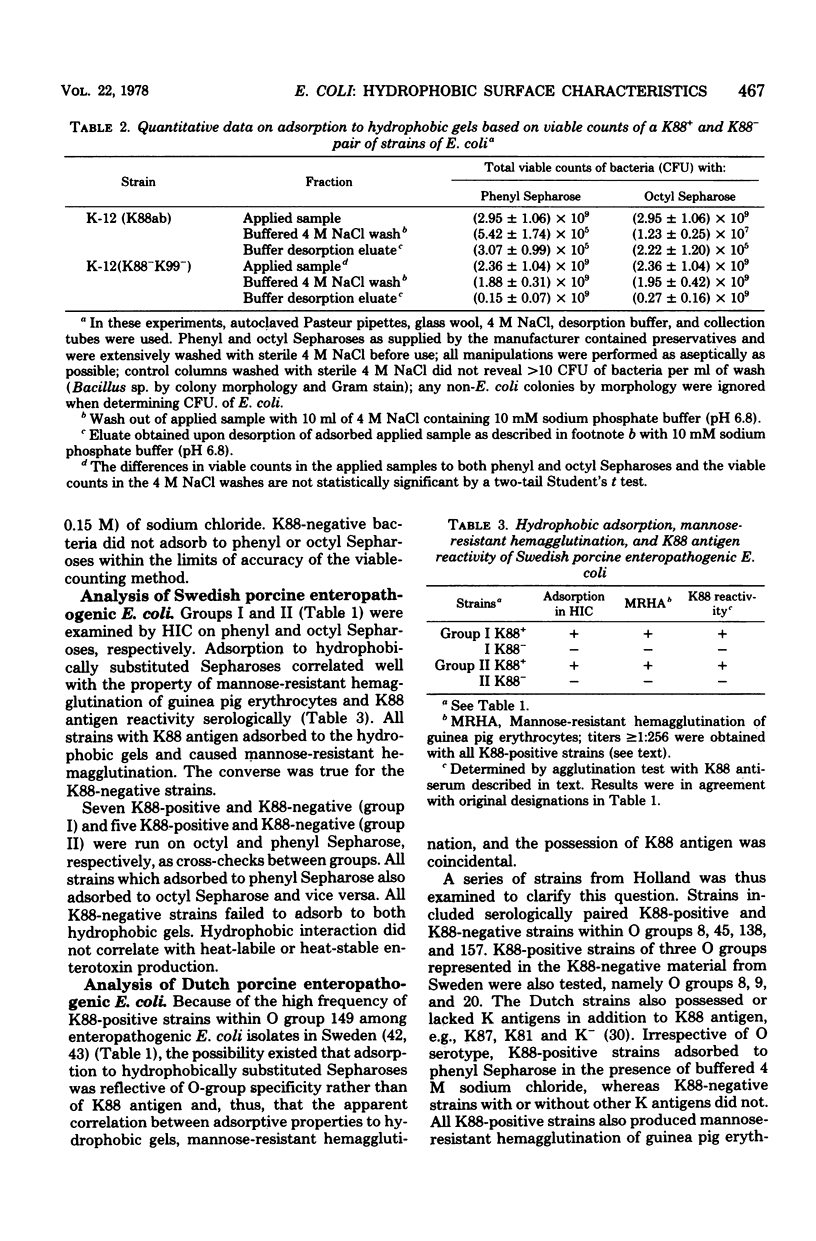
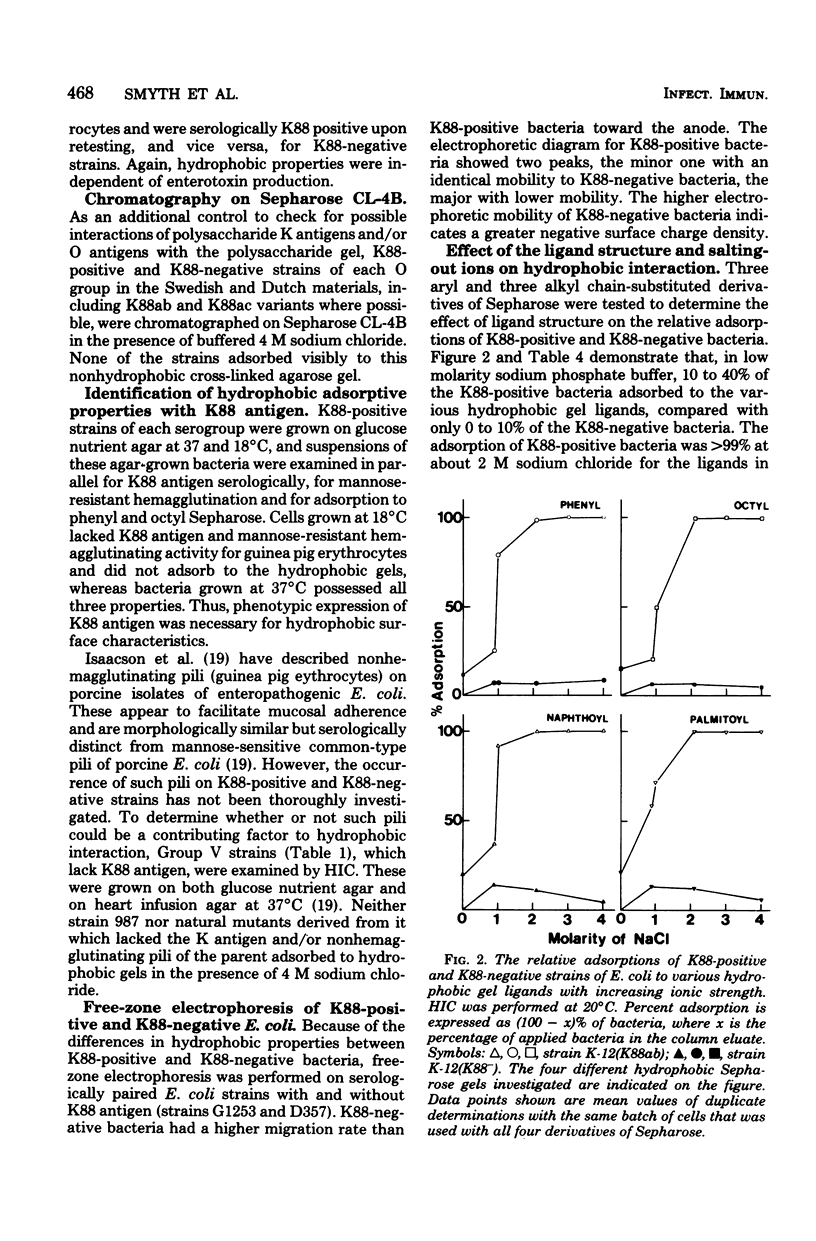
Porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains possessing or lacking K88 antigen were studied by using hydrophobic interaction chromatography on cross-linked agarose gels with alkyl or aryl substituents (amphiphilic gels) to determine whether or not they possessed surface-associated hydrophobic properties. Strains with K88ab or K88ac antigen adsorbed to phenyl and octyl Sepharose gels in the presence of 4 M sodium chloride. This property correlated with phenotypic expression of K88 antigen. Cells grown at 37 degrees C but not those grown at 18 degrees C possessed hydrophobic adsorptive characteristics in addition to the property of mannose-resistant hemagglutination of guinea pig erythrocytes. Adsorption of K88-positive strains to gels with hydrophobic ligands was independent of O group and enterotoxicity. Strains lacking K88 antigen did not adsorb to the hydrophobically substituted derivatives of Sepharose and lacked mannose-resistant hemagglutinating characteristics. Neither the presence of additional polysaccharide K antigens nor nonhemagglutinating pili conferred the property of hydrophobic interaction on the strains. K88-positive bacteria had a lower electrophoretic migration rate than did K88-negative bacteria of the same serotype in free-zone electrophoresis. K88-positive bacteria also adsorbed strongly to hydrophobic ligands in the presence of 1 M ammonium sulfate, whereas K88-negative strains did not. These observations provide evidence for the suspected role of hydrophobic interaction in the adhesive properties of certain enteropathogenic strains of E. coli. Moreover, hydrophobic interaction chromatography provides convenient and rapid alternative means of screening strains for a property potentially associated with adhesiveness.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINTON C. C., Jr, BUZZELL A., LAUFFER M. A. Electrophoresis and phage susceptibility studies on a filament-producing variant of the E. coli B bacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Dec;15(4):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldt D. H., Speckart S. F., Richards R. L., Alving C. R. Interactions of lectins with glycolipids in liposomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 10;74(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Sellwood R. An attempt to identify the intestinal receptor for the K88 adhesin by means of a haemagglutination inhibition test using glycoproteins and fractions from sow colostrum. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Feb;86(2):228–240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-2-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. N., Hogg S. D., Phillips G. O. Gradient elution of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli strains from a DEAE-cellulose column. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;41(1):189–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin G., Shaltiel S. Homologous series of aklyl agaroses discriminate detween erythrocytes from different sources. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1497–1503. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Blackett B., Everson J. S., Ward M. E. The influence of surface charge on the attachment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):359–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Chen K. C., Buchanan T. M. Neisseria pili proteins: amino-terminal amino acid sequences and identification of an unusual amino acid. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):442–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjertén S. Free zone electrophoresis. Chromatogr Rev. 1967 Dec;9(2):122–219. doi: 10.1016/0009-5907(67)80003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Nagy B., Moon H. W. Colonization of porcine small intestine by Escherichia coli: colonization and adhesion factors of pig enteropathogens that lack K88. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):531–539. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. The association of K88 antigen with haemagglutinating activity in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):135–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V. Competitive binding among oral strptococci to hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1977 Feb;56(2):157–165. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560021001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L., Johansson G. The tendency of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria and lipopolysaccharide to hydrophobic and ionic interaction, as studied in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Jun;85(3):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Special O:K:H serotypes among enterotoxigenic E. coli strains from diarrhea in adults and children. Occurrence of the CF (colonization factor) antigen and of hemagglutinating abilities. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Jul 18;163(2):99–110. doi: 10.1007/BF02121825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Wittig W., Sweeney E. J. A new E. coli serotype O149:K9 (B), K88ac (L): H10 isolated from diseased swine. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(3):491–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perers L., Andåker L., Edebo L., Stendahl O., Tagesson C. Association of some enterobacteria with the intestinal mucosa of mouse in relation to their partition in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):308–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren J., Pählman S., Glad M., Hjertén S. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography on non-charged Sepharose derivatives. Binding of a model protein, related to ionic strength, hydrophobicity of the substituent, and degree of substitution (determined by NMR). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 18;412(1):51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G., Robrish S. A., Bowen W. H. Interaction of hydroxyapatite and protein-coated hydroxyapatite with Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherberich J. E., Schäfer K., Mondorf W., Gauhl C., Sietzen W. Escherichia coli receptors on human kidney brush-border membranes. Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1181–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to pig intestinal brush borders: the existence of two pig phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S. Hydrophobic chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:126–140. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherbet G. V., Lakshmi M. S. Characterisation of Escherichia coli cell surface by isoelectric equilibrium analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):50–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speirs J. I., Stavric S., Konowalchuk J. Assay of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin with vero cells. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):617–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.617-622.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Edebo L., Magnusson K. E., Tagesson C., Hjertén S. Surface-charge characteristics of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria determined by aqueous two-phase partitioning and free zones electrophoresis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):334–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Magnusson K. E., Tagesson C., Cunningham R., Edebo L. Characterization of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by counter-current distribution in an aqueous two-polymer phase system. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):573–577. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.573-577.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo M. Partition of Salmonella typhimurium in a two-polymer acqueous phase system in relation to liability to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.36-41.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernström I., Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Tagesson C. Liability to hydrophobic and charge interaction of smooth Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS sensitized with anti-MS immunoglobulin G and complement. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.261-265.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O., Möllby R. Studies on Escherichia coli in pigs V. Determination of enterotoxicity and frequency of O groups and K 88 antigen in strains from 200 piglets with neonatal diarrhoea. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1978 Nov;25(9):719–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O. Studies on Escherichia coli in pigs. II. Serological investigations. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1971 Oct;18(8):569–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1971.tb01661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bosch J., McConnell M. Fusion of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicle membranes induced by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4409–4413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


