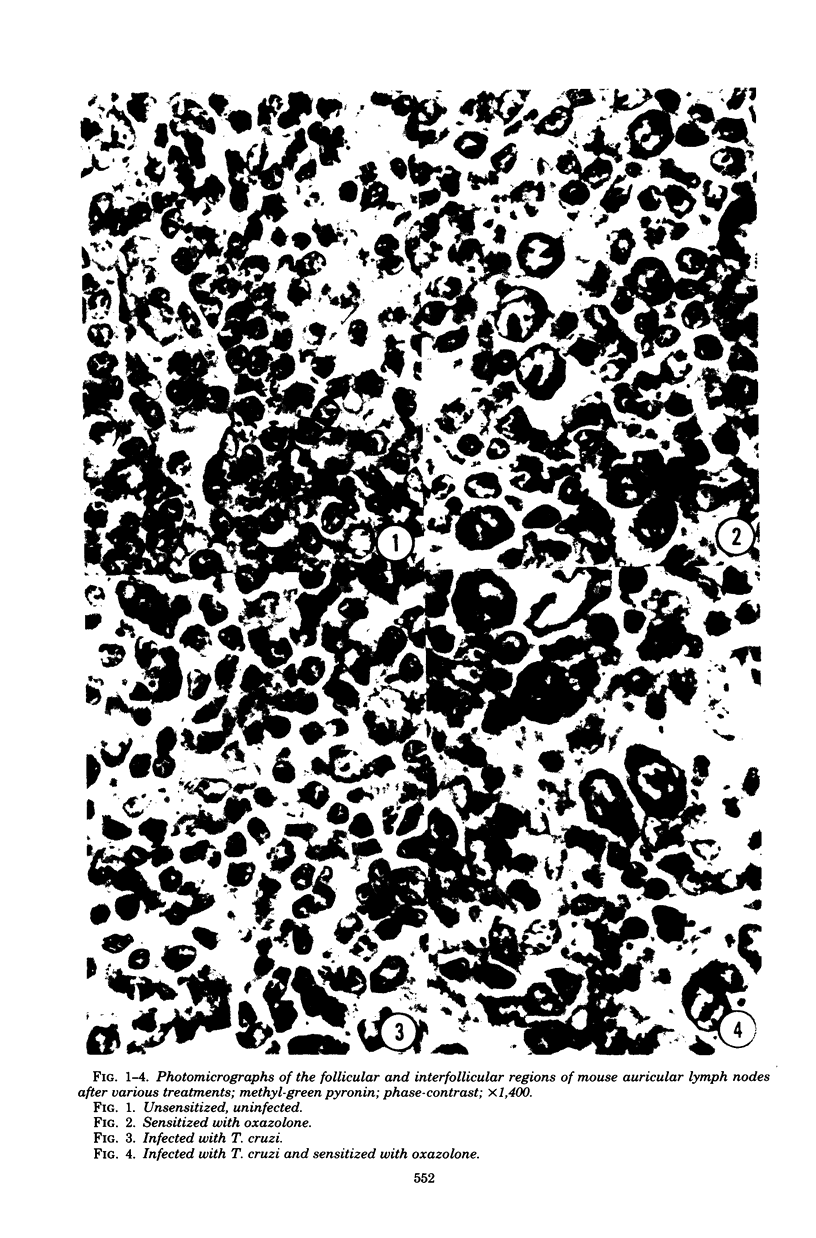
Abstract
Mechanisms of depression of contact sensitivity responses in C57BL/10 mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi were studied. Cellular involvement during sensitization with oxazolone was investigated in mice acutely infected with T. cruzi. Contact sensitivity was not expressed in mice during the latter stages of the acute infection. Spleen cells from sensitized, infected mice which were unable to respond to oxazolone could confer contact sensitivity upon normal syngenic mice as effectively as spleen cells from uninfected, sensitized donors. The ability of mice infected with T. cruzi to respond to an eliciting dose of oxazolone was significantly improved when macrophages from normal syngenic donors were administered to them at the time of skin test. When either normal or infected mice were used as recipients of lymphocytes from sensitized donors, the normal mice responded significantly better than did infected mice after administration of an eliciting dose of oxazolone. An increase in pyroninophilic cells was observed in draining lymph nodes after application of a sensitizing dose of oxaxolone to the ears of either normal or acutely infected mice. These results indicate that suppression of contact sensitivity during acute T. cruzi infection is directed toward the efferent arm rather than the afferent arm of the response.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. B., Seed J. R. Effects of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense infections in Microtus montanus on susceptibility to Ehrlich's tumors. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):388–391. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.388-391.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Ptak W. Contact and delayed hypersensitivity in the mouse. I. Active sensitization and passive transfer. Immunology. 1968 Sep;15(3):405–416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia. 3. Immunological studies. IV. Pathogenesis of diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970;64(3):380–393. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(70)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Ortiz-Ortiz L., Garcia W., Martinez T., Capin R. Trypanosoma cruzi: early immune responses in infected mice. Exp Parasitol. 1975 Jun;37(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(75)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Stauber L. A., Palczuk N. C. Leishmania donovani: antibody response to chicken ovalbumin by infected golden hamsters. Exp Parasitol. 1969 Aug;25(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(69)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Jayawardena A. N. Suppressor cells in mice infected with Trypanosoma brucei. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Bradley-Moore A. M., Bryceson A. D., Palit A. Immunosuppression in children with malaria. Lancet. 1972 Jan 22;1(7743):169–172. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Brown J. C., De Jesus D. G., Holborow E. J. Immunosuppression in murine malaria. II. The effect on reticulo-endothelial and germinal centre function. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Sep;9(3):345–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Playfair J. H., Torrigiani G. Immunosuppression in murine malaria. I. General characteristics. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Mar;8(3):467–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Whittle H. C., Molyneux D. H. Immunosuppression in Gambian trypanosomiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1973;67(6):846–850. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(73)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes R. J., Handwerger B. S., Terry W. D. Synergy between subpopulations of mouse spleen cells in the in vitro generation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity: evidence for the involvement of a non-T cell. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1646–1659. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huldt G., Gard S., Olovson S. G. Effect of Toxoplasma gondii on the thymus. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):301–303. doi: 10.1038/244301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Waksman B. H. Suppressor cells in experimentally trypanosomiasis. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):539–541. doi: 10.1038/265539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. M., Wallace J. H. Suppression of cell-mediated immunity in experimental African trypanosomiasis. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):335–339. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.335-339.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. K., Jennings F. W., Murray M., Urquhart G. M. The nature of immunosuppression in Trypanosoma brucei infections in mice. II. The role of the T and B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):825–840. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptak W., Asherson G. L. Contact and delayed hypersensitivity in the mouse. II. The role of different cell populations. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):769–775. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Larson C. L., Speer C. A. Suppression of cell-mediated immunity in experimental Chagas' disease. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Jun 3;52(1):11–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00380553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland G. T., Petitt L. E., Voller A. Immunodepression in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Jul;22(4):452–455. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L. Cytology of the induction of hypersensitivity. Br Med Bull. 1967 Jan;23(1):3–8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart G. M., Murray M., Murray P. K., Jennings F. W., Bate E. Immunosuppression in Trypanosoma brucei infections in rats and mice. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1973;67(4):528–535. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(73)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]