Abstract
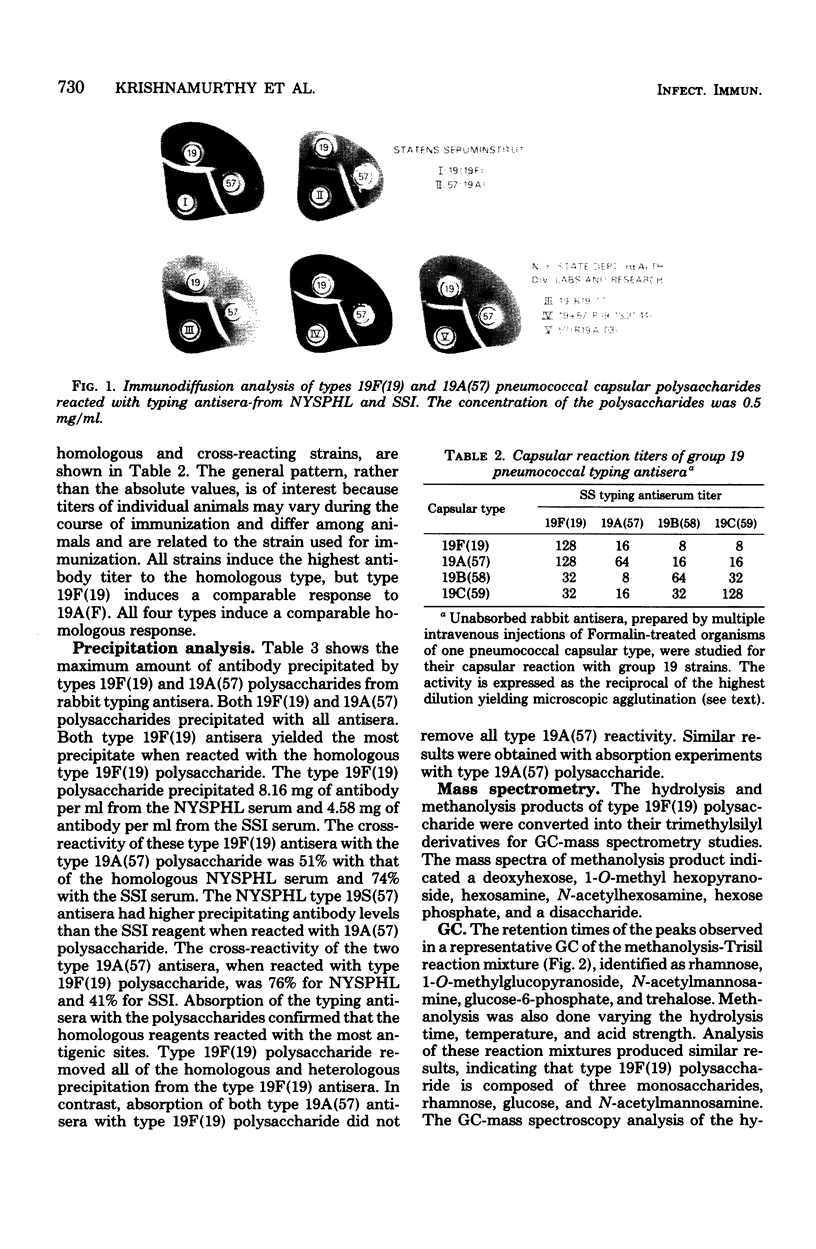
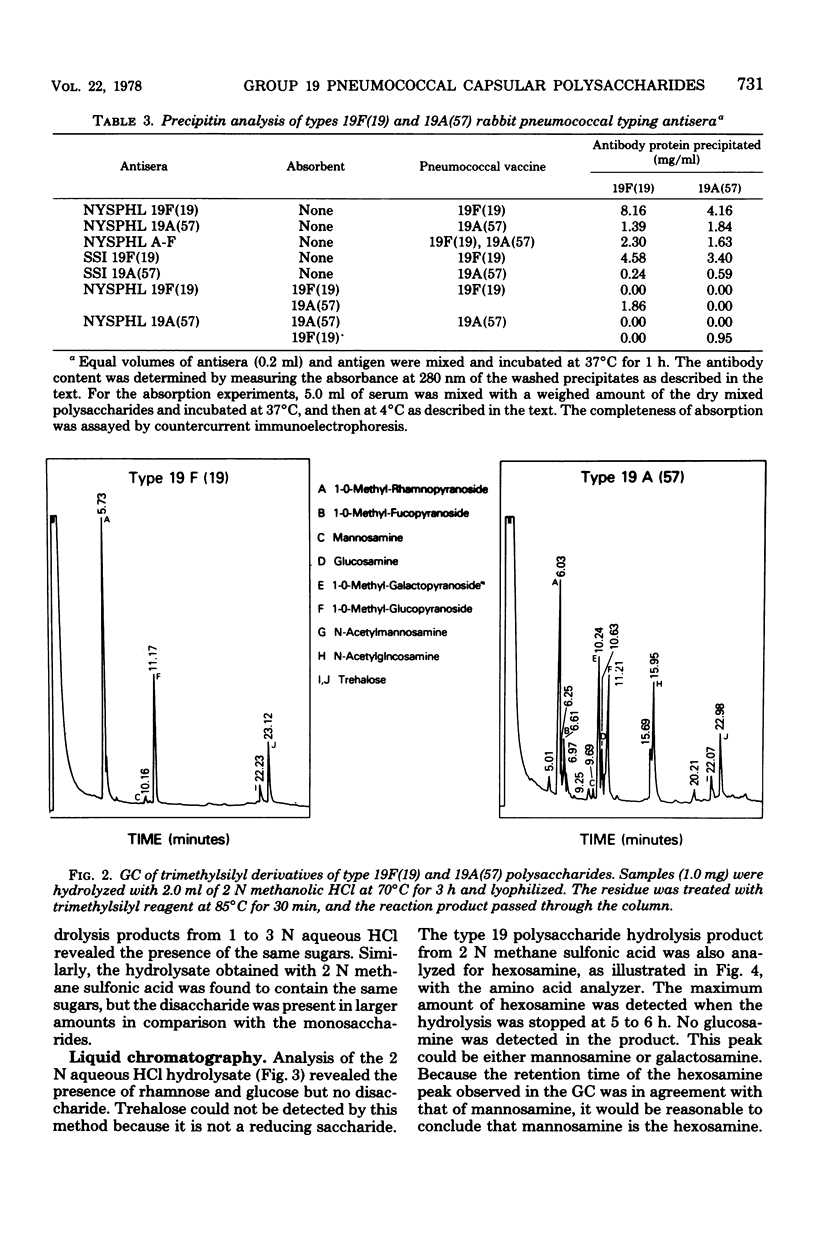
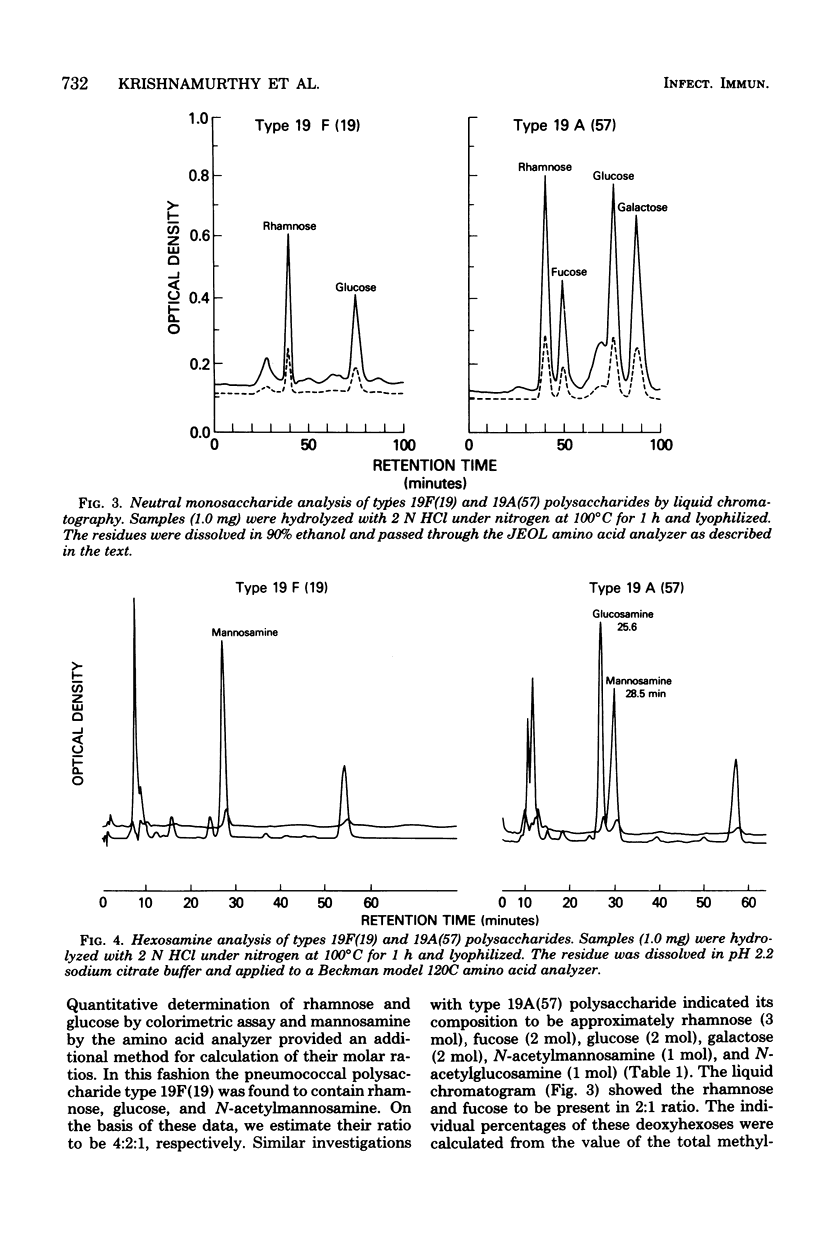
The immunological relation, physicochemical characteristics, and chemical composition of type 19F(19) and 19A(57) within the cross-reactive group 19 pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides were studied. By using rabbit hyperimmune diagnostic antisera in agglutination, immunodiffusion, quantitative precipitation, and absorption assays, extensive cross-antigenicity and cross-immunogenicity were demonstrable between the disease-associated types 19F(19) and 19A(57). Types 19B(58) and 19C(59), rarely associated with human disease, were extensively cross-reactive with each other but reacted weakly with types 19F(19) and 19A(57). Both types 19F(19) and 19A(57) polysaccharides contained trace amounts of protein and nucleic acid and had comparable molecular sizes as determined by gel filtration. Compositional analysis showed type 19F(19) to contain rhamnose, glucose, N-acetylmannosamine, and a phosphate ester. Type 19A(57) contained these four moieties, and in addition, contained fucose, galactose, and N-acetylglucosamine. Plans for using this information to evaluate current and proposed formulation of multivalent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann A. J., Addiego J., Wara D. W., Lubin B., Smith W. B., Mentzer W. C. Polyvalent pneumococcal-polysaccharide immunization of patients with sickle-cell anemia and patients with splenectomy. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 27;297(17):897–900. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710272971701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum P. C., Bhamjee A., Scragg J. N., Hallett A. F., Bowen A. J., Cooper R. C. Streptococcus pneumoniae resistant to penicillin and chloramphenicol. Lancet. 1977 Nov 12;2(8046):995–997. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92892-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R., Douglas R. M., Schiffman G., Coetzee A. M., Koornhof H. J., Hayden-Smith S., Reid R. D. Prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia by vaccination. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1976;89:184–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R., Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H. The bacteriology of pneumococcal otitis media. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1977 Sep;141(3):104–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R. The quellung reaction, a neglected microbiologic technique. Mt Sinai J Med. 1976 Nov-Dec;43(6):699–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgoño J. M., McLean A. A., Vella P. P., Woodhour A. F., Canepa I., Davidson W. L., Hilleman M. R. Vaccination and revaccination with polyvalent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines in adults and infants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jan;157(1):148–154. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finland M., Barnes M. W. Changes in occurrence of capsular serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae at Boston City Hospital during selected years between 1935 and 1974. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):154–166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.154-166.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortt A. A., Wysocki R. J., Liu T. Y. Primary structure of streptococcal proteinase. I Isolation, composition, and amino acid sequences of the tryptic and chymotryptic peptides of cyanogen bromide fragments 1 to 4. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUND E. Antigenic relationship between pneumococci and non-hemolytic streptococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1950;27(1):110–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1950.tb05200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larm O., Lindberg B. The pneumococcal polysaccharides: a re-examination. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1976;33:295–322. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Jonssen E. K., Wysocki J. R. Studies on the meningococcal polysaccharides. I. Composition and chemical properties of the group A polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2849–2858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Munksgaard A., Stewart S. M. A new pneumococcus type. Type 47 A. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):497–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson C. F., Alexander H. E., Leidy G. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION, IN TYPE-SPECIFIC ANTISERA TO HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE, OF THE ANTIBODY THAT CROSS-REACTS WITH ENCAPSULATED PNEUMOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1949 Apr;57(4):443–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.4.443-446.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. B., Stevens R. W., Gaafar H. A. Latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A. Sickle cell anemia and severe infections due to encapsulated bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S25–S30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powars D., Schroeder W. A., White L. Rapid diagnosis of sickle cell disease at birth by microcolumn chromatography. Pediatrics. 1975 May;55(5):630–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for AUGUST 11, 1944. Public Health Rep. 1944 Aug 11;59(32):1041–1076. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao E. V., Buchanan J. G., Baddiley J. The type-specific substance from Pneumococcus type 10A(34). Structure of the dephosphorylated repeating unit. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):801–810. doi: 10.1042/bj1000801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao E. V., Watson M. J., Buchanan J. G., Baddiley J. The type-specific substance from Pneumococcus type 29. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(4):547–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1110547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeler R. A., Metzger W., Mufson M. A. Diplococcus pneumoniae infections in children with sickle cell anemia. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jan;123(1):8–10. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110070058003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit P., Oberholzer D., Hayden-Smith S., Koornhof H. J., Hilleman M. R. Protective efficacy of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines. JAMA. 1977 Dec 12;238(24):2613–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASHKO M. E., RICE E. W. Determination of glucose by an improved enzymatic procedure. Clin Chem. 1961 Oct;7:542–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel R. E., Vella P. P., McLean A. A., Woodhour A. F., Davidson W. L., Hilleman M. R. Studies in human subjects of polyvalent pneumococcal vaccines (39894). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Oct;156(1):144–150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Barrera O., Sutton A., May J., Hochstein D. H., Robbins J. D., Robbins J. B., Parkman P. D., Seligmann E. B., Jr Standardization and control of meningococcal vaccines, group A and group C polysaccharides. J Biol Stand. 1977;5(3):197–215. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(77)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




