Abstract
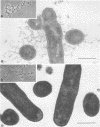
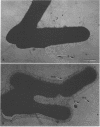
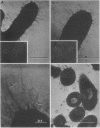
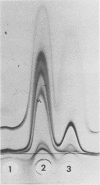
The morphology and serology of Actinomyces viscosus T14V and T14AV were compared. When grown in supplemented tryptic soy broth, the virulent strain (T14V) possessed an extensive network of cell surface fibrils. In this medium, the avirulent strain (T14AV) possessed a microcapsule, absent on strain T14V, and a comparatively small number of surface fibrils. Mild acid extraction (Lancefield procedure) solubilized common antigenic components on both strains as well as components detectable only in the virulent strain T14V (virulence-associated antigens 1 and 2). When grown in Socransky chemically defined medium or Carlsson complex medium, the avirulent strain possessed increased amounts of surface fibrils and virulence-associated antigens. Whole cells and extracts of avirulent cells grown in Socransky medium absorbed antibodies to virulence-associated antigens with approximately the same efficiency as did whole cells and extracts of strain T14V, suggesting antigenic similarity between the two cell types. The results strongly support the hypothesis that observable differences between A. viscosus strains T14V and T14AV represent quantitative, rather than qualitative, differences in particular cell surface components. In addition, the magnitude of these differences can be modified by changing growth conditions.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cisar J. O., Vatter A. E., McIntire F. C. Identification of the virulence-associated antigen on the surface fibrils of Actinomyces viscosus T14. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):312–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.312-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. Peptide requirements for the synthesis of streptococcal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith C. J., Carlsson J. Mechanism of ammonia assimilation in streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond B. F., Steel C. F., Peindl K. S. Antigens and surface components associated with virulence of Actinomyces viscosus. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A19–A25. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500111011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN H. V., KEYES P. H. AEROBIC, GRAM-POSITIVE, FILAMENTOUS BACTERIA AS ETIOLOGIC AGENTS OF EXPERIMENTAL PERIODONTAL DISEASE IN HAMSTERS. Arch Oral Biol. 1964 Jul-Aug;9:401–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(64)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Fitzgerald R. J., Stanley H. R. Plaque formation and periodontal pathology in gnotobiotic rats infected with an oral actinomycete. Am J Pathol. 1965 Dec;47(6):1157–1167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Hammond B. F. Filamentous bacteria isolated from human root surface caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Sep;17(9):1333–1342. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Keyes P. H., Bellack S. Periodontal lesions in hamsters and gnotobiotic rats infected with actinomyces of human origin. J Periodontal Res. 1972;7(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1972.tb00627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröll J. Immunochemical identification of specific precipitin lines in quantitative immunoelectrophoresis patterns. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;24(1):55–60. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F. A modified technique of immunoelectrophoresis facilitating the identification of specific precipitin arcs. J Immunol. 1960 Jan;84:93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetherell J. R., Jr, Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans: characterization of a polysaccharide antigen from walls of strain GS-5. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1341–1348. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1341-1348.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoeven J. S. A slime-producing microorganism in dental plaque of rats, selected by glucose feeding. Chemical composition of extracellular slime elaborated by Actinomyces viscosus, strain Nyl. Caries Res. 1974;8(3):193–210. doi: 10.1159/000260109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]