Abstract
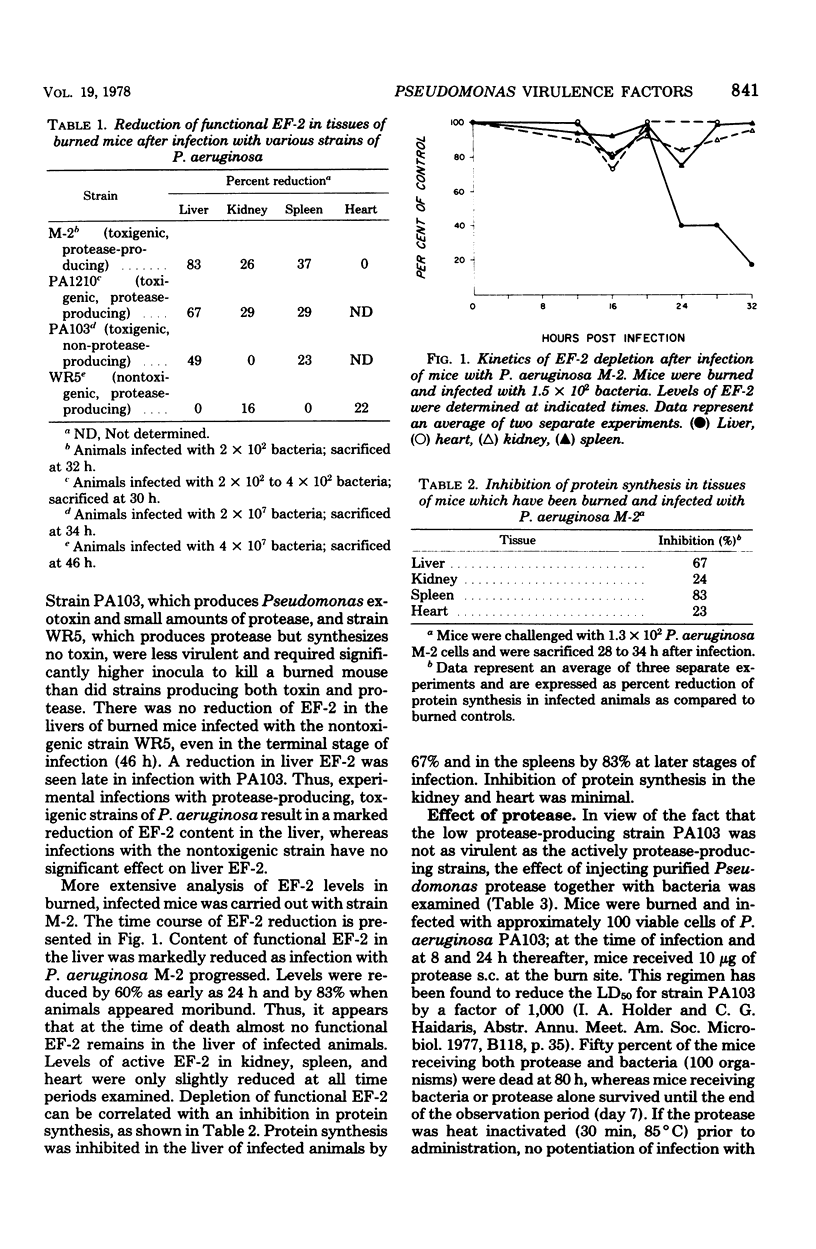
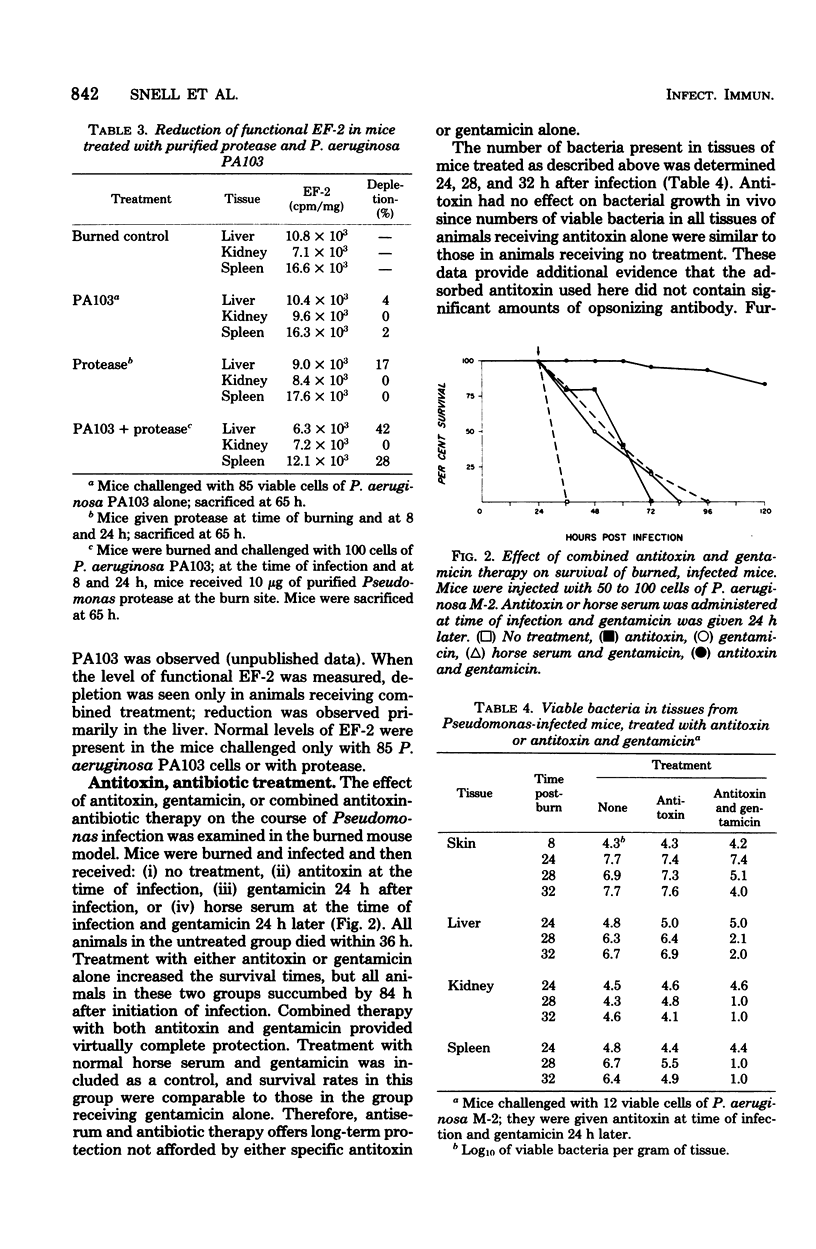
Evidence is presented which suggests that both the proteases and the exotoxin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa multiplying in situ in a burned mouse model are virulence factors. A 50% decrease in functional elongation factor 2 (EF-2) was seen 16 h postinfection in the liver of mice infected with the toxigenic, protease-producing P. aeruginosa strain M-2; at the time of death EF-2 was depleted by 80%. This correlates with a reduction in the level of protein synthesis in the liver of infected animals. Treatment with specific antitoxin extended the mean time to death and blocked depletion of EF-2. Administration of gentamicin 24 h after infection caused rapid clearance of bacteria and extended the mean time to death, but all animals treated with either antitoxin or gentamicin eventually died. In contrast, treatment with both antitoxin and gentamicin provided virtually complete protection. Infection of mice with P. aeruginosa WR5 (protease-producing, nontoxigenic) or with P. aeruginosa PA103 (toxigenic, slow protease producer) required several logs more bacteria and did not result in the same extensive depletion in EF-2 content. When challenge with PA103 was supplemented by injection of purified Pseudomonas protease, the mean time to death was shortened and significant reduction in liver EF-2 was observed. It is suggested that both toxin and proteases are required for the full expression of virulence in Pseudomonas infections.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Vasil M. L., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Incidence of exotoxin production by Pseudomonas species. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.362-366.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Imhoff J. G. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. I. Protein synthesis in guinea pig tissues. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1107–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D., Shearer W. T. Opportunistic infection in children. II. In the compromised host. J Pediatr. 1975 Nov;87(5):677–694. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. The elongation factor 2 content of mammalian cells. Assay method and relation to ribosome number. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):654–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Hsieh H. C. Inhibition of protease production of various bacteria by ammonium salts: its effect on toxin production and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):406–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.406-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Yoshii S., Hsieh H. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Concentration, purification, and characterization of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):514–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P., Holder I. A., MacMillan B. G. Burn wounds: microbiology, local host defenses, and current therapy. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–100. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Gordon F. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: effect on cell cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):631–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: localization and effect on protein synthesis. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.540-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Voelker F. A., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: histopathology and serum enzyme changes. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):253–259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Taylor N. S. Serum antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin measured by a passive hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.58-61.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelinger C. B., Snell K., Holder I. A. Experimental studies on the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: direct evidence for toxin production during Pseudomonas infection of burned skin tissues. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):555–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Výmola F., Lochmann O. Characteristics of Pseudomonas haemolysin. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):302–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



