Abstract
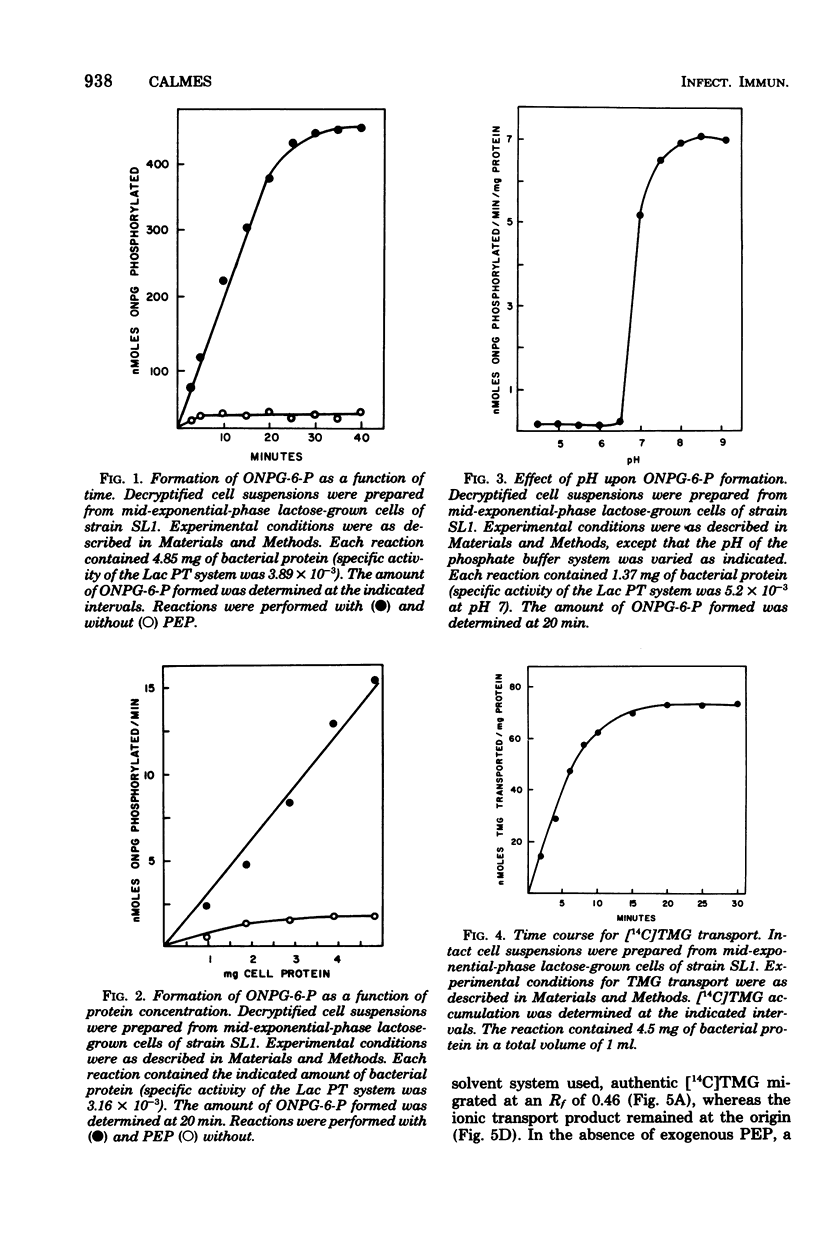
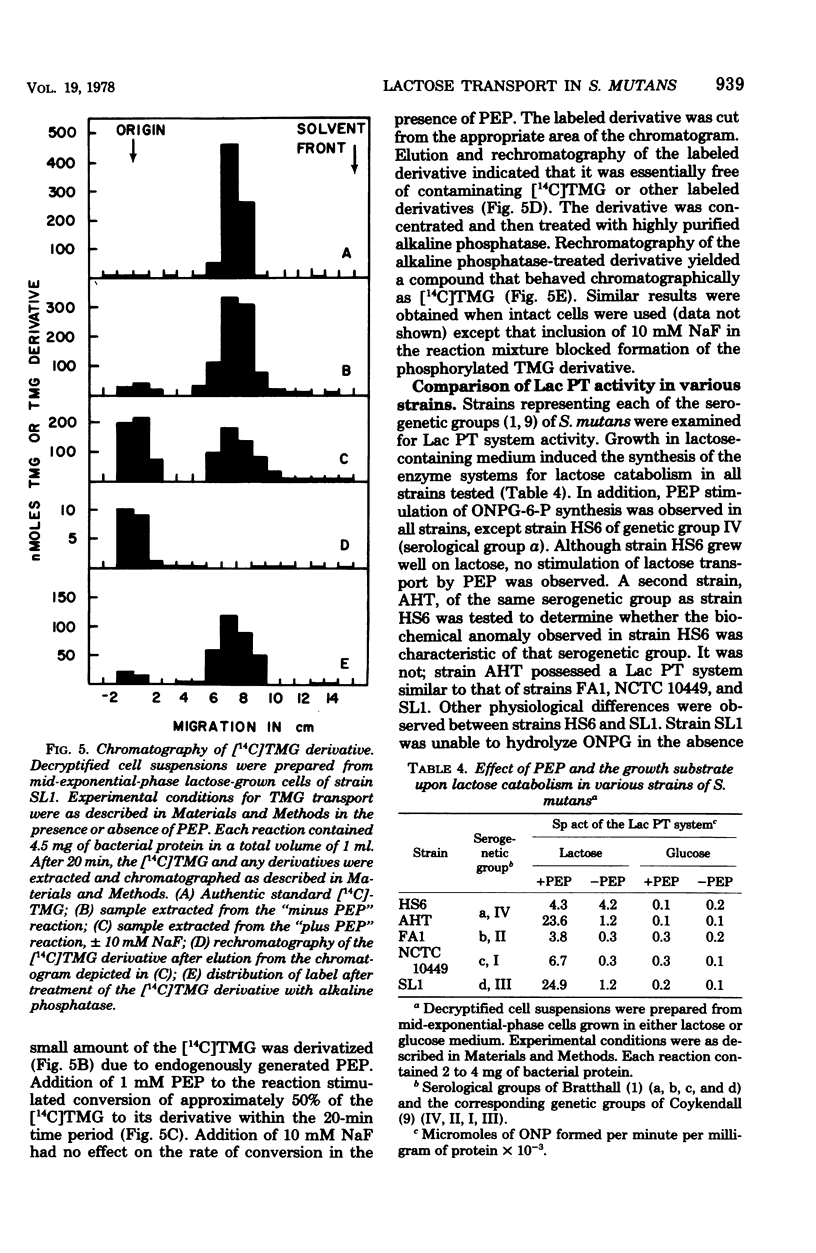
The mechanisms for transport and hydrolysis of lactose were investigated in five cariogenic strains (HS6, AHT, FA1, NCTC 10449, and SL1) representing the four serogenetic groups of Streptococcus mutans. The systems for transport and hydrolysis of lactose had the characteristics of a phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent lactose (Lac) phosphotransferase (PT) system and phospho-β-galactosidase (P-β-gal), respectively, in all strains tested, except strain HS6. Decryptified cells required PEP and Mg2+ for transport of the non-metabolizable model β-galactosides o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (ONPG) and thiomethyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (TMG). Substitution of 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PG) for PEP also stimulated the Lac PT system. Other potential high-energy phosphate donors (adenosine tri-, di-, and monophosphates and guanosine triphosphate) did not stimulate the Lac PT system. Sodium fluoride had no effect upon the PEP-dependent Lac PT system in decryptified cells with PEP as the energy source; however, when 2-PG was used as the energy source, F− inhibited ONPG phosphorylation. With intact cells which must generate PEP endogenously, the presence of F− in concentration ≥ 10 mM completely inhibited the Lac PT system, presumably through inhibition of 2-PG hydrolyase (EC 4.2.1.11; enolase). Both intact and decryptified cells accumulated a phosphorylated derivative of TMG that behaved chromatographically as TMG-phosphate. After alkaline phosphatase treatment, the derivative had an Rf identical to that of TMG. No β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity was detected with ONPG as the substrate; hydrolysis occurred only when ONPG-6-phosphate was supplied as the substrate. Strain HS6 apparently transported lactose by an active transport-type system in which the accumulated intracellular product was the free disaccharide based on the following criteria: (i) ONPG transport and hydrolysis in decryptified cells was not stimulated by PEP; (ii) ONPG hydrolysis occurred in the absence of PEP; and (iii) ONPG-6-phosphate was not hydrolyzed. These data indicate that, in all strains tested except strain HS6, lactose transport was mediated by a PEP-dependent Lac PT system, resulting in accumulation of lactose-phosphate that was hydrolyzed by an enzyme similar to the P-β-gal of group N streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus; conversely, strain HS6 transported and hydrolyzed lactose by a PEP-independent transport system and β-gal, respectively.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Patterson C. E. Heterogeneity of Streptococcus mutans strains based on their mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenases: criterion for rapid classification. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):422–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.422-424.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T. The role of dietary carbohydrates in plaque formation and oral disease. Nutr Rev. 1975 Dec;33(12):353–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1975.tb05089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Wittenberger C. L. Fructose-1,6-diphosphate-dependent lactate dehydrogenase from a cariogenic streptococcus: purification and regulatory properties. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.604-615.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calmes R., Deal S. J. Fatty acid transport by the lipophilic bacterium Nocardia asteroides. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):751–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.751-757.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi J. E., Hageage G. J., Jr, Wittenberger C. L. Multicomponent nature of the glucosyltransferase system of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C87–C96. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500330011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cords B. R., McKay L. L. Characterization of lactose-fermenting revertants from lactose-negative Streptococcus lactis C2 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):830–839. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.830-839.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L. Four types of Streptococcus mutans based on their genetic, antigenic and biochemical characteristics. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):327–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaCosta T., Gibbons R. J. Hydrolysis of levan by human plaque streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. 3. Studies of the transport process. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 4;112(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6585(96)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frostell G., Keyes P. H., Larson R. H. Effect of various sugars and sugar substitutes on dental caries in hamsters and rats. J Nutr. 1967 Sep;93(1):65–76. doi: 10.1093/jn/93.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Burckhardt J. J. Isolation and properties of a dextranase from streptococcus mutans OMZ 176. Helv Odontol Acta. 1974 Oct;18(2):101–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., König K. G., Herzog E., Mühlemann H. R. The cariogenicity of different dietary carbohydrates tested on rats in relative gnotobiosis with a Streptococcus producing extracellular polysaccharide. Helv Odontol Acta. 1966 Oct;10(2):101–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R. Effects of fluoride on enzymatic regulation of bacterial carbohydrate metabolism. Caries Res. 1977;11 (Suppl 1):262–291. doi: 10.1159/000260304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. V. The accumulation of phosphorylated carbohydrate derivatives, and evidence for a new enzyme-splitting lactose phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):274–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. VI. The nature of the derivatives accumulated. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1881–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN H. V., FITZGERALD R. J., BOWLER A. E. Inhibition of experimental caries by sodium metabisulfite and its effect on the growth and metabolism of selected bacteria. J Dent Res. 1960 Jan-Feb;39:116–123. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390010501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanapka J. A., Hamilton I. R. Fluoride inhibition of enolase activity in vivo and its relationship to the inhibition of glucose-6-P formation in Streptococcus salivarius. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Sep;146(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Protonmotive force in fermenting Streptococcus lactis 7962 in relation to sugar accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):879–886. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Role of metabolic energy in the transport of -galactosides by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.784-789.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. The beta-d-galactosidase of Escherichia coli, strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):381–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.381-392.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. H., Wittenberger C. L. Mannitol transport in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1475–1481. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1475-1481.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Walter L. A., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.603-610.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L., Miller A., 3rd, Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Mechanisms of lactose utilization by lactic acid streptococci: enzymatic and genetic analyses. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):804–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.804-809.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. L., Hill K. L., Egan J. B., Hengstenberg W. Metabolism of lactose by Staphylococcus aureus and its genetic basis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2270–2274. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2270-2274.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandian J., Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M., Lovelace S. M. Ultrastructure of Mutants of Streptococcus mutans with Reference to Agglutination, Adhesion, and Extracellular Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1170–1179. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1170-1179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Ciba Found Symp. 1975;(31):225–241. doi: 10.1002/9780470720134.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F. Glucose transport in Streptococcus mutans: preparation of cytoplasmic membranes and characteristics of phosphotransferase activity. J Dent Res. 1975 Mar-Apr;54(2):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Mayo J. A. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose transport in oral streptococci. J Dent Res. 1973 Nov-Dec;52(6):1209–1215. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520060801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Brown A. T., McInerney M. F. Identification, preliminary characterization, and evidence for regulation of invertase in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):192–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.192-202.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Brown A. T., McInerney M. F., Woodiel F. N. Comparative study of invertases of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):318–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.318-327.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Thomas T. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate and 2-phosphoglycerate: endogenous energy source(s) for sugar accumulation by starved cells of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.583-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., Jansen H. M. Levan degradation by streptococci isolated from human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jul;13(7):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



