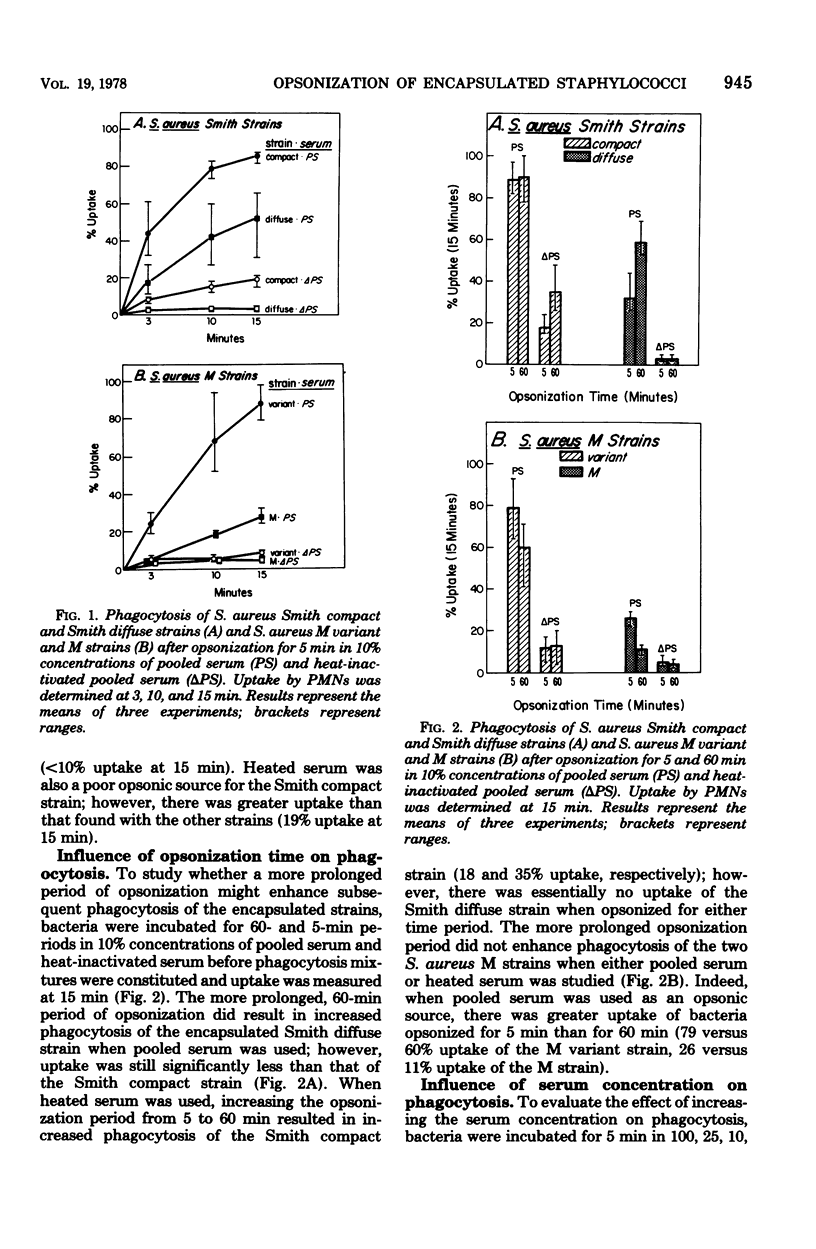
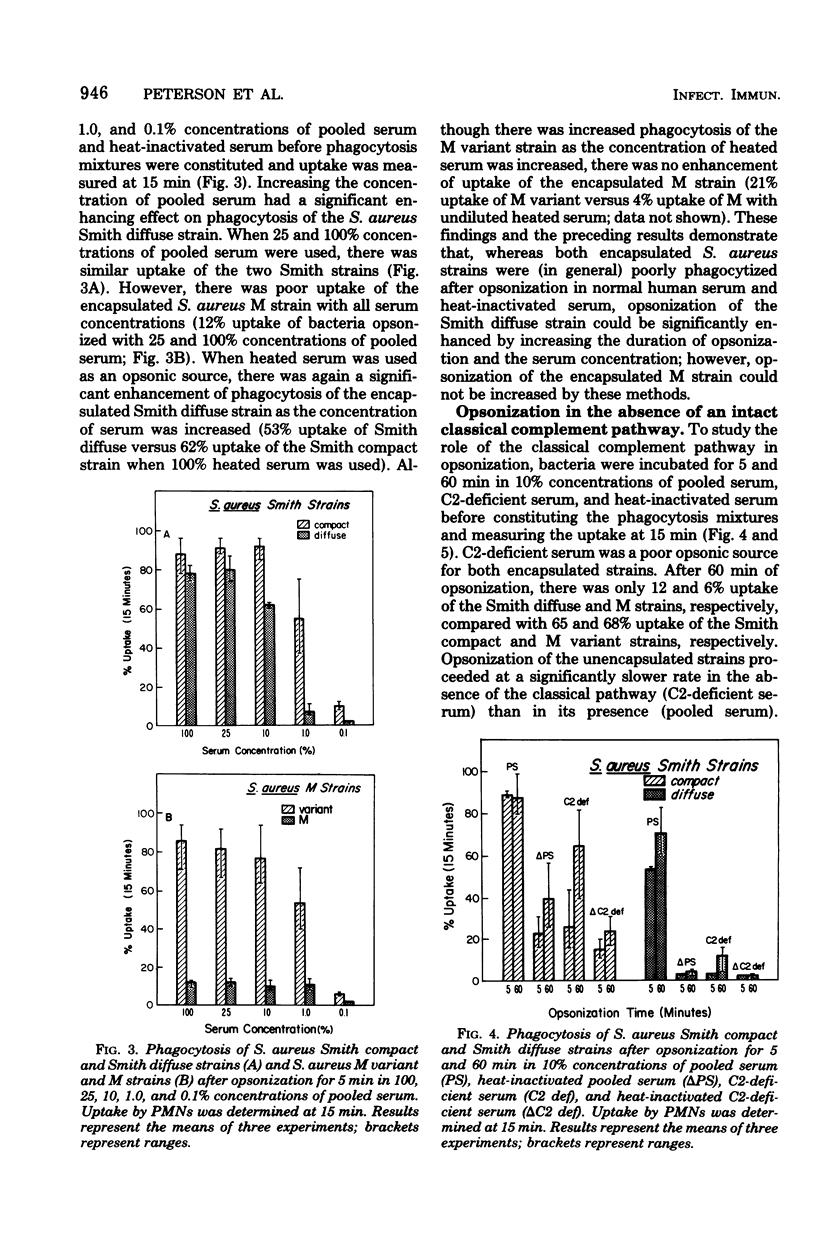
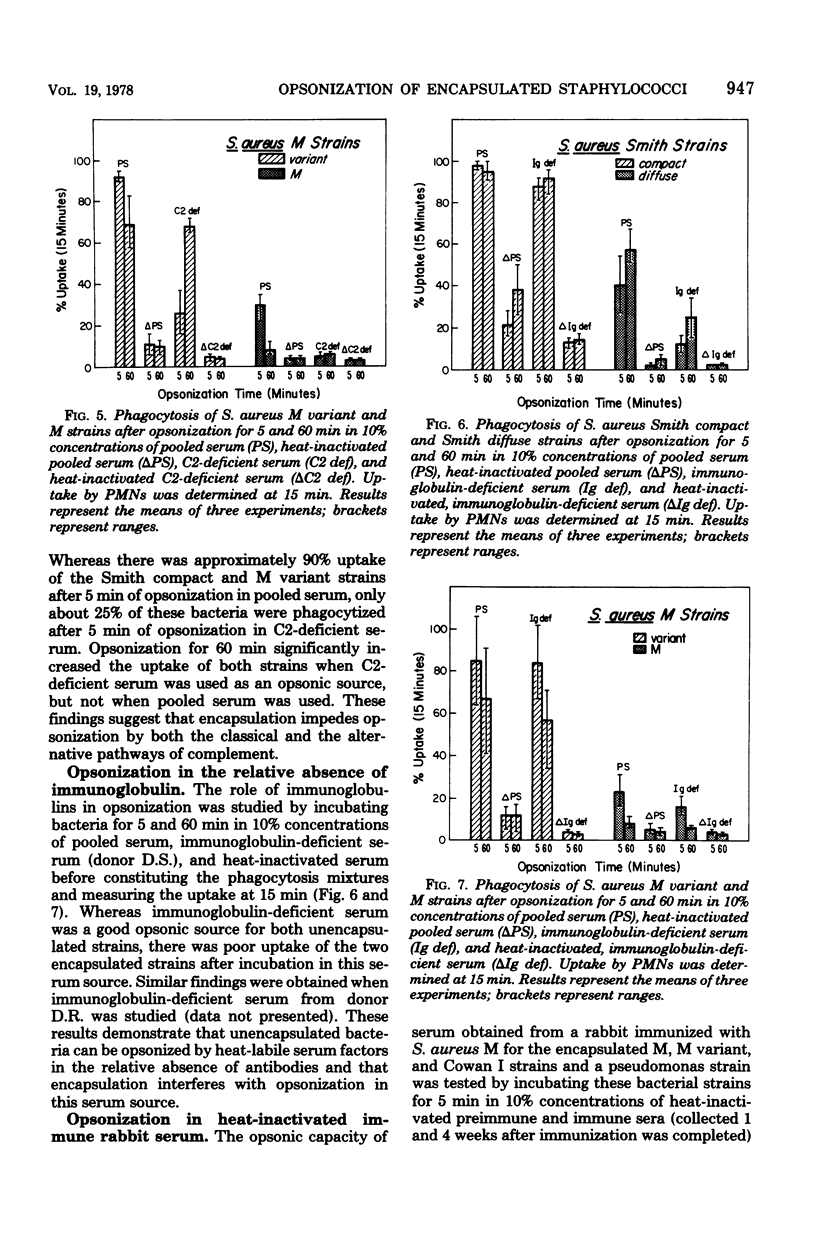
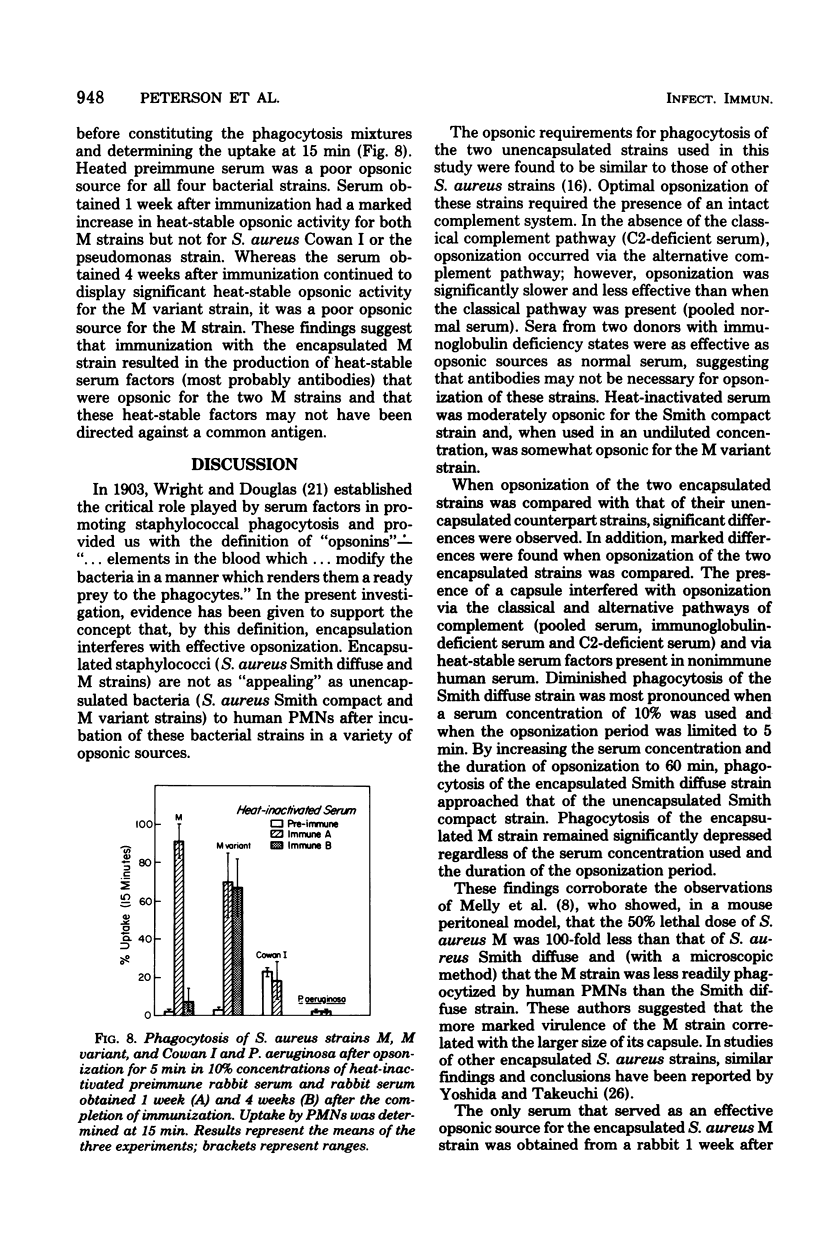
Abstract
In previous studies, encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus strains have been shown to resist phagocytosis. In this investigation, the nature of the interference with phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes was examined by studying the opsonization of two pairs of unencapsulated (Smith compact and M variant) and encapsulated (Smith diffuse and M) S. aureus strains. The uptake of [3H]glycine-labeled bacteria by normal leukocytes was quantitatively measured after incubation of bacteria in pooled serum, C2-deficient serum, immunoglobulin-deficient serum, and serum from a rabbit immunized with S. aureus M. The presence of a capsule was found to interfere with opsonization by both the classical and alternative pathways of complement as well as by heat-stable opsonic factors in nonimmune human serum. This interference was significantly greater in the case of the S. aureus M strain than in the case of the Smith diffuse strain. The only effective opsonic source for S. aureus M was immune rabbit serum. It is proposed that encapsulation of S. aureus strains interferes with phagocytosis by preventing effective bacterial opsonization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ekstedt R. D., Yoshida K. Immunity to staphylococcal infection in mice: effect of living versus killed vaccine, role of circulating antibody, and induction of protection-inducing antigen(s) in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):745–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.745-750.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Effects of staphylococcal protein A on heat labile opsonins. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1177–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin R. W., Chatterjee A. N., Young F. E. Autolysis of microbial cells: salt activation of autolytic enzymes in a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):272–283. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.272-283.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. II. Observations on four mouse-pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:589–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Friend P. S., Dresner I. G., Yunis E. J., Michael A. F. Inherited deficiency of the second component of complement (C2) with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90881-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M. G., Melly M. A. The importance of surface antigens in staphylococcal virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):231–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE K. M., KNEELAND Y., Jr Further studies of the phenomenon of capsular swelling of Micrococcus pyogenes var. aureus in the presence of immune serum. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):229–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.229-230.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Effect of protein A on staphylococcal opsonization. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.760-764.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Kinetics of phagocytosis and bacterial killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):502–509. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS D. E., MELLY M. A. Observations on the immunology of pathogenic staphylococci. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:560–581. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., Clawson C. C., Friend P. S. Influence of a deficiency of the second component of complement on the bactericidal activity of neutrophils in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):802–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI108702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. C. A capsulate Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis: recognition and ingestion. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jan;12(1):83–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P., Kim Y., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Opsonic requirements for staphylococcal phagocytosis. Heterogeneity among strains. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):191–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Capsule production and virulence among strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):221–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Virulent and avirulent encapsulated variants of Staphyococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):998–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.998-1002.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K. Demonstration of Serologically Different Capsular Types Among Strains of Staphylococcus aureus by the Serum-Soft Agar Technique. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.535-539.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ekstedt R. D. Relation of mucoid growth of Staphylococcus aureus to clumping factor reaction, morphology in serum-soft agar, and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.902-908.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Nakamura A., Otomo T., Iwami S. Detection of capsular antigen production in unencapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):620–623. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.620-623.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Smith M. R., Naito Y. Biological and Immunological Properties of Encapsulated Strains of Staphylococcus aureus from Human Sources. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):528–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.528-532.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Takeuchi Y. Comparison of Compact and Diffuse Variants of Strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):523–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.523-527.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



