Abstract
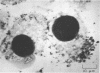
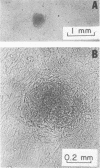
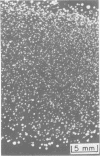
The vole agent described by Baker in 1946 was studied as an example of a bacterium that has been mistakenly regarded a rickettsia. Unlike rickettsiae, the vole agent killed chicken embryos with great irregularity, multipled primarily at the surface of avian or mammalian cells and not intracellularly, produced colonies rather than plaques on chicken embryo monolayers under agar, and developed small colonies after 4 to 7 days of cultivation on blood plates. It was most conveniently cultivated on monolayers of irradiated L cells and was purified by minor modifications of the Renografin gradient procedure used for rickettsiae. It actively catabolized glutamate, glutamine, succinate, and pyruvate, but not glucose or glucose-6-phosphate. Enzymatic activities of cell extracts were consistent with above findings. The base ratio (molar percent guanine plus cytosine) of its deoxyribonucleic acid was shown to be 39, which was identical to the base ratio of the deoxyribonucleic acid of Rochalimaea quintana tested simultaneously. Serological studies indicated no cross-reactivity with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, but strong cross-reaction with R. quintana was observed when a hyperimmune rabbit serum and a convalescent human serum were tested. We conclude that the vole agent is a strain of the trench fever rickettsia, R. quintana.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOZEMAN F. M., ELISBERG B. L. Serological diagnosis of scrub typhus by indirect immunofluorescence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:568–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozeman F. M., Masiello S. A., Williams M. S., Elisberg B. L. Epidemic typhus rickettsiae isolated from flying squirrels. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):545–547. doi: 10.1038/255545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozeman F. M., Shiral A., Humphries J. W., Fuller H. S. Ecology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. II. Natural infection of wild mammals and birds in Virginia and Maryland. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jan;16(1):48–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coolbaugh J. C., Progar J. J., Weiss E. Enzymatic activities of cell-free extracts of Rickettsia typhi. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):298–305. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.298-305.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Samms J. R., Weiss E. Biochemical characteristics of typhus group rickettsiae with special attention to the Rickettsia prowazekii strains isolated from flying squirrels. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.676-685.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J. Reexamination of the association between melting point, buoyant density, and chemical base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):738–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.738-754.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y. Metabolic Activity of the Trench Fever Rickettsia, Rickettsia quintana. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):853–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.853-859.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON E. B., DANAUSKAS J. X., COALE M. C., SMADEL J. E. Recovery of Rickettsia akari from the Korean vole Microtus fortis pelliceus. Am J Hyg. 1957 Nov;66(3):301–308. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. A. Propagation and growth cycle of Rickettsia quintana in a new liquid medium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):184–190. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.184-190.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E. Determination of antibiotic susceptibility of Rickettsia by the plaque assay technique. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):133–135. doi: 10.21236/ad0857810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Stakebake J. R., Gerone P. J. Plaque assay system for several species of Rickettsia. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):910–912. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.910-912.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKiel J. A., Bell E. J., Lackman D. B. Rickettsia canada: a new member of the typhus group of rickettsiae isolated from Haemaphysalis leporispalustris ticks in Canada. Can J Microbiol. 1967 May;13(5):503–510. doi: 10.1139/m67-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke W., Goldstein D. A., Hall M. R. Rapid isolation of mouse DNA from cells in tissue culture. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. F., Cutler L. D., Wisseman C. L., Jr Role of erythrocytes and serum in the nutrition of Rickettsia quintana. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):663–666. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.663-666.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. F., Osterman J. V., Wisseman C. L., Jr Nutritional studies of Rickettsia guintana: nature of the hematin requirement. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.89-95.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J., Jr, Weiss E., Millar D. B., Bozeman F. M., Ormsbee R. A. DNA base composition of rickettsiae. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINSON J. W., FULLER H. S. Studies on trench fever. I. Propagation of Rickettsia-like microorganisms from a patient's blood. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1961;24(Suppl):152–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson J. W. In vitro cultivation of the rickettsial agent of trench fever. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(2):155–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Growth and physiology of rickettsiae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):259–283. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.259-283.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman D. R., Weiss E., Dasch G. A., Bozeman F. M. Biological properties of Rickettsia prowazekii strains isolated from flying squirrels. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):853–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.853-860.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]