Abstract
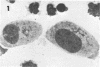
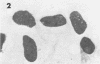
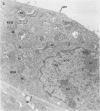
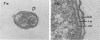
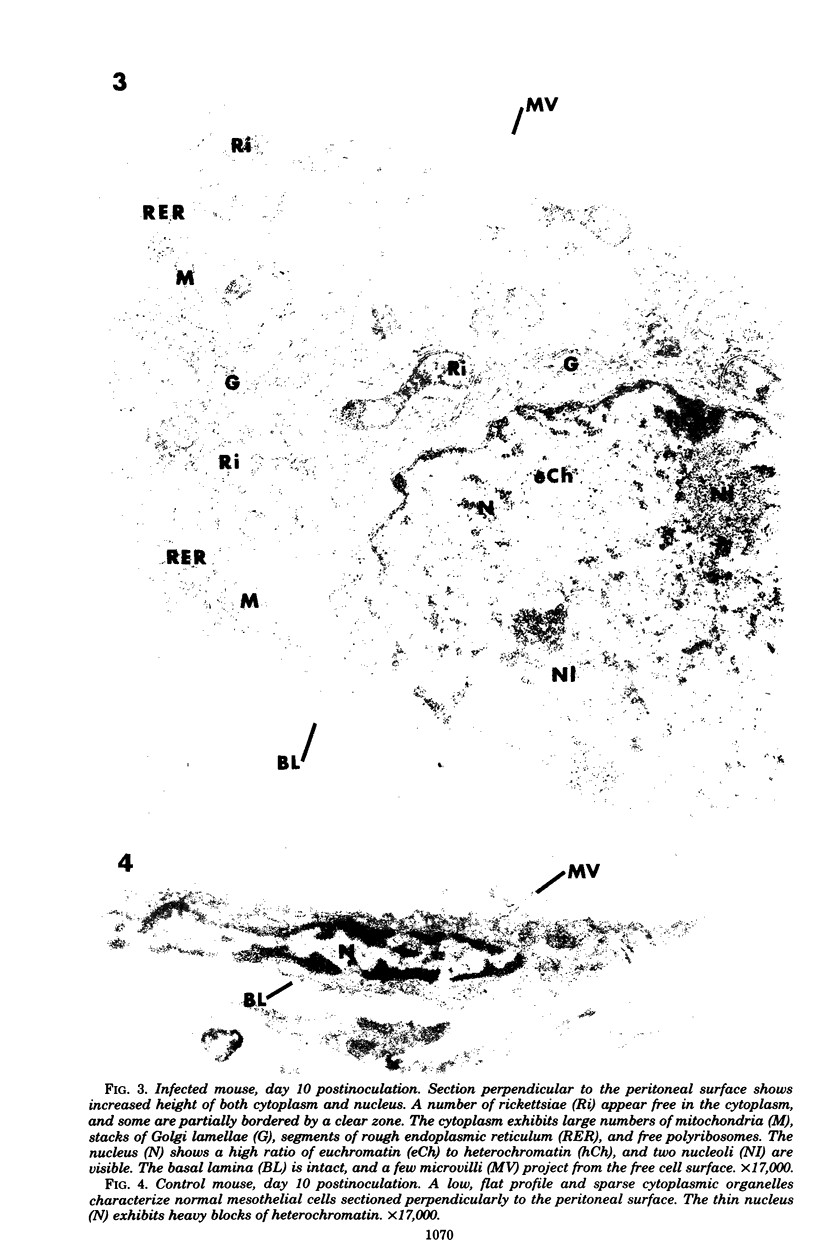
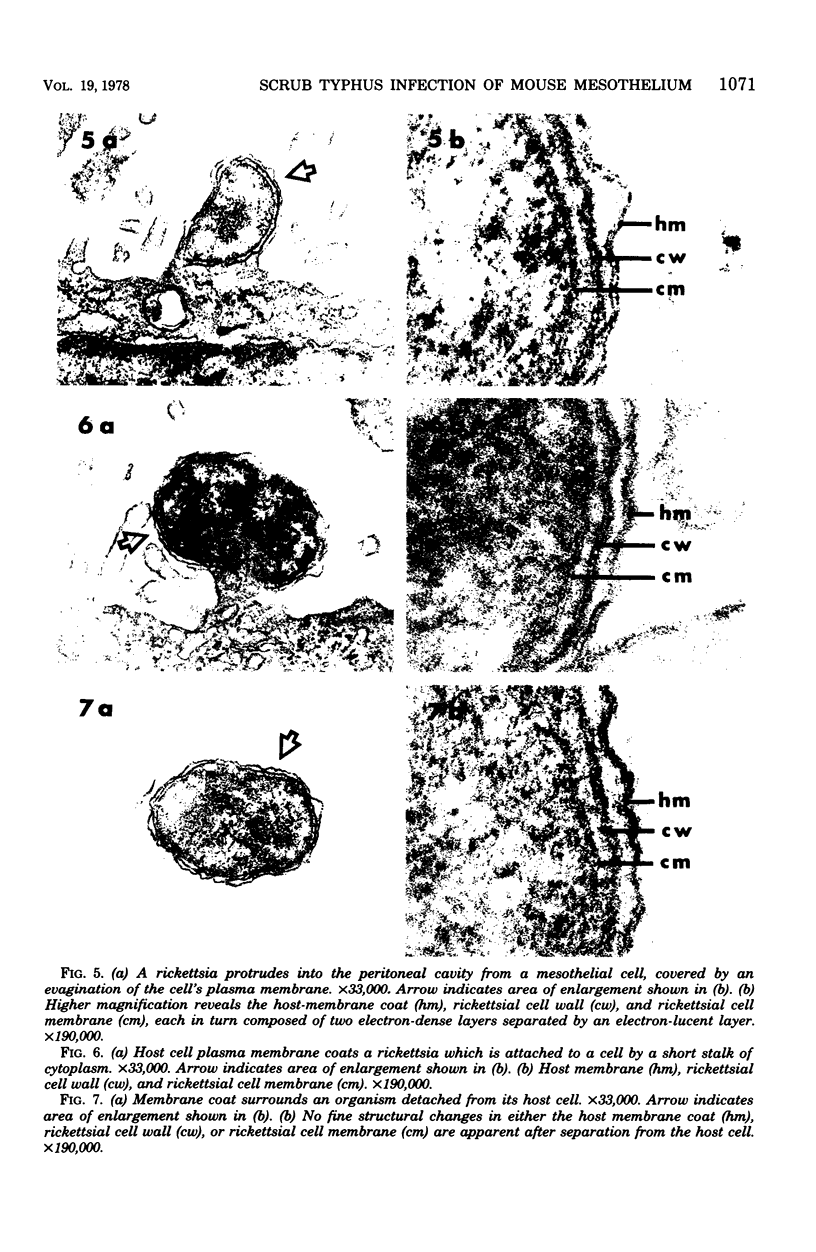
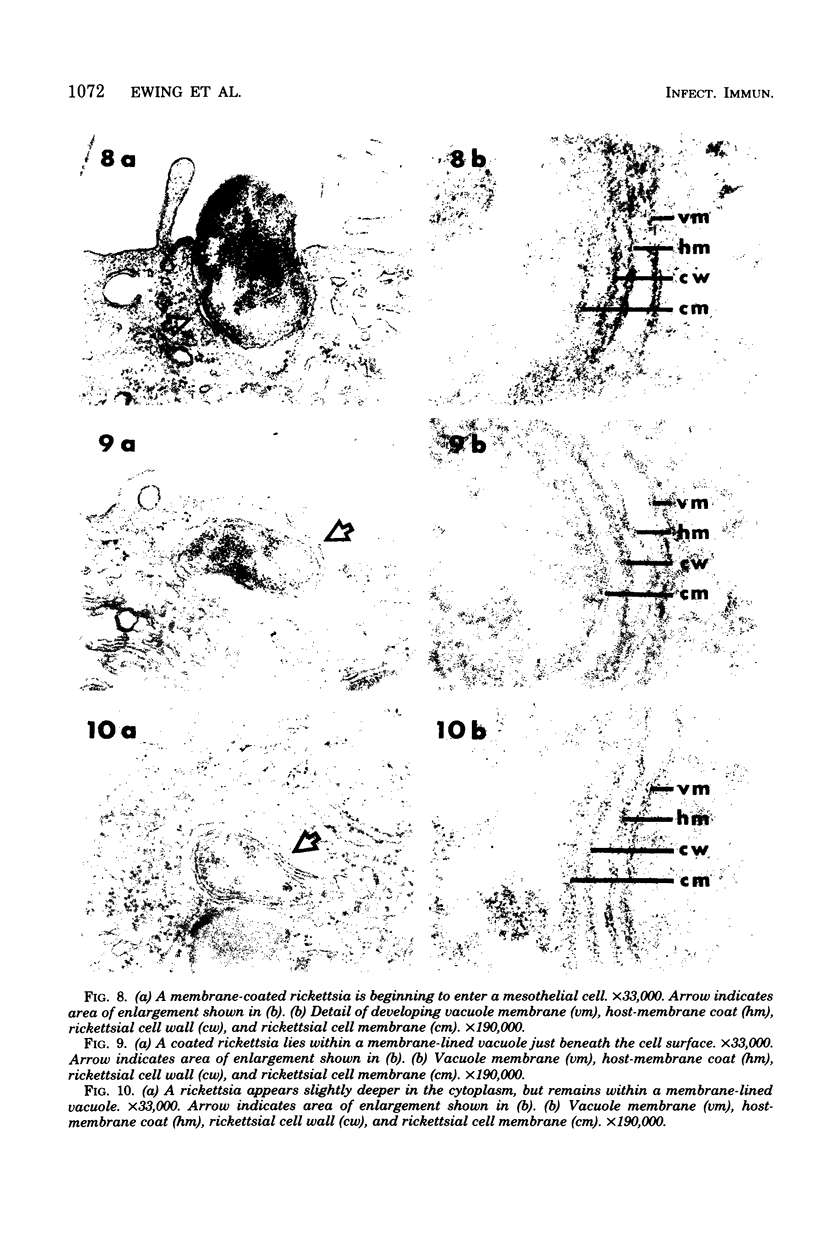
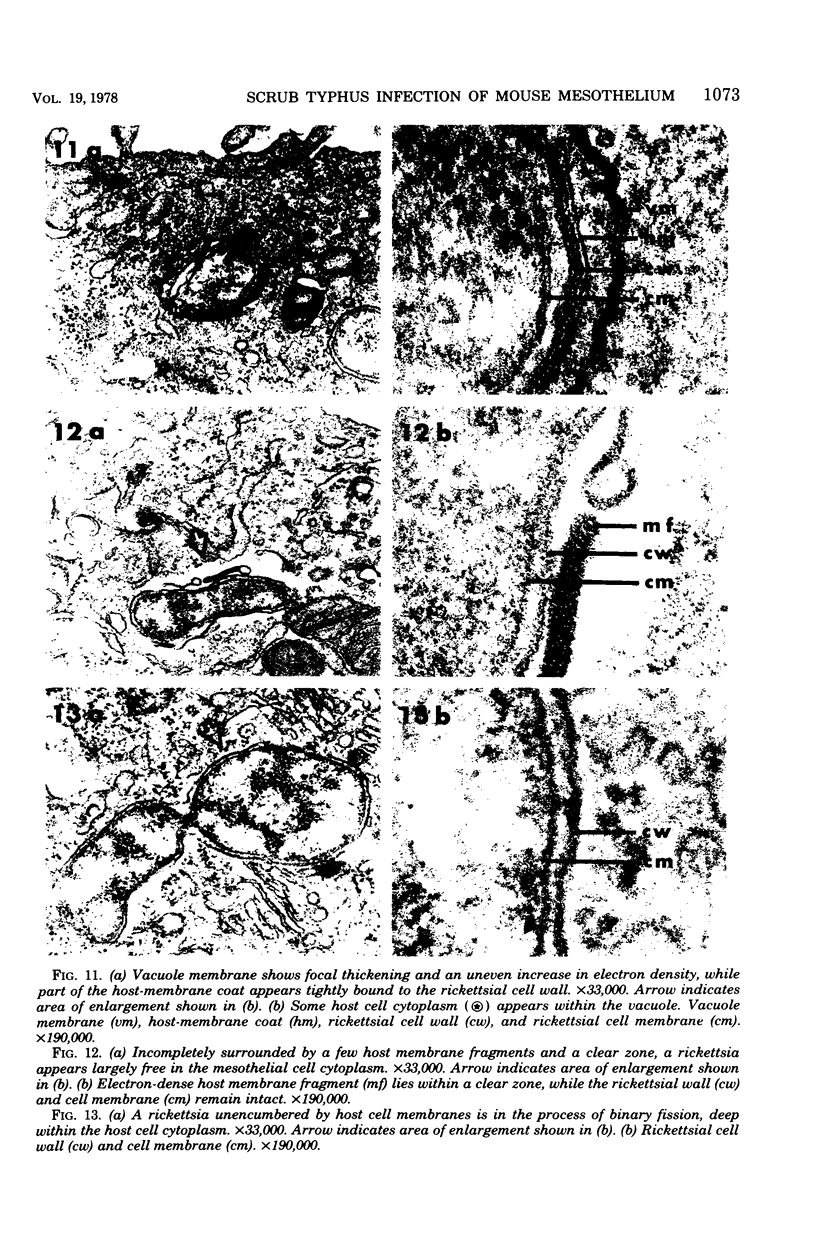
The infection cycle of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in mouse peritoneal mesothelial cells, observed late in the course of an established infection, intimately involved the host cell plasma membrane. Organisms multiplied in the cytoplasm, moved to the cell periphery, and acquired a host-membrane coat as they budded from the cell surface. Rickettsiae enveloped by this membrane entered other mesothelial cells, apparently by a phagocytic mechanism. Organisms escaped from the phagocytic vacuole as the vacuole membrane and host membrane coat disintegrated. Free rickettsiae replicated by binary fission in the cell cytoplasm. Rickettsial infection of mesothelial cells induced conspicuous cellular hypertrophy with increased numbers of unaltered cytoplasmic organelles.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOZEMAN F. M., HOPPS H. E., DANAUSKAS J. X., JACKSON E. B., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of Rickettsiae. I. A tissue culture system for quantitative estimations of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1956 Jun;76(6):475–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. F., Patt J. K., Hopps H. E. Titration and neutralization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):825–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I. Requirements for ingestion of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.645-651.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro P. J., Shirai A., Hilderbrandt P. K., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: histopathological correlates. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):861–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.861-875.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIN W. D., LIU C., HARMON P., RODINA P. PATHOGENESIS OF SCRUB TYPHUS INFECTION (RICKETTSIA TSUTSUGAMUSHI) AS STUDIED BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:772–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokorin I. N. Biological peculiarities of the development of rickettsiae. Acta Virol. 1968 Jan;12(1):31–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokorin I. N., Kyet C. D., Kekcheeva N. G., Miskarova E. D. Cytological investigation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infection of mice with different allotypic susceptibility to the agent. Acta Virol. 1976 Apr;20(2):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery A. T. Regeneration of parietal and visceral peritoneum: an electron microscopical study. J Anat. 1973 Sep;115(Pt 3):375–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., BOZEMAN F. M., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of Rickettsiae. II. Morphologic observations of living Rickettsiae in tissue culture cells. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Green A. E., Grays R., Newman L. M. Metabolism of Richettsia tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia rickettsi in irradiated host cells. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):4–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.4-7.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]