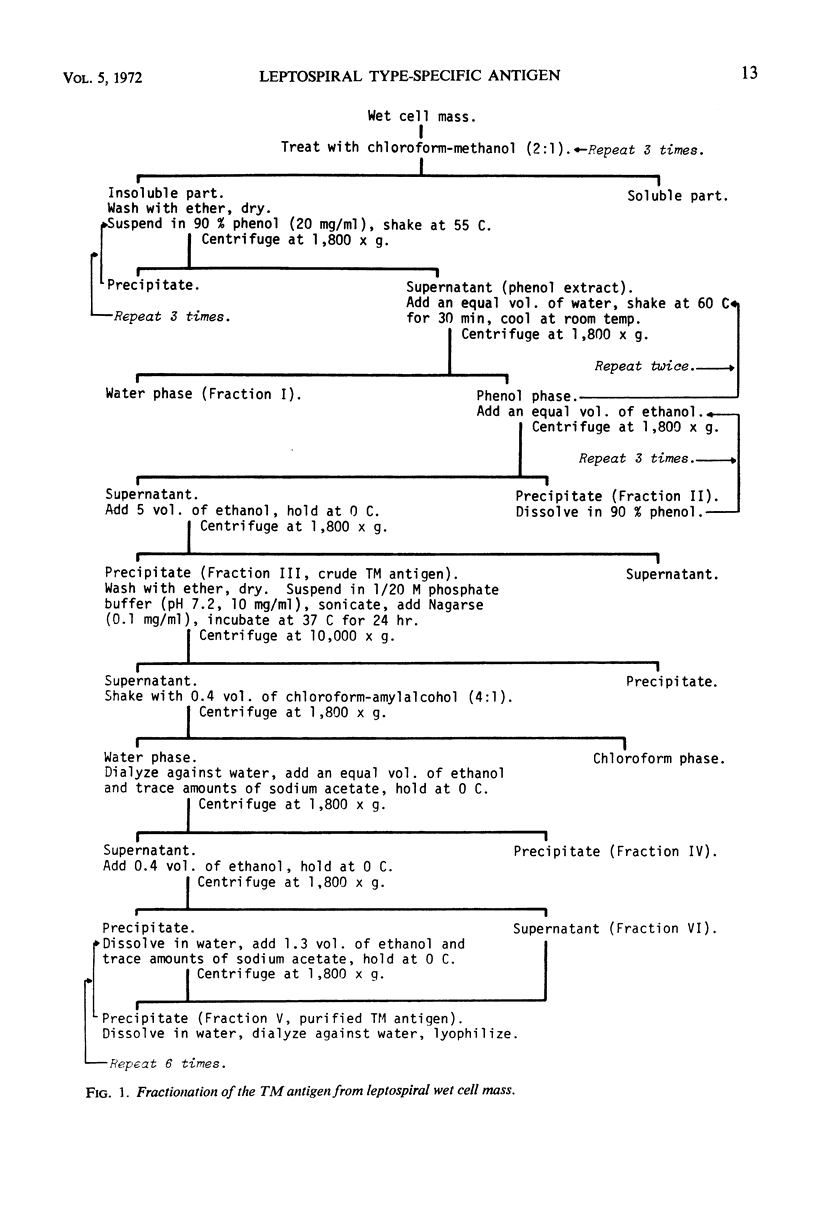
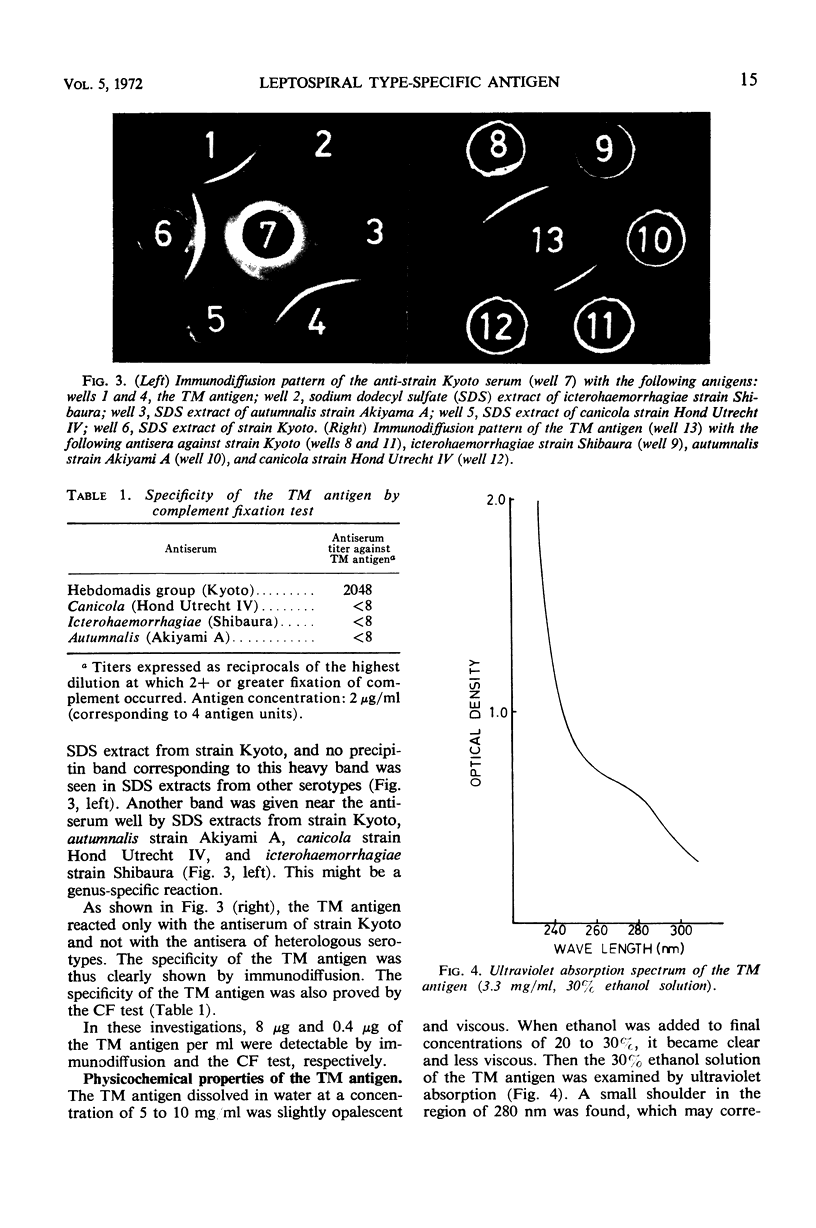
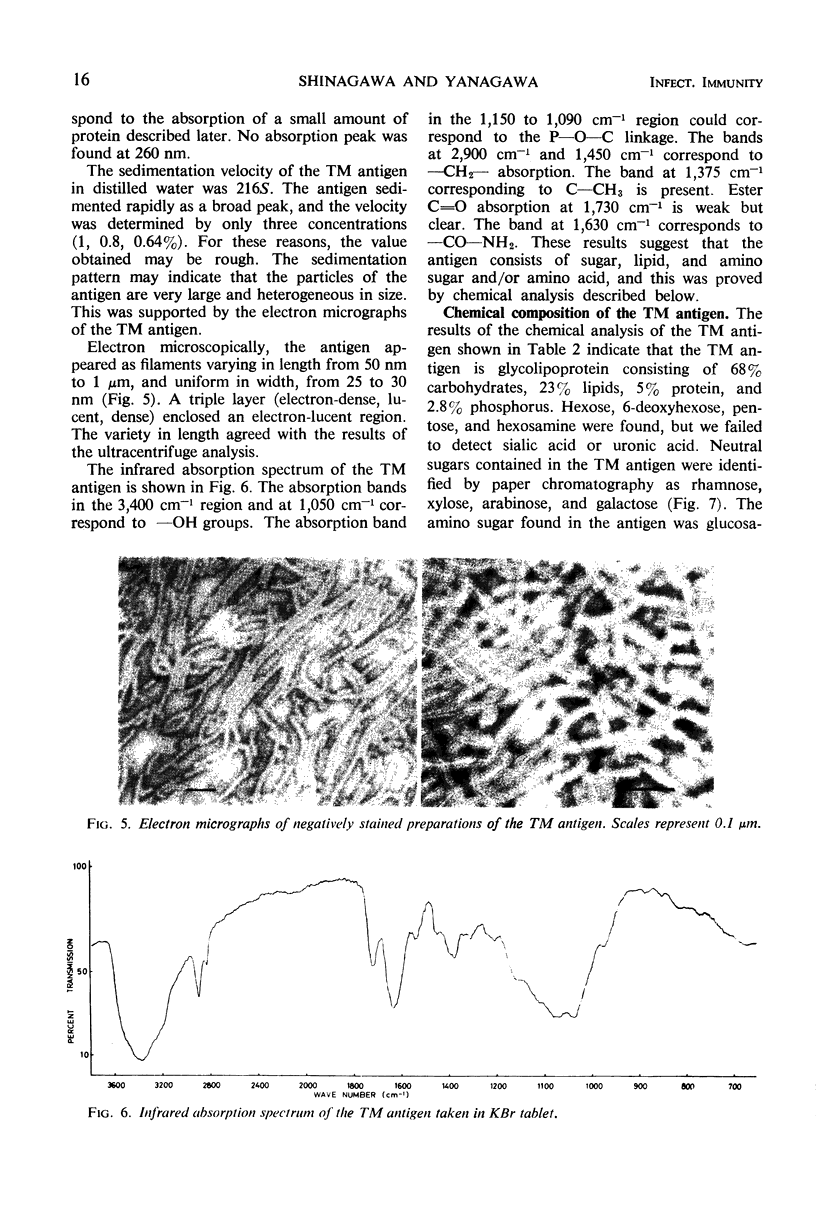
Abstract
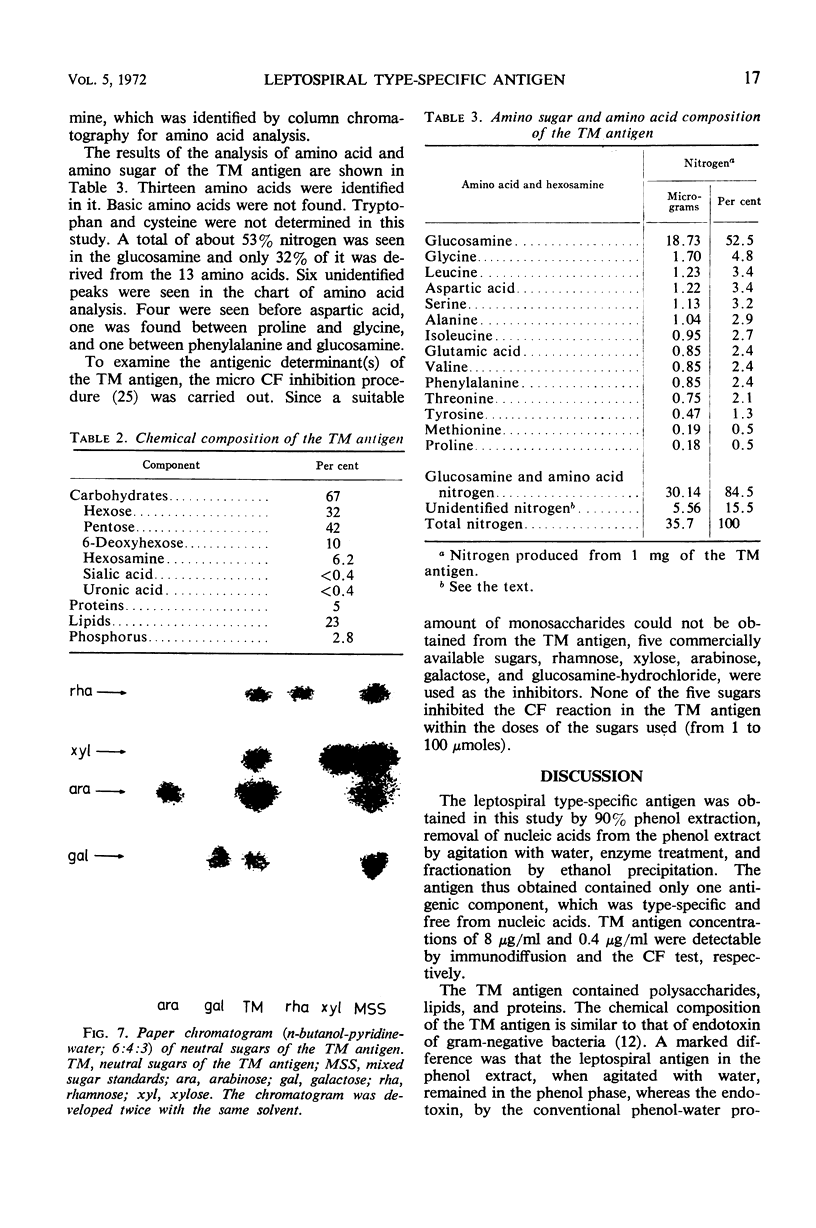
The type-specific main (TM) antigen was extracted from the leptospiral cells of strain Kyoto of the Hebdomadis group by 90% phenol and was purified mainly by ethanol precipitation. The TM antigen was specific, forming one precipitin band by immunodiffusion and reacting by complement fixation test with anti-strain Kyoto serum; so far as has been tested, it does not appear to react with antisera of other serotypes. The sedimentation velocity of the TM antigen was 216S. Morphologically the TM antigen was filamentous in shape with a uniform width of 25 to 30 nm and various lengths from 50 nm to 1 μm. The infrared absorption pattern of the TM antigen generally resembled that of gram-negative bacterial endotoxin, and this fact suggests that the antigen is composed mainly of lipopolysaccharides. Galactose, rhamnose, xylose, arabinose, glucosamine, 13 kinds of acidic and neutral amino acids, lipids, and phosphorus were found in the TM antigen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of free pentose and pentose in nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EZELL S. B., HOAG W. G., WARNER A. R., YAGER R. H., GOCHENOUR W. S., Jr Soluble specific leptospiral complement-fixing antigens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Jun;80(2):220–223. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIATT C. W., ROTHSTEIN N. Studies of the immunochemistry of leptospires. J Immunol. 1956 Oct;77(4):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAFT L. M., MELNICK J. L. Immunological reactions of the Coxsackie viruses. II. The complement fixation test. J Exp Med. 1950 Nov 1;92(5):483–497. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida H., Yanagawa R. Mutation of growth of leptospires in Shenberg's medium. Jpn J Vet Res. 1970 Mar;18(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E., Anacker R. L., Brown R., Haskins W. T., Malmgren B., Milner K. C., Rudbach J. A. Reaction of endotoxin and surfactants. I. Physical and biological properties of endotoxin treated with sodium deoxycholate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1493–1509. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1493-1509.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
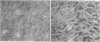
- SCHNEIDER M. D. Antigenic potency of cell-free extracts of leptospires. Exp Parasitol. 1955 Mar;4(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(55)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER M. D. Isolation and chemical composition of complement-fixing antigens from leptospires. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jan;85(1):32–37. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER M. D. Polysaccharide antigens of Leptospires. J Infect Dis. 1954 May-Jun;94(3):297–305. doi: 10.1093/infdis/94.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRICKER R. L., HANSON L. E. Precipitating antigens of leptospires. I. Chemical properties and serologic activity of soluble fractions of Leptospira pomona. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Jul;24:854–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefer M. Uber Antigenstruktur und Endotoxine der Leptospiren. (Vorläufige Mitteilung) Ann Soc Belges Med Trop Parasitol Mycol. 1966;46(2):259–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenberg E. Growth of pathogenic Leptospira in chemically defined media. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1598–1606. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1598-1606.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. I. Fractionation and microdetermination of cell carbohydrates. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):298–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0500298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura S., Miyazaki M. Analyses of pancreatic ribonuclease digests of Torulopsis utilis transfer ribonucleic acid's specific for alanine, valine and several other amino acids. J Biochem. 1969 Feb;65(2):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., SAGIN J. F., LANDY M., JOHNSON A. G. Studies on the O antigen of Salmonella typhosa. I. Purification of the antigen. J Immunol. 1955 Jun;74(6):455–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R., Faine S. Morphological and serological analysis of leptospiral structure. Nature. 1966 Aug 20;211(5051):823–826. doi: 10.1038/211823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara Y., Mifuchi I. Microfibers present in surface structure of Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2403–2406. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2403-2406.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]