Abstract
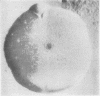
Meningococci isolated in primary cultures from nasopharyngeal carriers occasionally consisted of mixtures of smooth (S) and rough (R) strains. The R strains were separated from the S strains and their morphological and serological characteristics were studied. Some of these R strains reverted spontaneously to S strains which subsequently produced group-specific polysaccharide. Several R strains, grown in the presence of deoxyribonucleic acid from either an R strain of known parentage or an S strain, formed recombinants with serological group specificity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER H. E., LEIDY G. Determination of inherited traits of H. influenzae by desoxyribonucleic acid fractions isolated from type-specific cells. J Exp Med. 1951 Apr 1;93(4):345–359. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.4.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALEXANDER H. E., REDMAN W. Transformation of type specificity of meningococci; change in heritable type induced by type-specific extracts containing desoxyribonucleic acid. J Exp Med. 1953 Jun;97(6):797–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKMANN I., SUBBAIAH T. V., STOCKER B. A. ROUGH MUTANTS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. II. SEROLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1299–1301. doi: 10.1038/2011299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOEVRE K. STUDIES ON TRANSFORMATION IN MORAXELLA AND ORGANISMS ASSUMED TO BE RELATED TO MORAXELLA. 1. A METHOD FOR QUANTITATIVE TRANSFORMATION IN MORAXELLA AND NEISSERIA, WITH STREPLOMYCIN RESISTANCE AS THE GENETIC MARKER. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;61:457–473. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.61.3.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANHAM S. E. A defense of Epimetheus. Development of knowledge concerning the meningococcus. J Am Med Womens Assoc. 1960 Jun;15:571–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATLIN B. W. Transformation of Neisseria meningitidis by deoxyribonucleates from cells and from culture slime. J Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:579–590. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.4.579-590.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine L. F., Hagerman C. R. Relationship of Serogroups of Neisseria meningitidis I. Microagglutination, Gel Diffusion, and Slide Agglutination Studies of Meningococcal Antisera Before and After Absorption with RAS-10 Strain of Meningococci. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):226–231. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.226-231.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. R., Artenstein M. S., Hunter D. H. Prevalence of meningococcal serogroups and description of three new groups. Am J Epidemiol. 1968 May;87(3):643–646. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S., MACLEOD C. M., KRAUSS M. R. Determination of type in capsulated transformants on pneumococcus by the genome of non-capsulated donor and recipient strains. J Exp Med. 1959 May 1;109(5):429–438. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.5.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIE S. STUDIES ON THE STREPTOMYCIN RESISTANCE SYSTEM OF NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:623–635. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.4.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt L. P., Bond J. O., Hall I. E., Jr, Dame G. M., Buff E. E., Marston C., Prather E. C. Meningococcal and ECHO-9 meningitis. Report of an outbreak. Neurology. 1970 Jan;20(1):45–51. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIKAIDO H., MIKAIDO K., SUBBAIAH T. V., STOCKER B. A. ROUGH MUTANTS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. III. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF NUCLEOTIDE-SUGAR COMPOUNDS. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1301–1302. doi: 10.1038/2011301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATERUS K. W., RUYS A. C., SIEBERG I. G. TYPES OF MENINGOCOCCI ISOLATED FROM CARRIERS AND PATIENTS IN A NON-EPIDEMIC PERIOD IN THE NETHERLANDS. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:265–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02046068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUBBAIAH T. V., STOCKER B. A. ROUGH MUTANTS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. I. GENETICS. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2011298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]