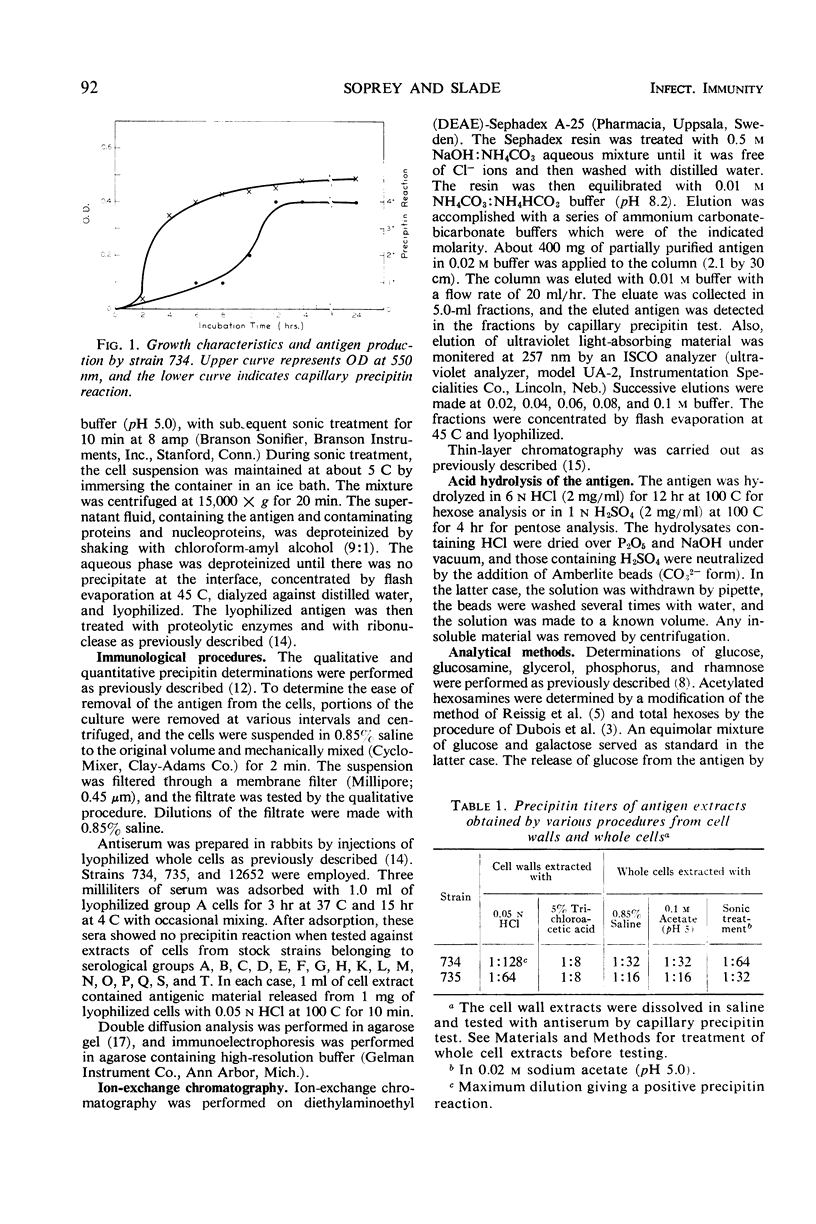
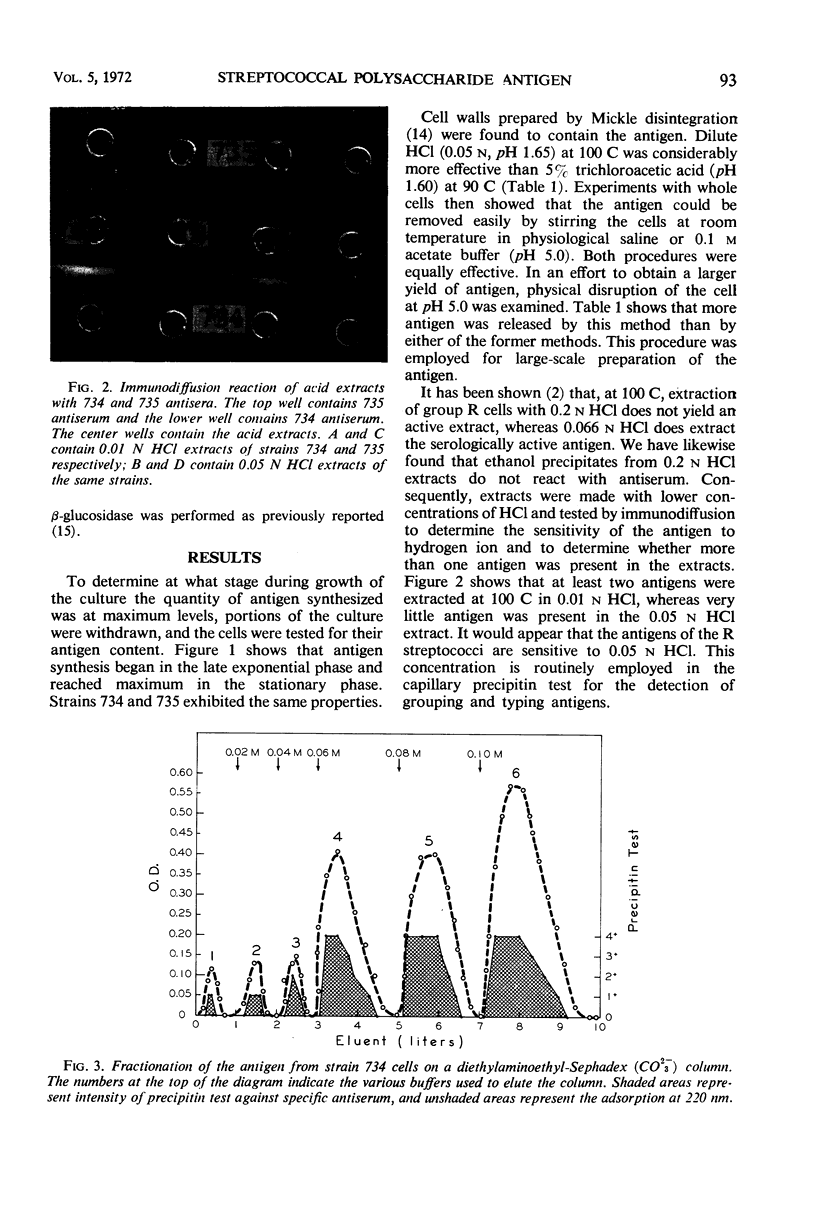
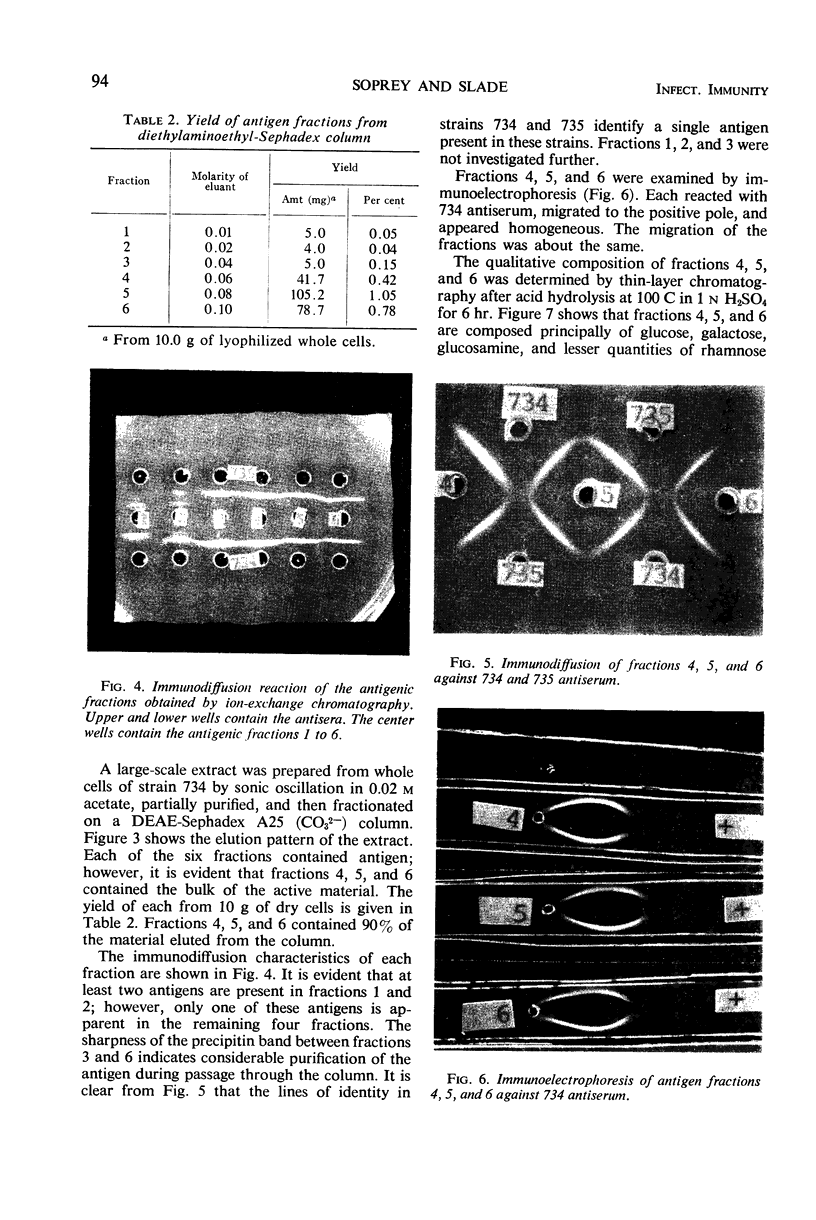
Abstract
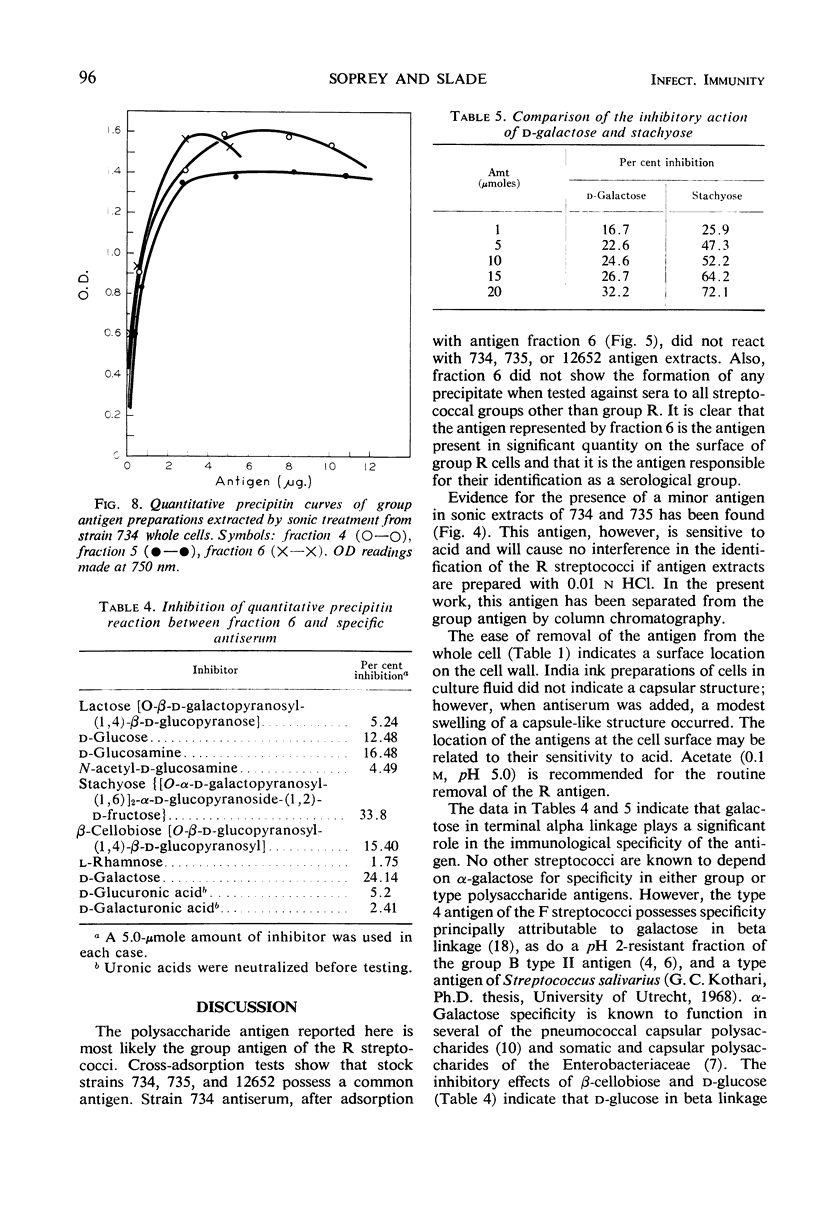
The group R streptococcal group antigen has been shown to be a polysaccharide located at the surface of the cell wall of the organism. The antigen was extracted from cell walls in 0.05 n HCl or 5% trichloracetic acid at 100 C, from whole cells at room temperature in 0.85% NaCl or 0.1 m acetate (pH 5.0), and by sonic oscillation. The antigen is largely destroyed when extracted from whole cells in 0.05 n HCl at 100 C. Acetate is recommended for routine extraction. The antigen extracted by sonic treatment was separated into six immunologically active fractions on diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex. The fractions were found to possess a common antigen which exhibited similar properties on immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. The purified antigen did not react with any other streptococcal group antisera. Adsorption of group R serum with the antigen removed all antibodies against whole cell antigen extracts of R cells. Chemical and enzymatic analysis of three fractions showed that the antigen was composed of d-glucose, d-galactose, rhamnose, and glucosamine. No significant quantities of phosphorus, glycerol, ribitol, or muramic acid were present. Significant inhibition of the quantitative precipitin determination by d-galactose and stachyose indicated that galactose in terminal alpha linkage was the immunodominant hexose in the antigen. d-Glucose and d-glucosamine possessed a partial inhibitory activity. N-acetyl-d-glucosamine and l-rhamnose did not produce significant inhibition. The results indicate that the R antigen is an immunologically specific structure which serves as a reliable means of identification of these streptococci as a serological group.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colman G., Williams R. E. The cell walls of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):375–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMOOR C. E. SEPTICAEMIC INFECTIONS IN PIGS, CAUSED BY HAEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI OF NEW LANCEFIELD GROUPS DESIGNATED R, S, AND T. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:272–280. doi: 10.1007/BF02046069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. II. The chemical basis for serological specificity of the type II HCl antigen. J Exp Med. 1967 Mar 1;125(3):381–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):191–203. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno T., Slade H. D. Composition and properties of a group A streptococcal teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):747–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.747-752.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kristjansen P., Skadhauge K. Group R streptococci pathogenic for man. Two cases of meningitis and one fatal case of sepsis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBERS P. A., HURWITZ E., HEIDELBERGER M. Immunochemistry of pneumococcal types II, V, and VI. II. Inhibition tests in the type VI precipitating system. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:920–926. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.920-926.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS W. S., STEWART F. S. The sugar composition of streptococcal cell walls and its relation to haemagglutination pattern. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Feb;24:253–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. Cell-wall composition and the grouping antigens of Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.345-351.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. Studies on Streptococcus pyogenes. V. Biochemical and microscopic aspects of cell lysis and digestion by enzymes from Streptomyces albus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jan;79:103–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.1.103-112.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade H. D. Extraction of Cell-Wall Polysaccharide Antigen from Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.667-672.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprey P., Slade H. D. Chemical structure and immunological specificity of the streptococcal group e cell wall polysaccharide antigen. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):653–658. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.653-658.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLERS J. M., MICHEL M. F., SYSMA M. J., WINKLER K. C. CHEMICAL ANALYSIS AND INHIBITION REACTIONS OF THE GROUP AND TYPE ANTIGENS OF GROUP F STREPTOCOCCI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jul;36:95–105. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]