Figure 1.
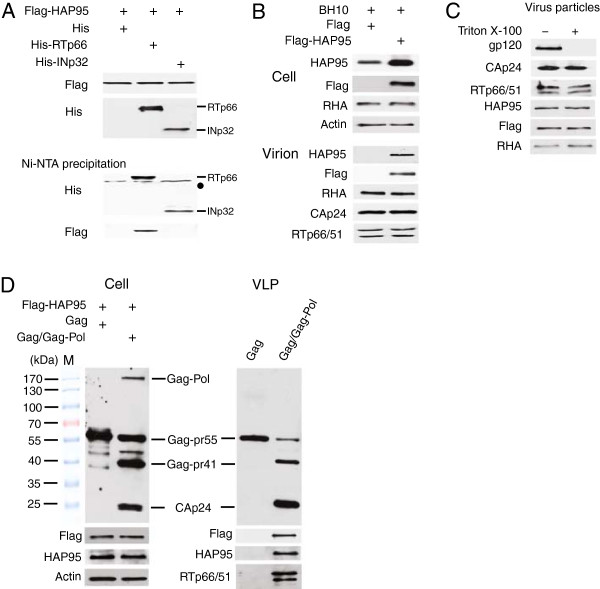
Incorporation of HAP95 into HIV-1 particles upon overexpression. (A) Co-precipitation of HAP95 with His-tagged RTp66. 293 T cells were cotransfected with DNAs encoding for Flag-HAP95 and either His-tagged RTp66 or His-tagged INp32, or His tag. Upper panels show Western blots of cell lysates probed with either anti-Flag or anti-His. The cell lysates were then incubated and precipitated with Ni-NTA agarose. The lower panels show the Western blots of the precipitates probed with either anti-His or anti-Flag. •, non-specific protein bands. The His-tag peptide alone was not detected in these Western blots. (B) Association of HAP95 with purified HIV-1 particles. 293 T cells were cotransfected with DNAs encoding for HIV-1 BH10 and either Flag-HAP95 or Flag tag. Upper panels show the Western blots of cell lysates probed with anti-HAP95, anti-Flag, anti-RHA, and anti-β-actin. Lower panels show the Western blots of purified HIV-1 particles probed with anti-HAP95, anti-Flag, anti-RHA, anti-p24, and anti-RT. (C) HIV-1 particles containing Flag-HAP95 were treated with Triton X-100. The viral cores were isolated and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-gp120, anti-p24, anti-RT, anti-HAP95, anti-Flag, and anti-RHA. (D) Incorporation of HAP95 into VLP. 293T cells were cotransfected with DNAs encoding for Flag-HAP95 and either BH10 Gag or BH10 Gag/Gag-Pol. VLPs were purified by step sucrose centrifugation at 48 hours posttransfection. Cell lysates and VLPs were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-p24, anti-Flag, anti-HAP95, anti-β-actin, or anti-RT. M, protein size marker shown in kDa.
