Abstract
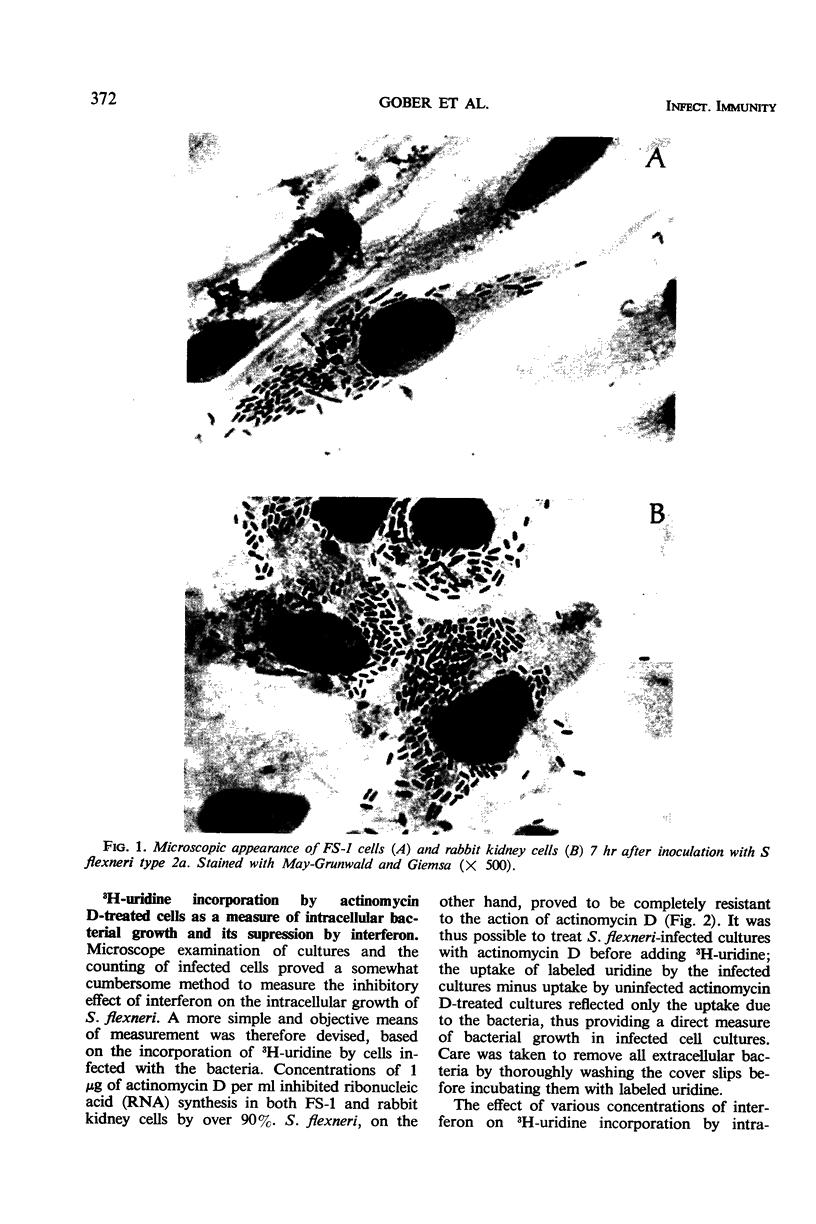
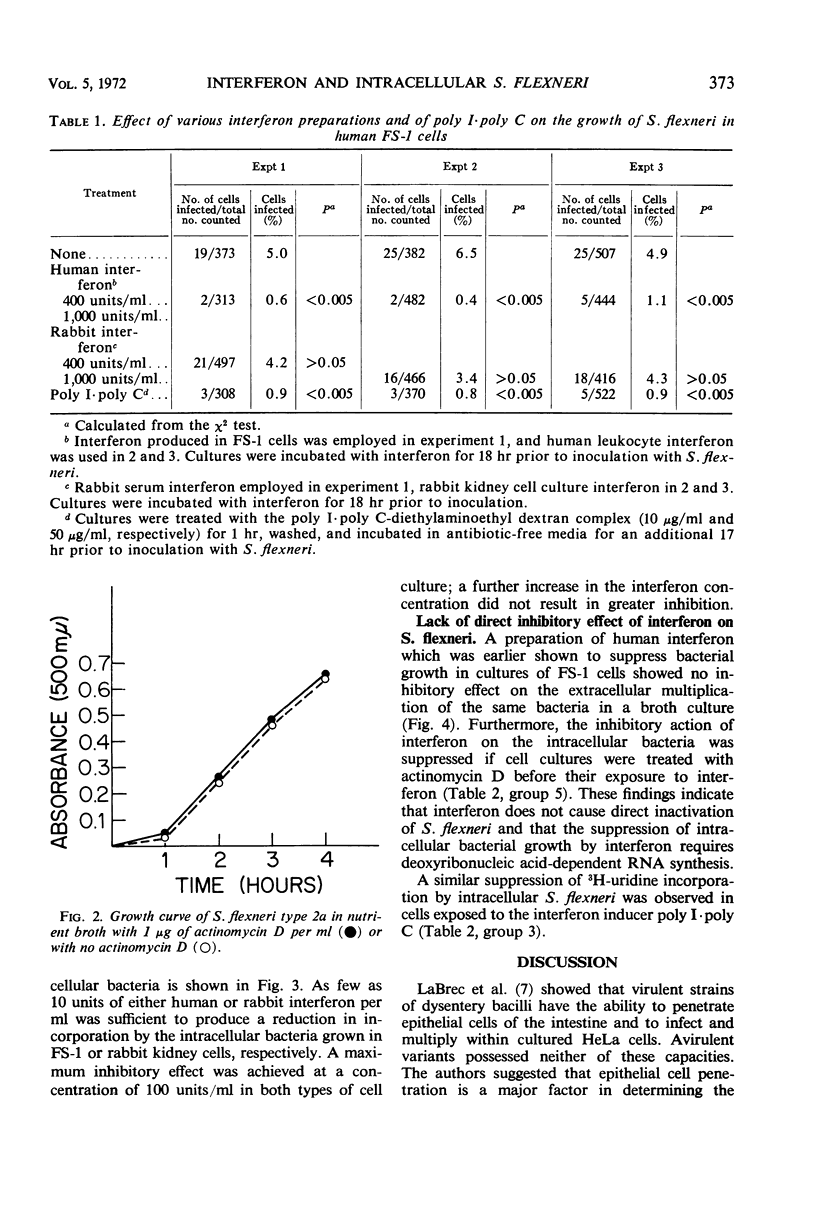
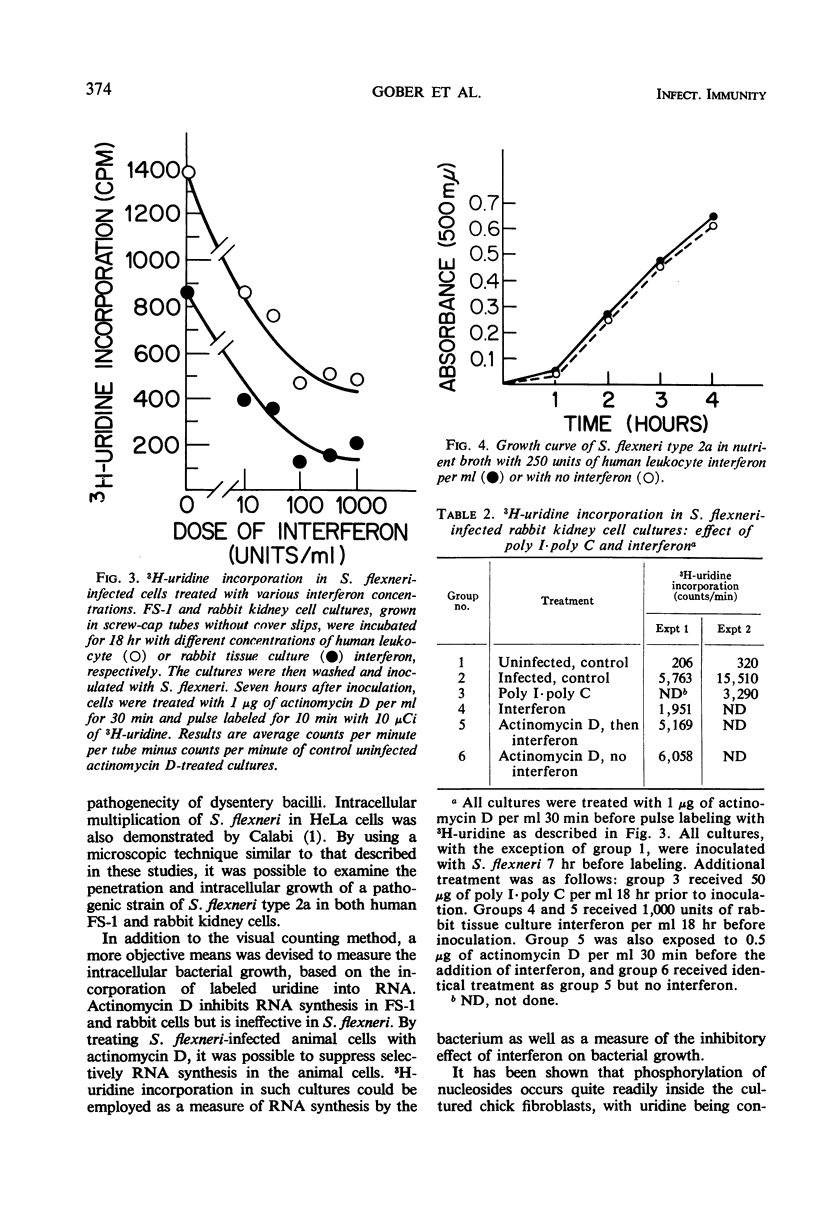
A strain of Shigella flexneri type 2a was found to multiply intracellularly in cultures of the diploid human cell strain FS-1 and in secondary rabbit kidney cells. When inoculated cultures were stained and observed under the light microscope, it appeared that the cytoplasm of infected cells became gradually filled with bacteria. Various preparations of human and rabbit interferon were found to suppress the intracellular bacterial growth in homologous cells. Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (poly I·poly C) had a similar inhibitory effect. Rabbit interferon preparations did not cause a significant suppression in human cells. Suppression of the bacterial growth could be demonstrated in two ways: (i) by showing that treatment with either homologous interferon or poly I·poly C reduced the proportion of infected cells determined by counting the total number of cells and the number of cells with 10 or more bacteria in several microscopic fields selected at random, or (ii) by showing that a suppression in 3H-uridine incorporation by bacteria occurs in infected cultures treated with actinomycin D after incubation with interferon or poly I·poly C. (Uridine incorporation by the bacterium is insensitive to actinomycin D.) Treatment of cells with actinomycin D before incubation with interferon prevented the development of cellular resistance to bacterial infection. Interferon preparations did not have an inhibitory effect on the extracellular growth of S. flexneri in a broth culture. These findings show that the range of activity of the interferon system apparently extends to intracellularly growing bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calabi O. In-vitro interaction of Shigella flexneri with leukocytes and HeLa cells. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jul-Aug;122(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.1-2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Brouty-Boyé D., Thomas M. T., Macieira-Coelho A. Interferon and cell division. I. Inhibition of the multiplication of mouse leukemia L 1210 cells in vitro by interferon preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1052–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna L., Merigan T. C., Jawetz E. Inhibition of TRIC agents by virus-induced interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):417–421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R., Vanderberg J. Interferon inducers protect mice against plasmodium berghei malaria. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Gillmore J. D., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):825–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.825-832.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Krautwurst P. A., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Rickettsia akari. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):819–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.819-824.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Carter W. A. Molecular basis of the action of interferon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B. Interferon and interferon inducers in the treatment of malignancies. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Interferon: protection of cells infected with an intracellular protozoan (Toxoplasma gondii). Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):804–806. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Synthetic polyanions protect mice against intracellular bacterial infection. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):361–363. doi: 10.1038/226361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Nucleotide metabolism in tissue culture cells at low temperatures. I. Phosphorylation of nucleosides and deoxynucleosides in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):228–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Nucleotide metabolism in tissue culture cells at low temperatures. II. Feedback mechanisms during the synthesis of nucleoside and deoxynucleoside triphosphates at low temperatures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):238–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H., Cantell K. Further studies on the production of interferon by human leukocyte in vitro. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1967;45(1):20–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueltenfuss E. A., Pollard M. Cytochemical Assay of Interferon Produced by Duck Hepatitis Virus. Science. 1963 Feb 15;139(3555):595–596. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3555.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Jahiel R. I. Action of interferon and its inducers aginst nonviral infectious agents. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):69–77. doi: 10.1001/archinte.126.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Ng M. H. Post-transcriptional control of interferon synthesis. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):588–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.588-594.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A., Came P. E. Induction of resistance to bacterial infections of mice with poly I-poly C. Nature. 1970 Apr 11;226(5241):170–170. doi: 10.1038/226170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]