Abstract
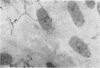
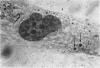
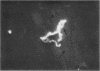
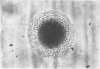
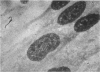
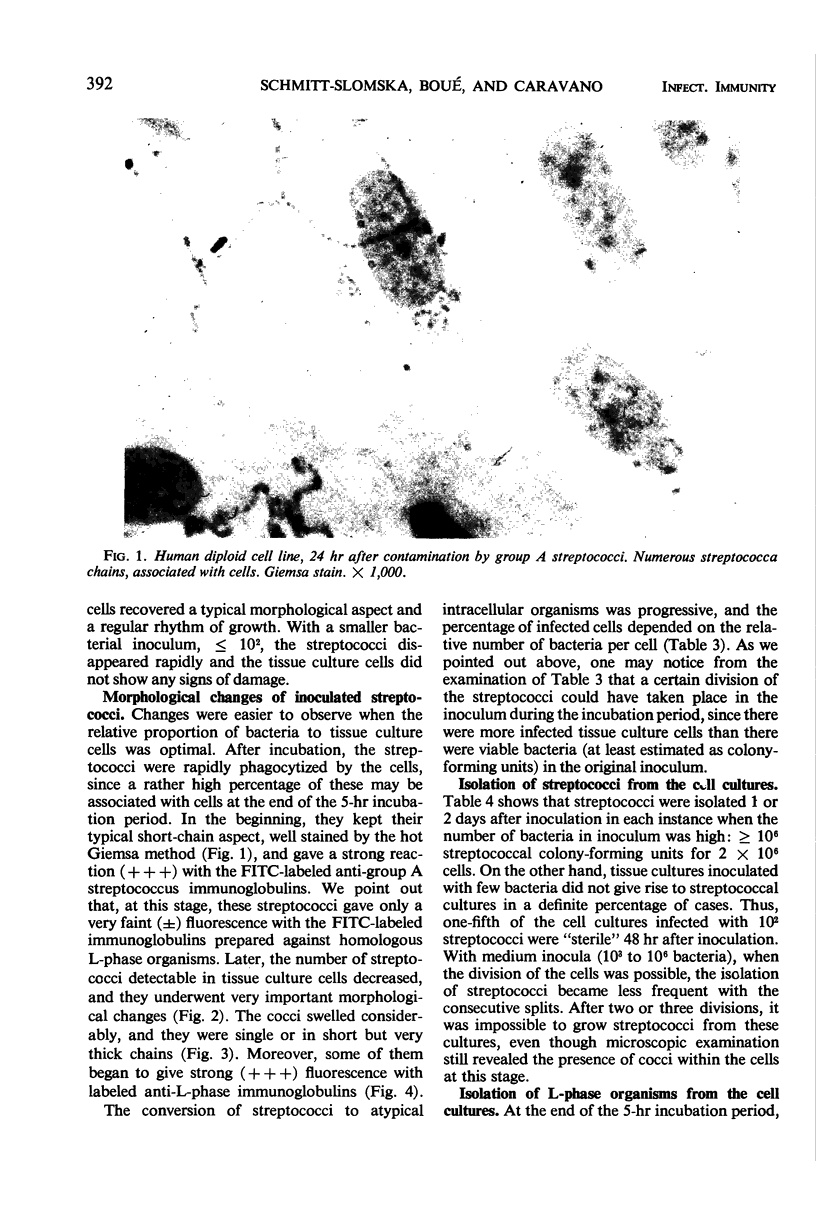
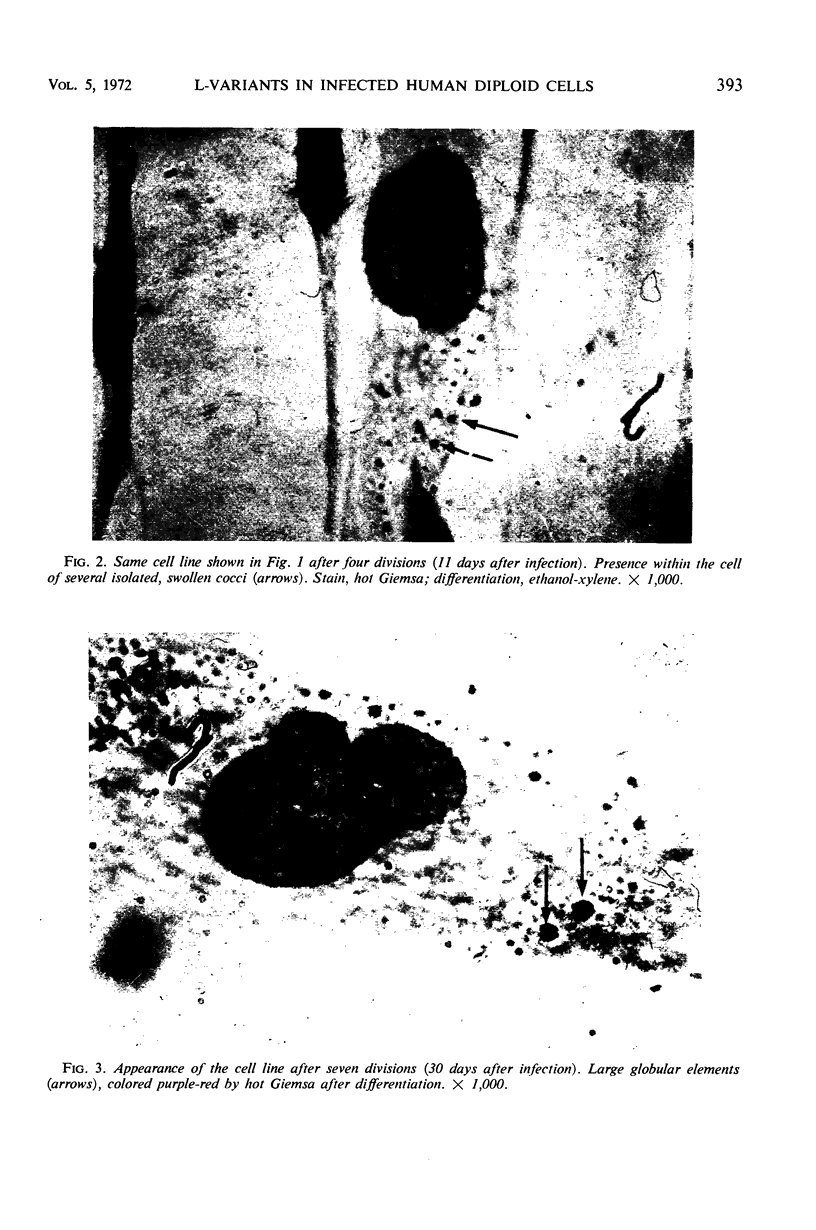
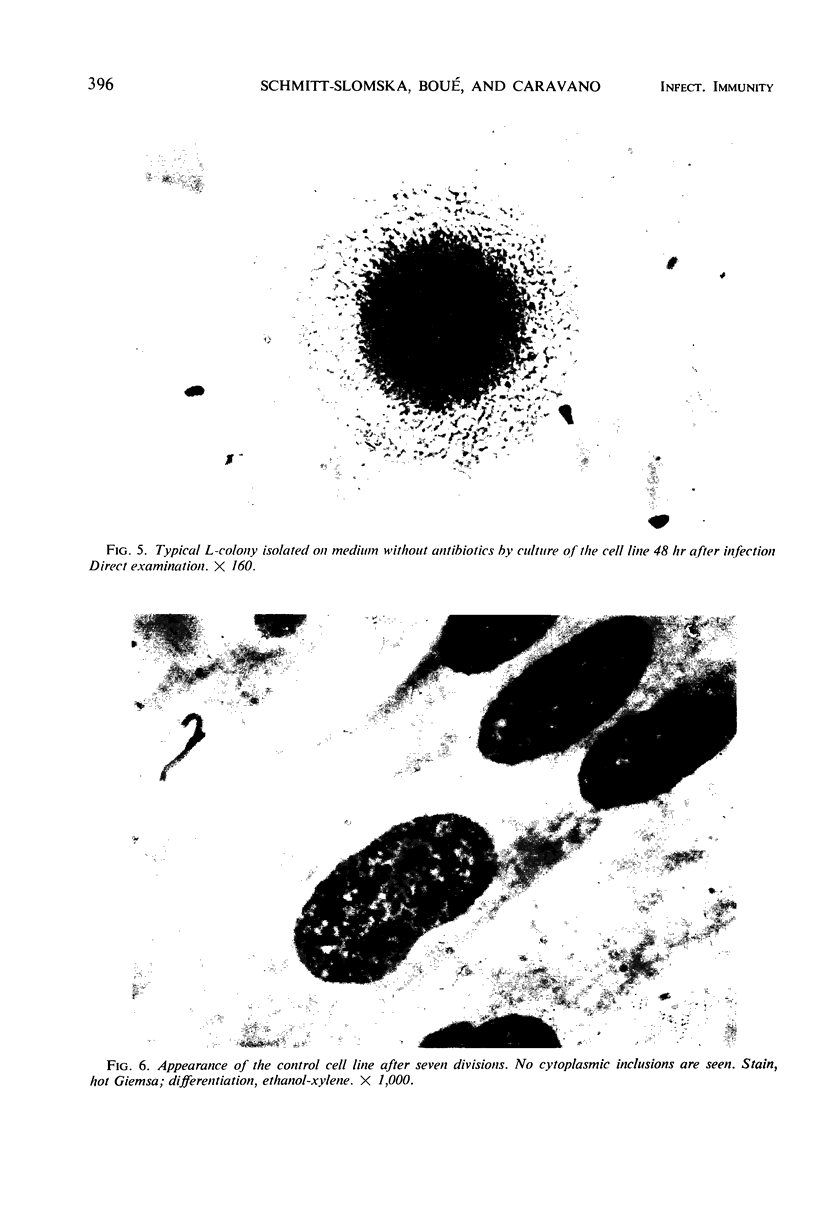
Human diploid cells in culture, infected with a balanced amount of living group A streptococci, were able to survive the infection and could be divided and propagated normally thereafter. The streptococci were rapidly phagocytized by the tissue culture cells. At the beginning, they kept their typical appearance, as well as their ability to fix dyes and group-specific immunoglobulins. After 1 to 2 days, the number of detectable streptococci decreased and they underwent important morphological changes. After some subsequent divisions of the cell line, streptococci persisted in cells only as large, isolated, swollen cocci, and no longer grew on suitable media. After six to eight divisions, a noticeable percentage of the tissue culture cells were very similar in appearance to the same cell line experimentally infected with “stable” L-variants. Cultures on L-phase media of supernatant fraction and cells, made 24 to 48 hr after inoculation, showed typical L-colonies. These grew well on media without antibiotics, as well as on media containing penicillin or vancomycin. They could be propagated on media with penicillin for months and were able to revert to group A streptococci after several subcultures on antibiotic-free media. Controls of uninoculated tissue culture cells never showed the presence of any microorganism. Group A streptococci inoculated into Eagle's basal medium, which was used for the tissue cultures, did not grow and never gave rise to L-colonies, even though the medium contained penicillin. Previous data suggest a biochemical explanation for this conversion, which otherwise is an occasional phenomenon.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayoub E. M., McCarty M. Intraphagocytic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Properties of the enzyme and its activity on group A streptococcal carbohydrate in comparison with a soil bacillus enzyme. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):833–851. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub E. M., White J. G. Intraphagocytic degradation of group A streptococci: electron microsopic studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):728–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.728-736.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARILE M. F., MALIZIA W. F., RIGGS D. B. Incidence and detection of pleuropneumonia-like organisms in cell cultures by fluorescent antibody and cultural procedures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84:130–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.1.130-136.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARSKI T. R., SHEPARD C. C. Pleuropneumonia-like (mycoplasma) infections of tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:626–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.626-635.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. G., FISHEL C. W. Growth of Bordetella pertussis in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(4):465–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.4.465-474.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELTON H. M., GAGGERO A., POMERAT C. M. Reactions of cells in tissue culture to Hemophilus pertussis. I. Effect of whole organisms on brain tissue and results of treatment with specific and normal serum. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1954;12(4):960–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., CHANOCK R. M. MYCOPLASMA SPECIES OF MAN. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Jun;29:185–221. doi: 10.1128/br.29.2.185-221.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PICKETT M. J. Intracellular behavior of Brucella variants in chick embryo cells in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Dec;93(3):476–479. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMGREN N. B., CAMPBELL W. E., Jr Tissue cell culture contamination in relation to bacterial pleuropneumonia-like organism-L form conversion. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jun;79:869–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.6.869-874.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten B. A., Sulkin S. E. Intracellular Production of Brucella L Forms I. Recovery of L Forms from Tissue Culture Cells Infected with Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):285–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.285-296.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourany M., Kendrick P. L. Interaction between a human monocytic cell line and Salmonella typhosa. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):495–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. THE SEROLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF MYCOPLASMA STRAINS (PLEURO-PNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS) FROM VARIOUS SOURCES. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Jun;62:199–219. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY P. N., QUINN R. W. EFFECT OF HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI ON TISSUE CELLS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:46–51. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I. A., ALLNER K. L forms of bacteria as contaminants in tissue culture. Nature. 1960 Jun 18;186:992–992. doi: 10.1038/186992a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMER E. A., Jr PRODUCTION OF L FORMS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI IN MICE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:159–163. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Rogul M., Wittler R. G. Molecular genetic studies of relationships among mycoplasma, L-forms and bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham-Huu-Trung, Schmitt-Slomska J., Boué A. Etude au microscope électronique des premiers stades de l'infection des cultures de cellules diploïdes humaines par des formes L du streptocoque du groupe A. Pathol Biol. 1968 Apr;16(7):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn R. W., Lowry P. N. Effect of Streptococcus pyogenes on tissue cells. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1825–1831. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1825-1831.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Prendergast T. J., Karakawa W. W., Harmon C. K., Krause R. M. Enhanced resistance to streptococcal infection induced in mice by cell wall mucopeptide. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):877–890. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux J., Ramuz M., Serre J. C. Action de la chlortétracycline sur les brucella intracellulaires. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Jan;116(1):49–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAFFER J. M., KUCERA C. J., SPINK W. W. The protection of intracellular brucella against therapeutic agents and the bactericidal action of serum. J Exp Med. 1953 Jan;97(1):77–90. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMADEL J. E. Intracellular infections. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1963 Mar;39:158–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Slomska J., Lucel-Varnier Y. Essai d'isolement de bactéries en phase L chez des souris inoculées avec des streptocoques du groupe A et traitées par la pénicilline. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Sep;117(3):347–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Slomska J., Sacquet E., Caravano R. Group A streptococcal L forms. I. Persistence among inoculated mice. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):451–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.451-455.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerson N. L., Reich P. R., Chanock R. M., Weissman S. M. Genetic differentiation by nucleic acid homology. 3. Relationships among mycoplasma, L-forms, and bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTLER R. G., CARY S. G., LINDBERG R. B. Reversion of a pleuropneumonia-like organism to a Corynebacterium during tissue culture passage. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):763–774. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]