Abstract
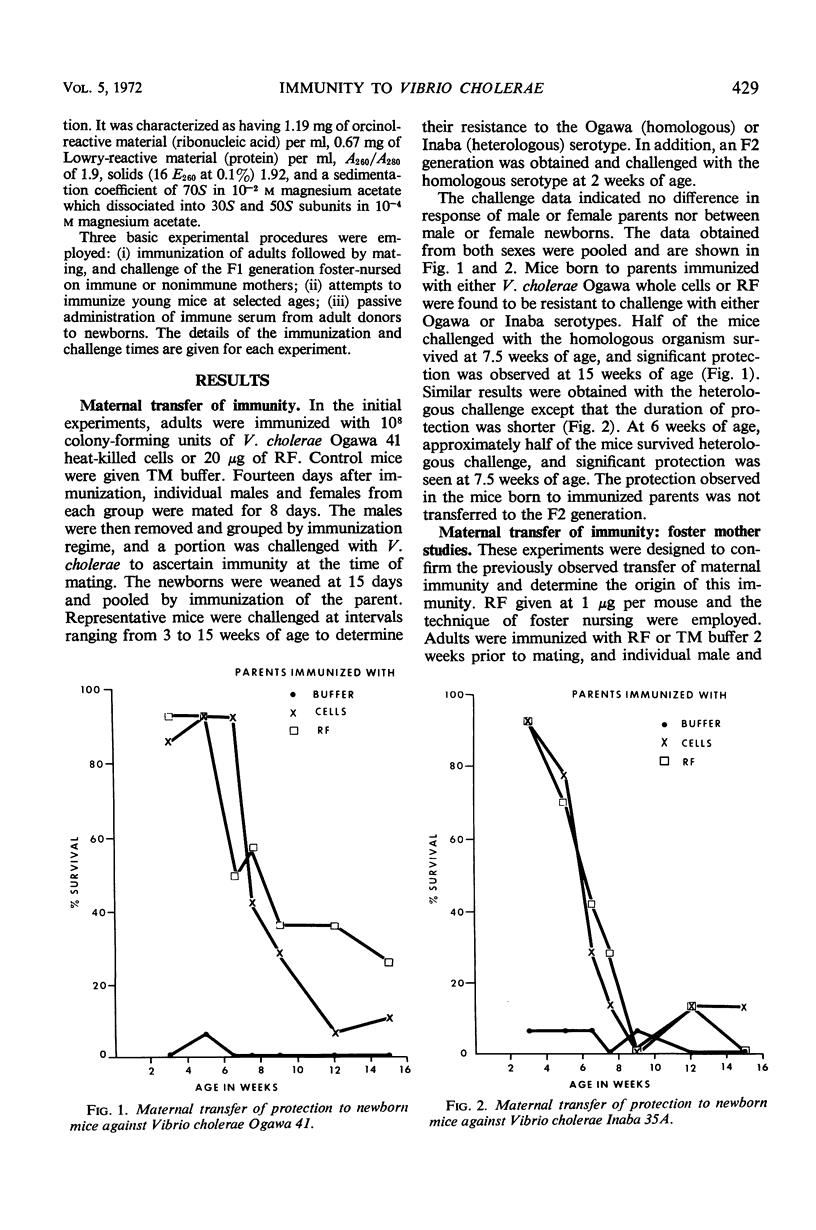
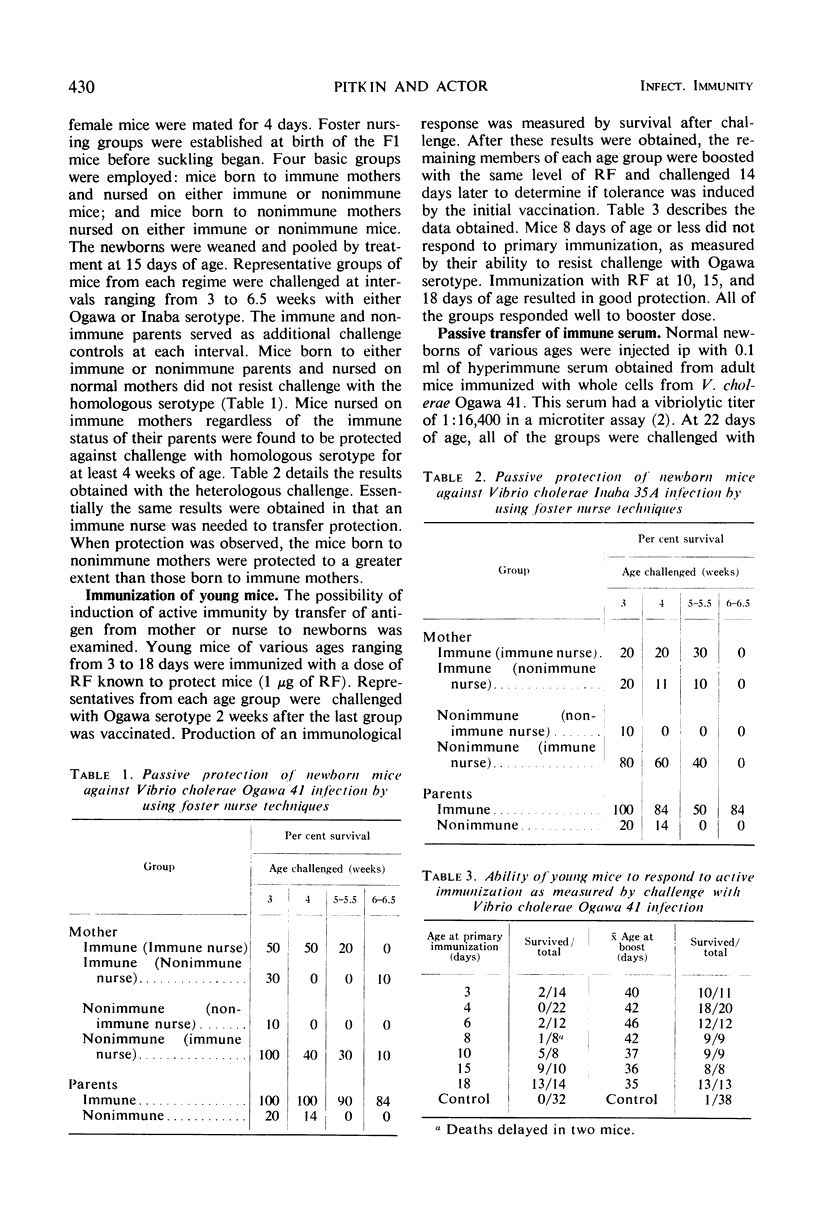
Mice were immunized subcutaneously with either killed cells or a ribosome-containing fraction (RF) obtained from Vibrio cholerae Ogawa 41. At appropriate time intervals, these mice or their progeny were challenged with uniformly lethal doses of Ogawa or Inaba serotype. Half of the offspring born to mice immunized with 20 μg of RF were protected against homologous challenge at 7.5 weeks of age, and significant protection was observed up to 15 weeks of age. Similar protection was observed with heterologous challenge, but the duration of protection was reduced. The duration of protection obtained in newborns was related to the quantity of RF given to the mother. Protection was transferred from mother to young via colostrum or milk. Protection was not due to transfer of antigen, as active immunity could not be induced in newborn mice immunized with RF.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM D. R., TERRY R. J. The absorption of 131I-labelled homologous and heterologous serum proteins fed orally to young rats. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):579–583. doi: 10.1042/bj0660579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMBELL F. W., HALLIDAY R., MORRIS I. G. Interference by human and bovine serum and serum protein fractions with the absorption of antibodies by suckling rats and mice. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jul 1;149(934):1–11. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUCE-CHWATT L. J., GIBSON F. D. Transplacental passage of Plasmodium berghei and passive transfer of immunity in rats and mice. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Jan;50(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(56)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S., Robinson R. L., Pickett M. J. Preliminary studies on the bioassay of anticholera vaccines in chinchillas. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):56+–56+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benenson A. S., Saad A., Mosley W. H. Serological studies in cholera. 2. The vibriocidal antibody response of cholera patients determined by a microtechnique. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(2):277–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaskovic D., Rathová V., Kocisková D., Kaplan M. M., Jamrichová O., Sádecký E. Experimental infection of weanling pigs with A-swine influenza virus. 3. Immunity in piglets farrowed by antibody-bearing dams experimentally infected a year earlier. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(5):771–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambell F. W. The transmission of immunity from mother to young and the catabolism of immunoglobulins. Lancet. 1966 Nov 19;2(7473):1087–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTA N. K., HABBU M. K. Experimental cholera in infant rabbits: a method for chemotherapeutic investigation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Jun;10(2):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta N. K., Dohadwalla A. N., Chakrabarti M. C. The antigenic interrelationships of live cholera vaccines and a method of bioassay. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(2):337–343. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., NORRIS H. T., DUTTA N. K. PATHOGENESIS EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA IN INFANT RABBITS. I. OBSERVATIONS ON THE INTRAINTESTINAL INFECTION AND EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA PRODUCED WITH CELL-FREE PRODUCTS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:203–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIDAY R. The absorption of antibodies from immune sera by the gut of the young rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1955 Mar 15;143(912):408–413. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1955.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIDAY R. The absorption of antibody from immune sera and from mixtures of sera by the gut of the young rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):92–103. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALISS N., DAGG M. K., STIMPFLING J. H. MATERNAL TRANSFER OF ISOANTIBODY IN MICE. Transplantation. 1963 Oct;1:535–545. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196301040-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUR J., SHRIVASTAV J. B. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON VIBRIO POLYSACCHARIDES. Indian J Med Res. 1964 Aug;52:809–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS I. G. The effects of heterologous sera on the uptake of rabbit antibody from the gut of young mice. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):84–91. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. The antigens of Vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):505–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANSE M. V., DUTTA N. K. CHOLERA VACCINES AND PLACENTAL TRANSMISSION OF ANTIBODIES. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:243–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANSE M. V., JHALA H. I., DUTTA N. K. PASSIVE IMMUNITY IN EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA. J Infect Dis. 1964 Feb;114:26–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN M., FEELEY J. C. Protective activity of cholera vaccines against E1 Tor cholera vibrios. Bull World Health Organ. 1963;28(3):379–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Carpenter C. C. Experimental canine cholera. I. Development of the model. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):138–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Carpenter C. C., Steenburg R. W., Pierce N. F. Experimental cholera. A canine model. Lancet. 1966 Jul 23;2(7456):206–207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajid M. A., McAlack R. F., Cerny J., Friedman H. Antibody plaque responses of mice given Vibrio cholerae antigen as neonates. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1301–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. J. Transmission of antimalarial immunity (Plasmodium berghei) from mother rats to their young during lactation. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Jan;50(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(56)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



