Abstract
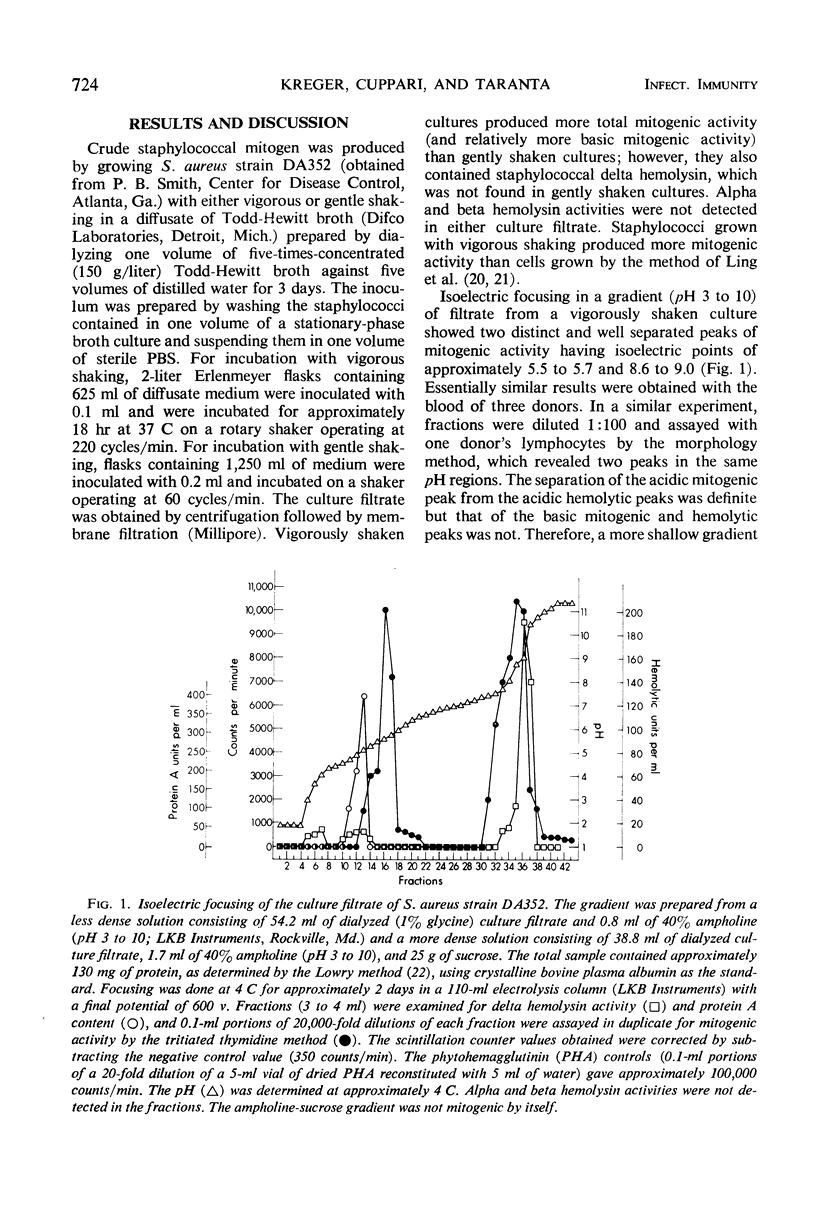
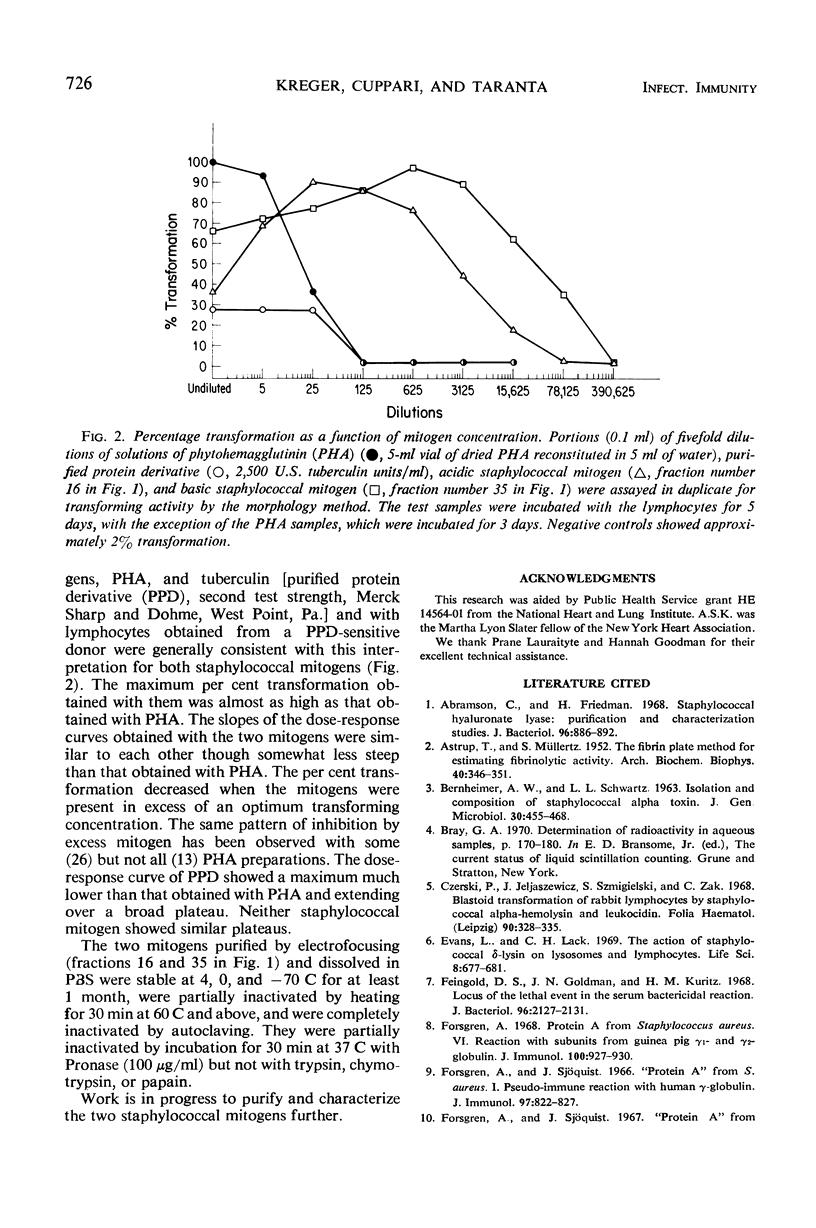
Staphylococcus aureus strain DA352, grown in a diffusate of Todd-Hewitt broth, produced two extracellular nondialyzable lymphocyte mitogens having isoelectric points of 5.5 to 5.7 and 8.6 to 9.0. The mitogens were separable from one another by isoelectric focusing and could be isolated free of detectable amounts of other staphylococcal products by ethanol precipitation followed by isoelectric focusing. Dose-response curves with both mitogens showed a maximum per cent transformation in the range (90%+) obtained with phytohemagglutinin (PHA), a decrease of transformation with excess mitogen, and, with decreasing concentrations, a slope somewhat less steep than that obtained with PHA. Incubation with undigested or pepsin-digested pooled human gamma globulin enhanced the activity of the basic mitogen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson C., Friedman H. Staphylococcal hyaluronate lyase: purification and characterization studies. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):886–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.886-892.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerski P., Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Zak C. Blastoid transformation of rabbit lymphocytes by staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin and leukocidin. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1968;90(4):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Lack C. H. The action of staphylococcal delta-lysin on lysosomes and lymphocytes. Life Sci. 1969 Jul 15;8(14):677–681. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the lethal event in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2127-2131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. VI. Reaction with subunits from guinea pig gamma-1- and gamma-2-globulin. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):927–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from Staphylococcus aureus. 3. Reaction with rabbit gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. VII. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(3):466–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone G. P., Yoshida A. The cytopathic action of purified staphylococcal delta-hemolysin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Feb;48(1):11–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Rosenau W., Burke G. C., Moon H. D. Dose-response of lymphocytes to purified, protein-free phytohemagglutinin: lack of metabolic inhibition with increasing concentrations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jun;134(2):459–461. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow J. A., Robinson J. Properties of purified staphylococcal beta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1026–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1026-1032.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J. Purification and properties of lysozyme produced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.376-384.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., HUSBAND E. M. SPECIFIC AND NON-SPECIFIC STIMULATION OF PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES. Lancet. 1964 Feb 15;1(7329):363–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., SPICER E., JAMES K., WILLIAMSON N. THE ACTIVATION OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES BY PRODUCTS OF STAPHYLOCOCCI. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jul;11:421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malveaux F. J., Clemente C. L. Staphylococcal acid phosphatase: extensive purification and characterization of the loosely bound enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1209–1214. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1209-1214.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., SELIGMAN A. M. Evidence for the specificity of esterase and lipase by the use of three chromogenic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):343–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigas D. A., Tisdale V. V. Bio-assay and dose-response of the mitogenic activity of the phytohemagglutinin of Phaseolus vulgaris. Experientia. 1969 Apr 15;25(4):399–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01899946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. Studies on rabbit lymphocytes in vitro. V. The induction of blast transformation with sheep antisera to rabbit IgG subunits. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):289–301. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Stålenheim G. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. IX. Complement-fixing activity of protein A-IgG complexes. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taranta A., Cuppari G., Quagliata F. Dissociation of hemolytic and lymphocyte-transforming activities of streptolysin S preparations. J Exp Med. 1969 Apr 1;129(4):605–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODIN A. M. Fractionation of a leucocidin from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1959 Oct;73:225–237. doi: 10.1042/bj0730225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D., Nossal G. J. Identification of human T and B lymphocytes in normal peripheral blood and in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1971 Oct 9;2(7728):788–791. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92741-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


