Abstract
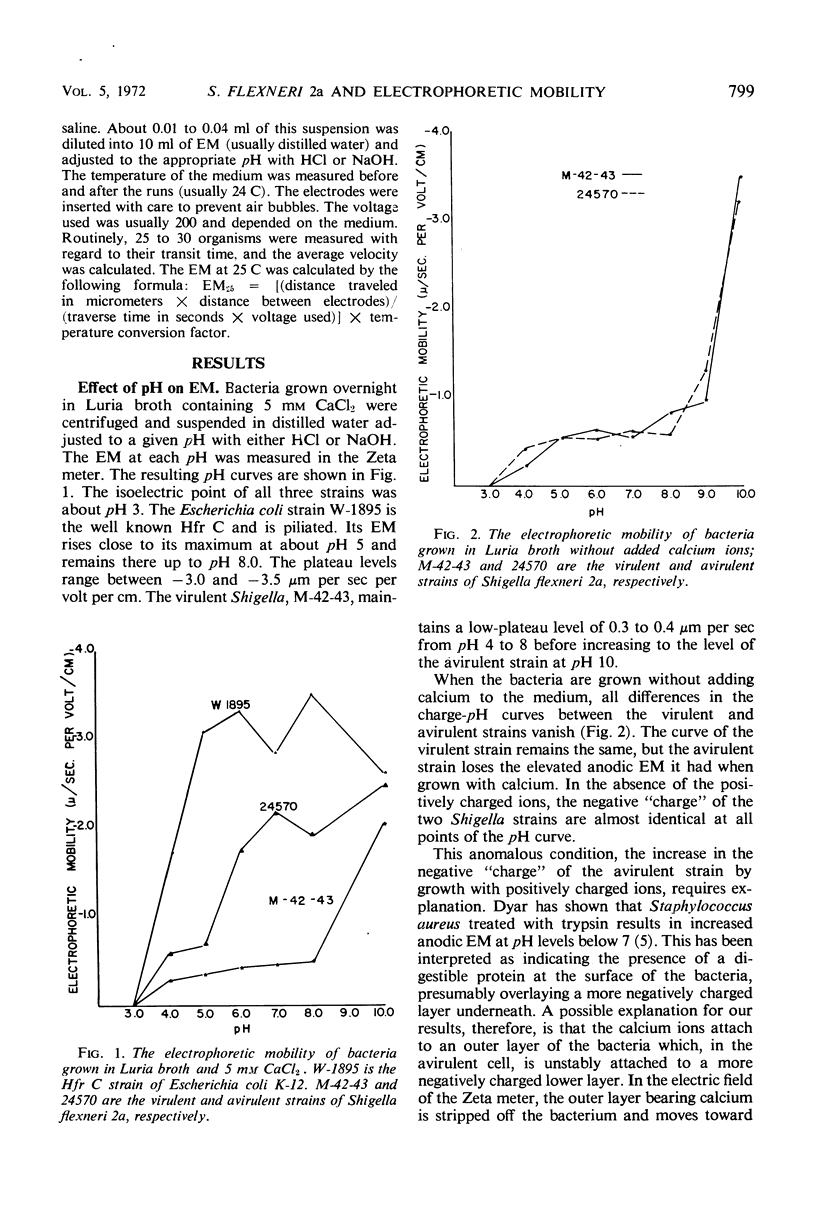
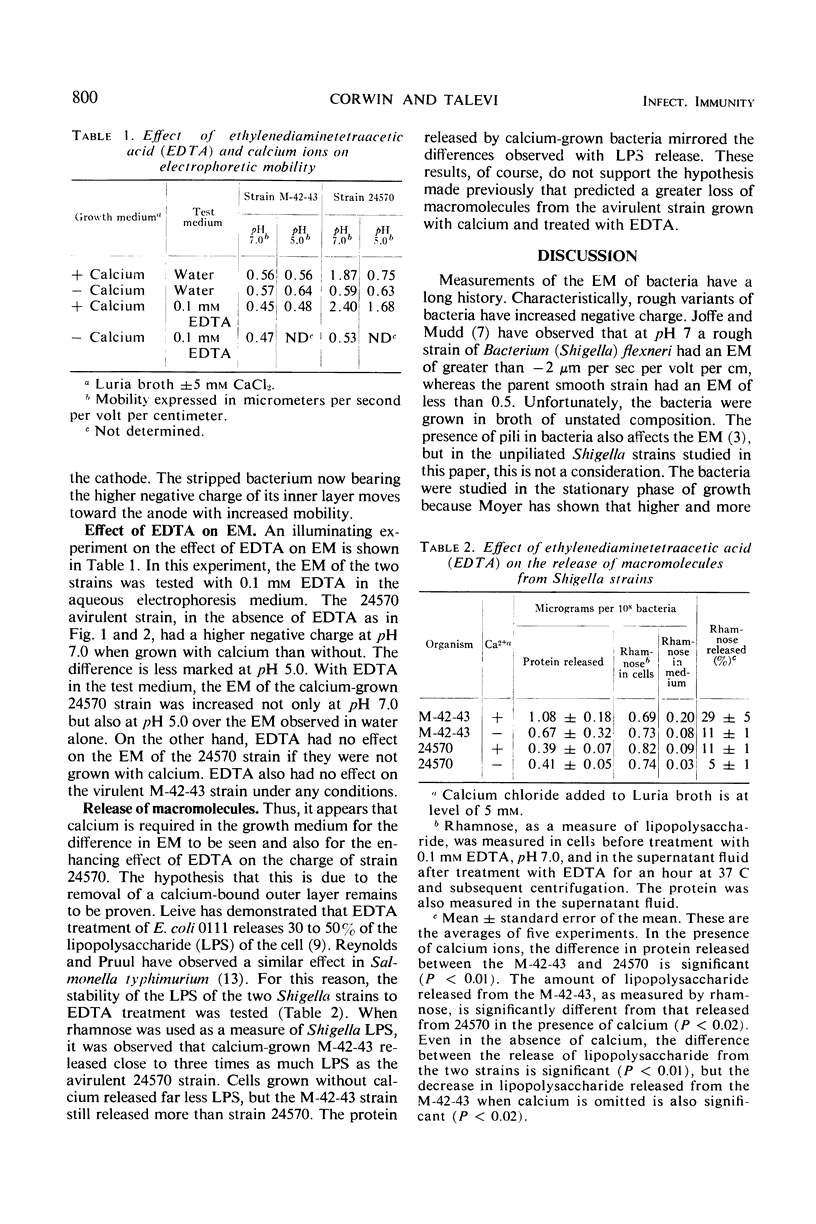
An avirulent mutant of Shigella flexneri 2a, when grown in broth containing calcium ions, was found to have a three- to fourfold increase in electrophoretic mobility toward the anode when compared to its virulent parent. Under these same growth conditions, it was found that the avirulent strain was made more electronegative in the presence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). EDTA had no effect on the electrophoretic mobility of the virulent strain. In the absence of added calcium in the growth medium, no differences between the strains were observed. The alteration which has resulted in an increased negative charge has also stabilized the avirulent strain against loss of lipopolysaccharide from EDTA treatment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. Role of Multivalent Cations in the Organization, Structure, and Assembly of the Cell Wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):380–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.380-387.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINTON C. C., Jr, BUZZELL A., LAUFFER M. A. Electrophoresis and phage susceptibility studies on a filament-producing variant of the E. coli B bacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Dec;15(4):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corwin L. M., Rothman S. W., Kim R., Talevi L. A. Mechanisms and genetics of resistance to sodium lauryl sulfate in strains of Shigella and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyar M. T. Electrokinetical Studies on Bacterial Surfaces: II. Studies on Surface Lipids, Amphoteric Material, and Some Other Surface Properties. J Bacteriol. 1948 Dec;56(6):821–834. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Shovlin V. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Physical, chemical, and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide released from Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6384–6391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer L. S. Changes in the Electrokinetic Potential of Bacteria at Various Phases of the Culture Cycle. J Bacteriol. 1936 Oct;32(4):433–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.4.433-464.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Nakamura A., Nakaya R. Cinemicrographic study of tissue cell cultures infected with Shigella flexneri. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Aug;21(4):259–273. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A. The immunochemistry of Shigella flexneri lipopolysaccharides. A quantitative analysis of their monosaccharide constituents. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):903–908. doi: 10.1042/bj0980903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


