Abstract
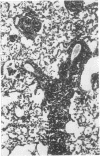
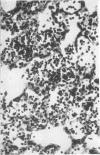
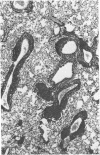
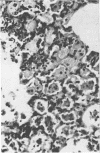
The lungs of conventional rats with chronic pneumonia contained Streptobacillus moniliformis and Mycoplasma pulmonis. These organisms singly and in combination failed to produce lung disease when inoculated into specific pathogen-free rats. On the other hand, diseased lung homogenate not containing cultivable organisms caused a chronic pneumonia when inoculated into specific pathogen-free rats. The organism involved was seen by electron microscopy and is morphologically indistinguishable from the grey lung agent of Andrewes and Glover and Nelson's enzootic bronchiectasis “virus.” All of these agents have morphological and biological properties which indicate close relationship to the mycoplasmas. However, we failed to culture them either in tissue cultures or on inanimate media and conclude that a group of highly fastidious mycoplasma-like agents are a cause of chronic pneumonia in rodents.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARD D. H. PPLO of human genital origin; serological classification of strains and antibody distribution in man. Br J Vener Dis. 1959 Mar;35(1):27–34. doi: 10.1136/sti.35.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMES P. C., BELL D. THE EFFECTS OF CHLORINE GAS ON THE LUNGS OF RATS WITH SPONTANEOUS PULMONARY DISEASE. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:317–327. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay F. W. Association of a Mycoplasma-like agent with chronic pneumonia and bronchiectasis in the rat. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):441–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.441-444.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay F. W., Attridge J. T. The fine structure of cytoplasmic inclusions in a mycoplasma-like infection in mice. J Cell Sci. 1967 Sep;2(3):445–450. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.3.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay F. W. Fine structure and location of the mycoplasma-like gray lung and rat pneumonia agents in infected mouse lung. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):2048–2061. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.2048-2061.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House W., Waddell A. Detection of mycoplasma in cell cultures. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):125–132. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INNES J. R., MCADAMS A. J., YEVICH P. Pulmonary disease in rats; a survey with comments on chronic murine pneumonia. Am J Pathol. 1956 Jan-Feb;32(1):141–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Baker H. J., Overcash R. G., Cassell G. H., Hunt C. E. Murine chronic respiratory disease. Significance as a research complication and experimental production with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):675–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsky I. I., Organick A. B. Pneumonia due to mycoplasma in gnotobiotic mice. I. Pathogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma salivarium, and Mycoplasma pulmonis for the lungs of conventional and gnotobiotic mice. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1154–1163. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1154-1163.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIVEN J. S. F. The histology of grey lung virus lesions in mice and cotton-rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Dec;31(6):759–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Organick A. B., Siegesmund K. A., Lutsky I. I. Pneumonia due to mycoplasma in gnotobiotic mice. II. Localization of Mycoplasma pulmonis in the lungs of infected gnotobiotic mice by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1164–1176. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1164-1176.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]