Abstract
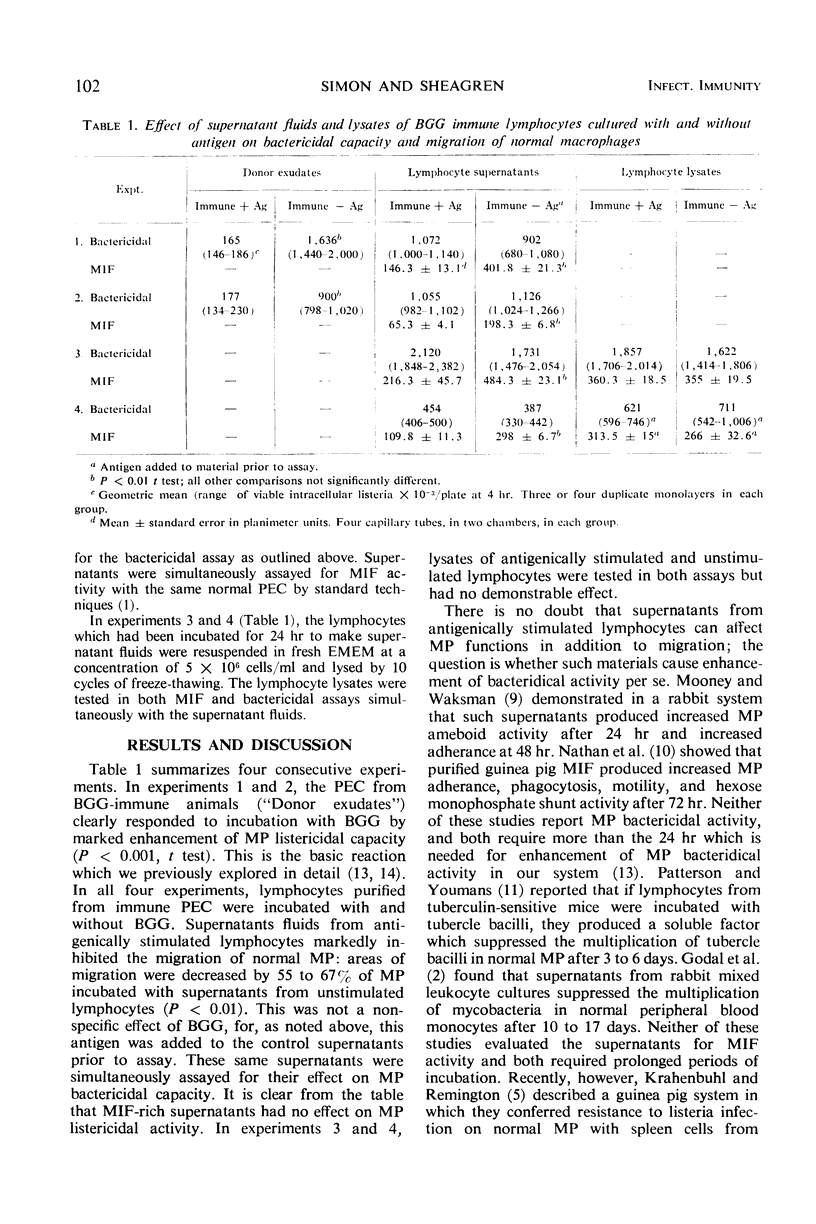
A homogeneous population of immunologically active lymphocytes was obtained from peritoneal exudates of guinea pigs with delayed hypersensitivity to bovine gamma globulin (BGG). The lymphocytes were cultured with and without BGG for 24 hr, and cell-free supernatant fluids were then assayed simultaneously for their ability to influence two in vitro parameters of macrophage function: migration from capillary tubes and bactericidal capacity. In four consecutive experiments, supernatants from antigenically stimulated lymphocytes exhibited substantial migration-inhibitory-factor activity without enhancing the ability of macrophages to kill Listeria monocytogenes. Lymphocyte lysates were inactive in both assays. Possible mechanisms of lymphocyte-macrophage interactions are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVID J. R., AL-ASKARI S., LAWRENCE H. S., THOMAS L. DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY IN VITRO. I. THE SPECIFICITY OF INHIBITION OF CELL MIGRATION BY ANTIGENS. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Rees R. J., Lamvik J. O. Lymphocyte-mediated modification of blood-derived macrophage function in vitro; inhibition of growth of intracellular mycobacteria with lymphokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):625–637. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A. Mechanisms of lymphocyte-induced cell and tissue destruction in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1970 Sep;60(3):469–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jureziz R. E., Thor D. E., Dray S. Transfer with RNA extracts of the cell migration inhibition correlate of delayed hypersensitivity in the guinea pig. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):823–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. In vitro induction of nonspecific resistance in macrophages by specifically sensitized lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.337-343.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKI K., MACKANESS G. B. THE PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:93–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney J. J., Waksman B. H. Activation of normal rabbit macrophage monolayers by supernatants of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1138–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Karnovsky M. L., David J. R. Alterations of macrophage functions by mediators from lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1356–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. J., Youmans G. P. Demonstration in tissue culture of lymphocyte-mediated immunity to tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):600–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.600-603.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Sell S., Nishio J. Activity in vitro of lymphocytes and macrophages in delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Cellular immunity in vitro. I. Immunologically mediated enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity by antigenically stimulated immune lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


