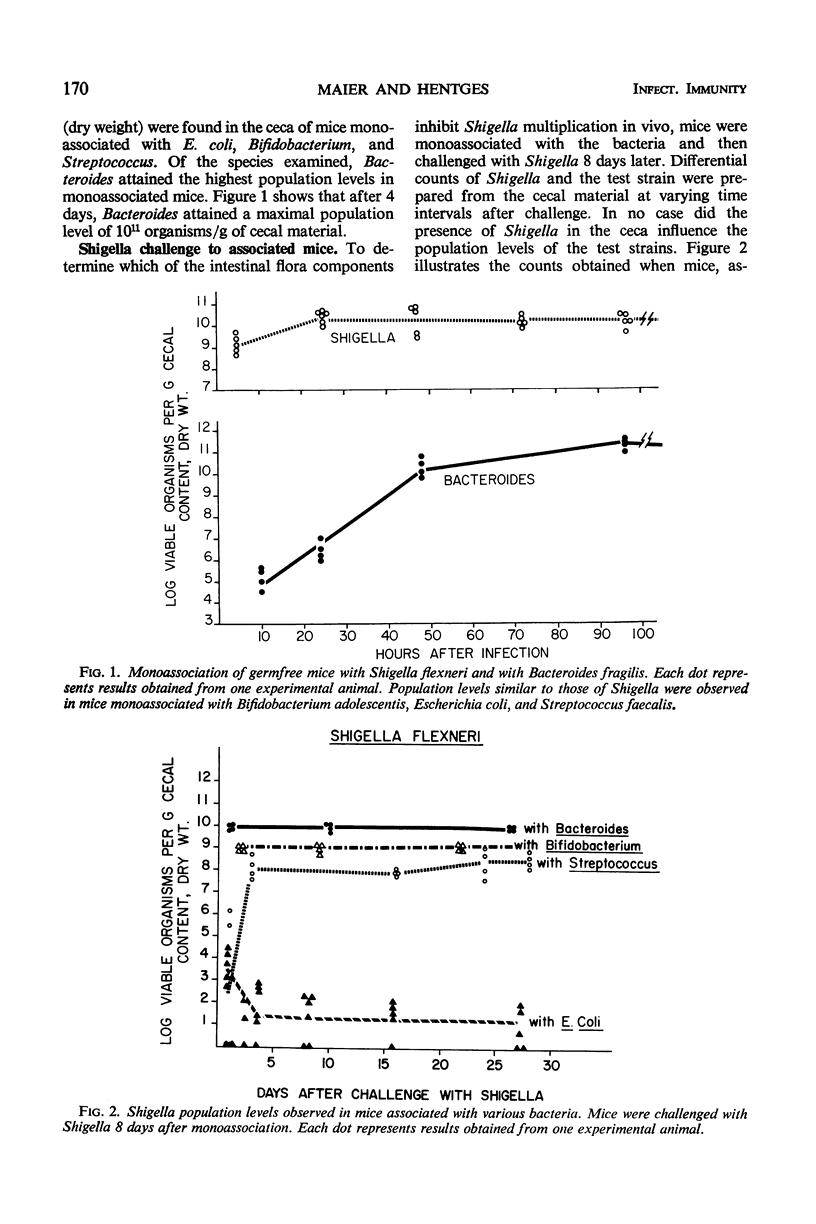
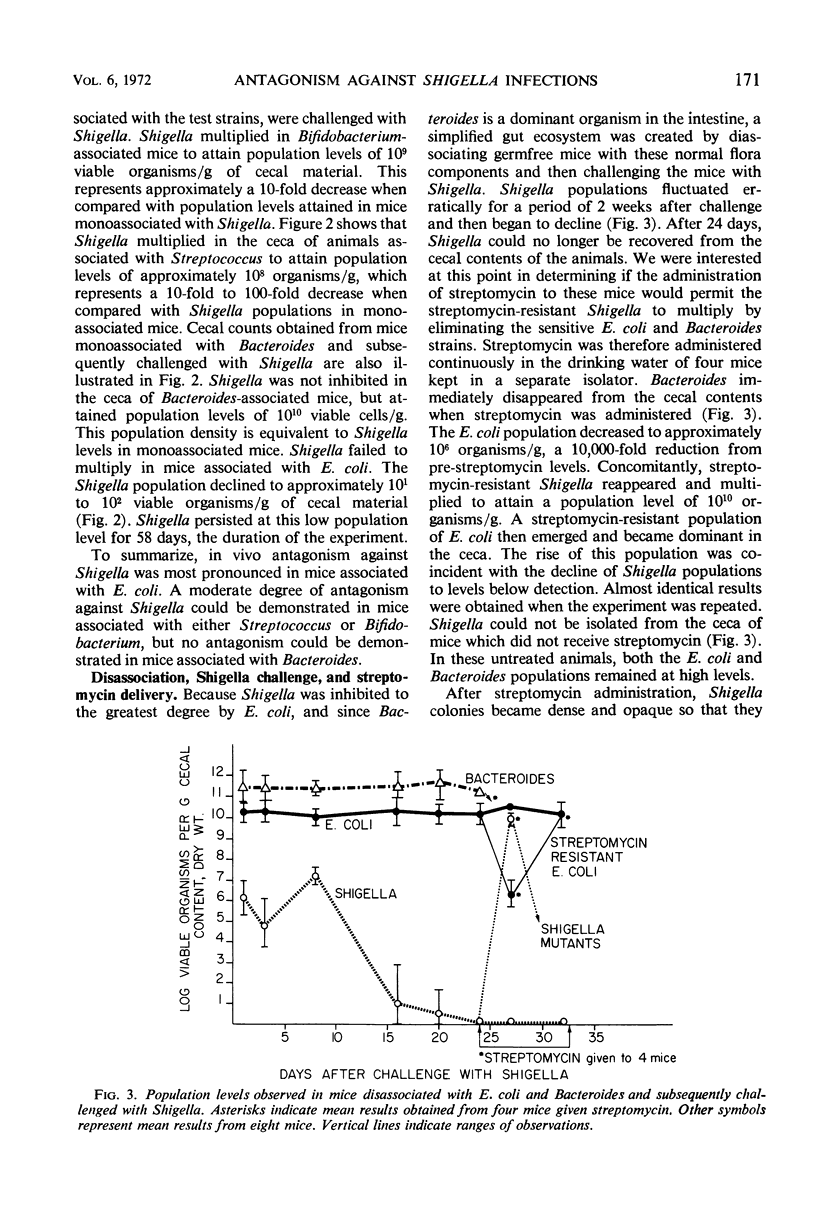
Abstract
Germfree mice were associated with selected species of human intestinal bacteria and then challenged with a streptomycin-resistant Shigella flexneri strain. Antagonism against Shigella was most pronounced in mice associated with Escherichia coli and least pronounced in mice associated with Bacteroides fragilis. A moderate degree of antagonism could be demonstrated in mice associated with either Streptococcus faecalis or Bifidobacterium adolescentis. Shigella persisted in the cecal contents of E. coli-associated mice at very low, stable levels. Shigella populations were reduced to levels below detection in the ceca of mice diassociated with E. coli and Bacteroides. Upon subsequent administration of streptomycin, Bacteroides disappeared from the ceca. The E. coli population was greatly reduced, and Shigella reappeared at very high population levels as an apparent recombinant which resembled E. coli biochemically. A streptomycin-resistant E. coli population subsequently emerged and became dominant in the ceca. Shigella concomitantly declined to levels below detection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arank A., Syed S. A., Kenney E. B., Freter R. Isolation of anaerobic bacteria from human gingiva and mouse cecum by means of a simplified glove box procedure. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):568–576. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.568-576.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. I. FACTORS WHICH INTERFERE WITH THE INITIATION OF INFECTION BY ORAL INOCULATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:805–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Shiner M., McLeod G. M. Studies on the intestinal flora. I. The bacterial flora of the gastrointestinal tract in healthy and achlorhydric persons. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G., SPRINZ H., KUNDEL D., SCHNEIDER H., HOROWITZ R. E., FORBES M. Experimental Shigella infections. V. Studies in germ-free guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:284–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.2.284-287.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. Experimental enteric Shigella and Vibrio infections in mice and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1956 Sep 1;104(3):411–418. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Sutter V. L., Boyle J. D., Shimada K. The normal flora of ileostomy and transverse colostomy effluents. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):376–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENTGES D. J. A simplified plating technic for bacteriologic examination of specimens of urine. Am J Clin Pathol. 1962 Sep;38:304–305. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/38.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENTGES D. J., FRETER R. In vivo and in vitro antagonism of intestinal bacteria against Shigella flexneri. I. Correlation between various tests. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:30–37. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS A. R., FLOYD T. M., KADER M. A. Studies in shigellosis. II. Observations on incidence and etiology of diarrheal disease in Egyptian village children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1955 Mar;4(2):271–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J. Inhibition of Shigella flexneri by the normal intestinal flora. I. Mechanisms of inhibition by Klebsiella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1369–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1369-1373.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J. Inhibition of Shigella flexneri by the normal intestinal flora. II. Mechanisms of inhibition by coliform organisms. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):513–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.513-517.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J., Maier B. R. Inhibition of Shigella flexneri by the Normal Intestinal Flora III. Interactions with Bacteroides fragilis Strains in Vitro. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):364–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.364-370.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., BURROUS J. W. Hybridization between Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Bacteriol. 1957 Oct;74(4):461–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.4.461-476.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER C. P., BOHNHOFF M. CHANGES IN THE MOUSE'S ENTERIC MICROFLORA ASSOCIATED WITH ENHANCED SUSCEPTIBILITY TO SALMONELLA INFECTION FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Infect Dis. 1963 Jul-Aug;113:59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szturm-Rubinsten S., Piéchaud D., D'Hauteville H., Sarrat H. Variété gazogène du sérotype provisoire de shigella: 2000-53. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Sep;119(3):320–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubrzycki L., Spaulding E. H. STUDIES ON THE STABILITY OF THE NORMAL HUMAN FECAL FLORA. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83(5):968–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.968-974.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


