Abstract
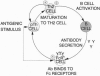
The phenotype and antigenic specificity of cells secreting interleukin (IL) 4, IL-6, and interferon gamma was studied in mice during primary and secondary immune responses. T lymphocytes were the major source of interferon gamma, whereas non-B/non-T cells were the dominant source of IL-4 and IL-6 in the spleens of immunized animals. Cytokine-secreting non-B/non-T cells expressed surface receptors for IgE and/or IgG types II/III. Exposing these cells to antigen-specific IgE or IgG in vivo (or in vitro) "armed" them to release IL-4 and IL-6 upon subsequent antigenic challenge. These findings suggest that non-B/non-T cells may represent the "natural immunity" analogue of CD4+ T helper type 2 cells and participate in a positive feedback loop involved in the perpetuation of T helper type 2 cell responses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Burke F. The cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sasson S. Z., Le Gros G., Conrad D. H., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Cross-linking Fc receptors stimulate splenic non-B, non-T cells to secrete interleukin 4 and other lymphokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. A., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Falco J., Ihle J. N., Paul W. E. B cell stimulatory factor-1/interleukin-4 mRNA is expressed by normal and transformed mast cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner T., Heusser C. H., Dahinden C. A. Human peripheral blood basophils primed by interleukin 3 (IL-3) produce IL-4 in response to immunoglobulin E receptor stimulation. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):605–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicco N. A., Lindemann A., Content J., Vandenbussche P., Lübbert M., Gauss J., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Inducible production of interleukin-6 by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):2049–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H., Ben-Sasson S. Z., Le Gros G., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis or injection of anti-IgD antibodies markedly enhances Fc-receptor-mediated interleukin 4 production by non-B, non-T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1497–1508. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuturi M. C., Anegón I., Sherman F., Loudon R., Clark S. C., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Production of hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors by human natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):569–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Nilsson L. A., Klareskog L., Ouchterlony O. Reverse ELISPOT assay for clonal analysis of cytokine production. I. Enumeration of gamma-interferon-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 25;110(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Else K. J., Finkelman F. D., Maliszewski C. R., Grencis R. K. Cytokine-mediated regulation of chronic intestinal helminth infection. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):347–351. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa K., Suzuki R., Matsui H., Shimizu Y., Kumagai K. Natural killer (NK) cells as a responder to interleukin 2 (IL 2). II. IL 2-induced interferon gamma production. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):988–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Mutha S. S., Locksley R. M. Production of interferon gamma, interleukin 2, interleukin 4, and interleukin 10 by CD4+ lymphocytes in vivo during healing and progressive murine leishmaniasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7011–7015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Haynes B. F., Conover J. Activation of interleukin 4- and interleukin 6-secreting cells by HIV-specific synthetic peptides. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1995 Jan;11(1):97–105. doi: 10.1089/aid.1995.11.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Swain S. L., Singer S. J. The specific direct interaction of helper T cells and antigen-presenting B cells. II. Reorientation of the microtubule organizing center and reorganization of the membrane-associated cytoskeleton inside the bound helper T cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1565–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gros G., Ben-Sasson S. Z., Conrad D. H., Clark-Lewis I., Finkelman F. D., Plaut M., Paul W. E. IL-3 promotes production of IL-4 by splenic non-B, non-T cells in response to Fc receptor cross-linkage. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2500–2506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Vieira P., Fiorentino D. F., Trounstine M. L., Khan T. A., Mosmann T. R. Homology of cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (IL-10) to the Epstein-Barr virus gene BCRFI. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1230–1234. doi: 10.1126/science.2161559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Garra A., Barbis D., Harada N., Lee F., Howard M. Constitutive production of lymphokines by cloned murine B-cell lymphomas--CH12 B lymphoma produces interleukin-4. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1989;4(3):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parronchi P., De Carli M., Manetti R., Simonelli C., Sampognaro S., Piccinni M. P., Macchia D., Maggi E., Del Prete G., Romagnani S. IL-4 and IFN (alpha and gamma) exert opposite regulatory effects on the development of cytolytic potential by Th1 or Th2 human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2977–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Pleiotropy and redundancy: T cell-derived lymphokines in the immune response. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Seder R. A., Plaut M. Lymphokine and cytokine production by Fc epsilon RI+ cells. Adv Immunol. 1993;53:1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccinni M. P., Macchia D., Parronchi P., Giudizi M. G., Bani D., Alterini R., Grossi A., Ricci M., Maggi E., Romagnani S. Human bone marrow non-B, non-T cells produce interleukin 4 in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon and Fc gamma receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8656–8660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo W. J., Conrad L., Janeway C. A., Jr Receptor-directed focusing of lymphokine release by helper T cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):378–380. doi: 10.1038/332378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer R. P., Sterbinsky S. A., Kaiser J., Bickel C. A., Klunk D. A., Tomioka K., Newman W., Luscinskas F. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, McIntyre B. W. IL-4 induces adherence of human eosinophils and basophils but not neutrophils to endothelium. Association with expression of VCAM-1. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1086–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Paul W. E., Davis M. M., Fazekas de St Groth B. The presence of interleukin 4 during in vitro priming determines the lymphokine-producing potential of CD4+ T cells from T cell receptor transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1091–1098. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Paul W. E., Dvorak A. M., Sharkis S. J., Kagey-Sobotka A., Niv Y., Finkelman F. D., Barbieri S. A., Galli S. J., Plaut M. Mouse splenic and bone marrow cell populations that express high-affinity Fc epsilon receptors and produce interleukin 4 are highly enriched in basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2835–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Holmes K., Klinman D. Detection and quantitation of cells secreting IL-6 under physiologic conditions in BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):793–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Sierra V., Kelly C. I., Klinman D. M. Individual cells simultaneously produce both IL-4 and IL-6 in vivo. Cytokine. 1994 May;6(3):329–336. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Sierra V., Kelly C. I., Klinman D. M. Individual cells simultaneously produce both IL-4 and IL-6 in vivo. Cytokine. 1994 May;6(3):329–336. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Hu-Li J., Seder R. A., Fazekas de St Groth B., Paul W. E. Interleukin 4 suppresses interleukin 2 and interferon gamma production by naive T cells stimulated by accessory cell-dependent receptor engagement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5914–5918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terebuh P. D., Otterness I. G., Strieter R. M., Lincoln P. M., Danforth J. M., Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W. Biologic and immunohistochemical analysis of interleukin-6 expression in vivo. Constitutive and induced expression in murine polymorphonuclear and mononuclear phagocytes. Am J Pathol. 1992 Mar;140(3):649–657. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Kullberg M. C., Barbieri S., Caspar P., Berzofsky J. A., Seder R. A., Sher A. Fc epsilon receptor-positive cells are a major source of antigen-induced interleukin-4 in spleens of mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):1910–1916. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloski B. M., Fuller G. M. Identification and partial characterization of hepatocyte-stimulating factor from leukemia cell lines: comparison with interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]