Abstract
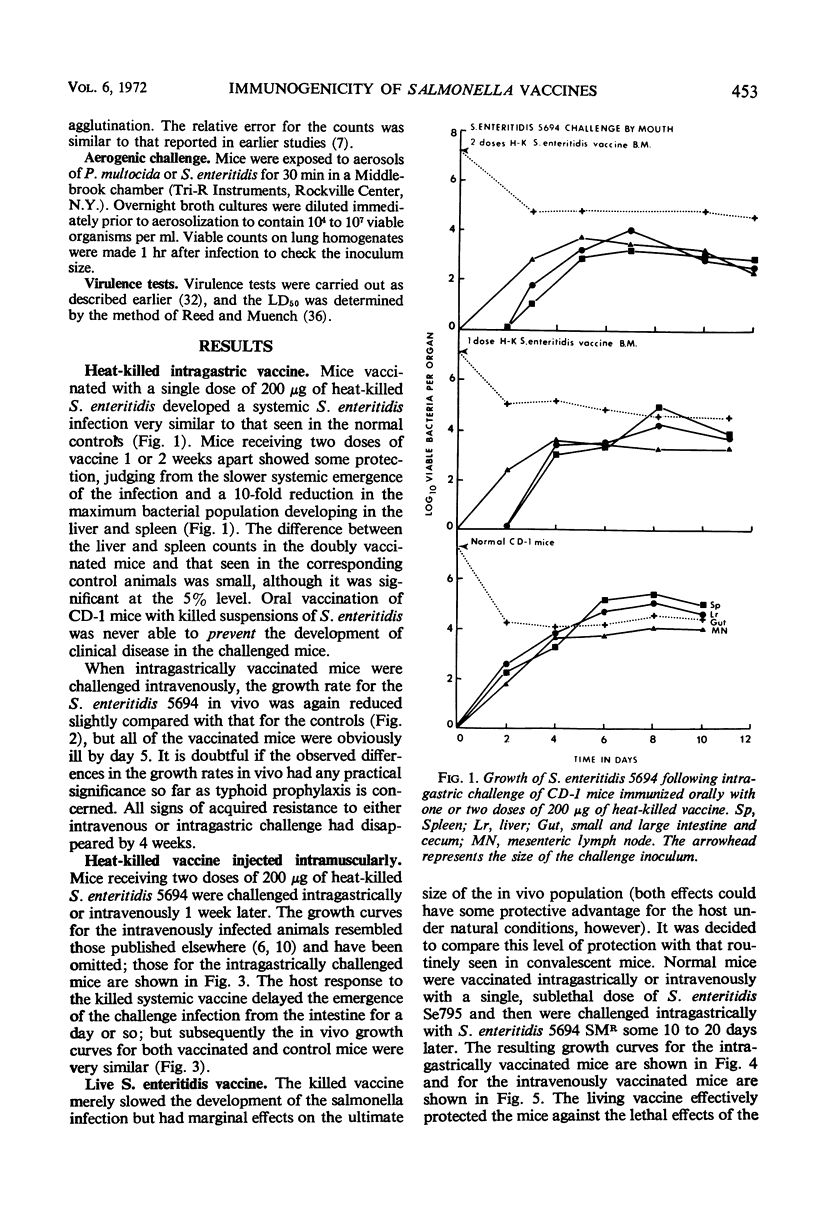
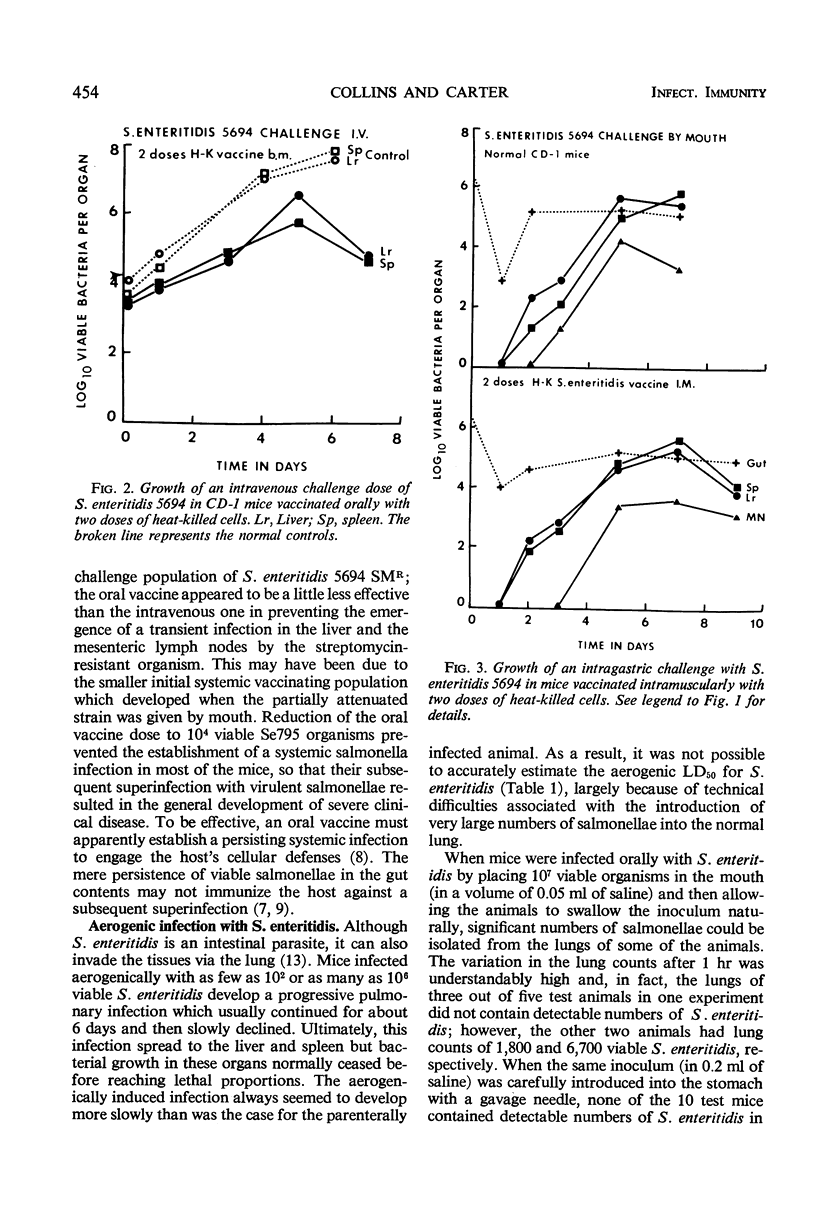
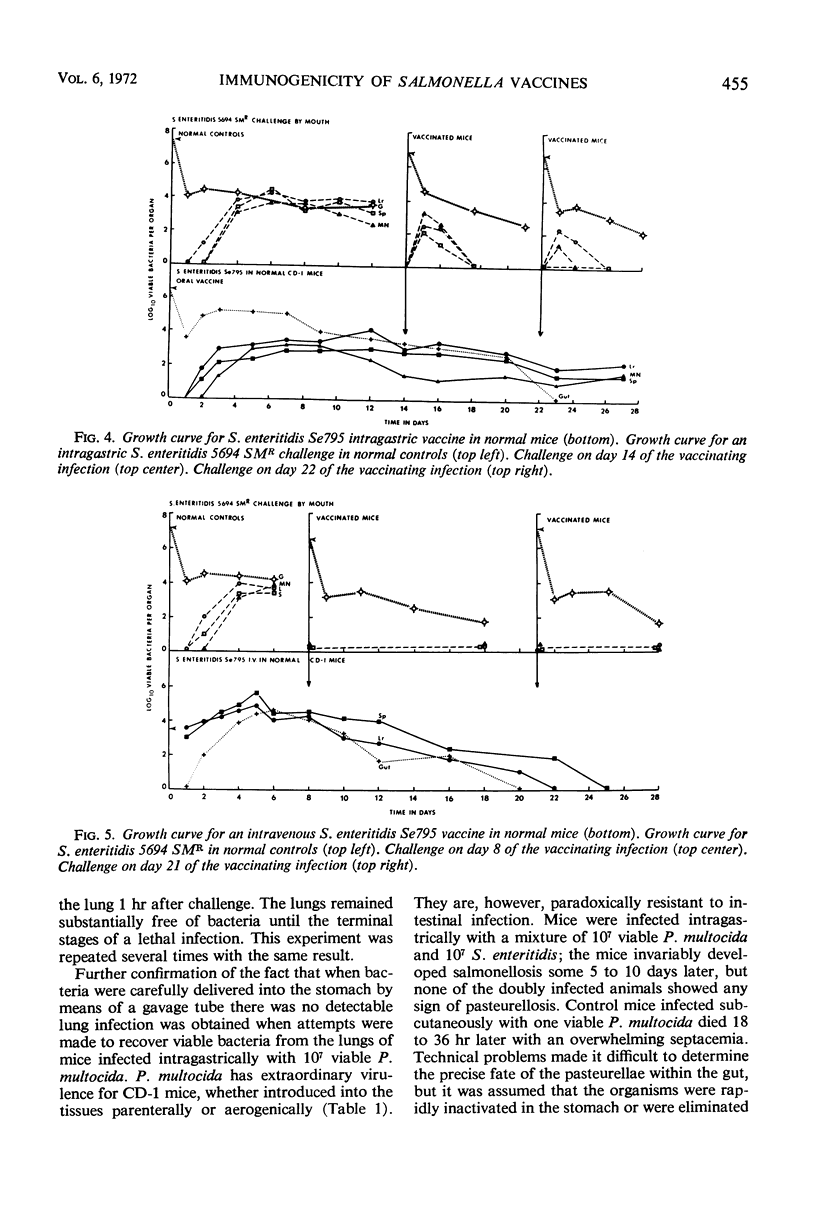
CD-1 mice were vaccinated intragastrically or intramuscularly with one or two doses of 200 μg of heat-killed Salmonella enteritidis 5694. Control mice were vaccinated with sublethal doses of living S. enteritidis Se795. The mice were challenged intragastrically with approximately 106S. enteritidis 5694 SMR 7 to 14 days later, and the growth of the challenge population in the liver, spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes, lungs, and intestine was measured quantitatively. Mice receiving two doses of heat-killed vaccine by mouth were able to delay the systemic emergence of a gastrically introduced salmonella infection by 1 to 2 days. The corresponding liver and spleen populations were slightly lower than those seen in the normal controls. On the other hand, mice receiving the living, attenuated vaccine (either intravenously or intragastrically) developed an effective anti-salmonella immunity against subsequent reinfection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on the resistance of the small intestine to infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1604–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1604-1608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS F. M. THE EFFECT OF THE GROWTH RATE ON THE COMPOSITION OF S. ENTERITIDIS CELL WALLS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:255–262. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuttani C. S., Prakash K., Vergese A., Sharma U., Singha P., Ray B. G. Effectiveness of oral killed typhoid vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(4):445–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice preimmunized with living or ethyl alcohol-killed vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.676-683.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Immunity to enteric infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.243-250.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mechanisms in antimicrobial immunity. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jul;10(1):58–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Recall of immunity in mice vaccinated with Salmonella enteritidis or Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2014–2021. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2014-2021.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Salmonellosis in orally infected specific pathogen-free C57B1 mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):191–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.191-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. N., Fahey K. J. Oral Immunization in Experimental Salmonellosis III. Behavior of Virulent and Temperature-Sensitive Mutant Strains in the Intestinal Tissues of Rats. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):192–200. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.192-200.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cvjetanović B., Mel D. M., Felsenfeld O. Study of live typhoid vaccine in chimpanzees. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(4):499–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARLOW H. M., BALE W. R., CARTER G. B. Infection of mice by the respiratory route with Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1961 Sep;59:303–308. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolezel J., Bienenstock J. Immune response of the hamster to oral and parenteral immunization. Cell Immunol. 1971 Aug;2(4):326–334. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Immunity in shigellosis. II. Protection induced by oral live vaccine or primary infection. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):12–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Dawkins A. T., Heiner G. G., Woodward T. E. Studies of immunity in typhoid fever. Protection induced by killed oral antigens or by primary infection. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;44(5):667–672. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSALL G., GAINES S., LANDY M., TIGERTT W. D., SPRINZ H., TRAPANI R. J., MANDEL A. D., BENENSON A. S. Studies on infection and immunity in experimental typhoid fever. I. Typhoid fever in chimpanzees orally infected with Salmonella typhosa. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:143–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., Cooper G. N. Oral Immunization in Experimental Salmonellosis II. Characteristics of the Immune Response to Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Given by Oral and Parenteral Routes. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.183-191.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., Cooper G. N. Oral immunization against experimental salmonellosis I. Development of temperature-sensitive mutant vaccines. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):263–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.263-270.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAINES S., TULLY J. G., TIGERTT W. D. Studies on infection and immunity in experimental typhoid fever. II. Susceptibility of recovered animals to re-exposure. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1023–1036. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERICHTER C. B. The dissemination of Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi A and S. paratyphi B through the organs of the white mouse by oral infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Sep;58:307–319. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordes I., Kordes B., Pichl H., Ganze B., Raettig H. Orale Immunisierung mit nichtvermehrungsfähigen Mikroorganismen oder ihren Antigenen. Immunogenität verschieden inaktivierter S. typhi murium-Vollantigene im Mäusechutztest. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1971 Jun;217(2):242–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre H., Pichl H., Werner H. J., Wiener A., Lissy A. Vergleichende Untersuchung der Intestinalantiköper nach oraler oder intraperitonealer Immunisierung von Mäusen mit Hammelerythrozyten. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1971 Aug;217(4):529–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre H., Uecker W., Blümel P., Raettig H. Untersuchungen zur oralen Immunisierung. Die sekundäre Immunreaktion nach primärer oraler und nachfolgender oraler bzw. parenteraler Applikation von bovinem Serumalbumin (BSA) beim Kaninchen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970 May;213(4):548–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMION D. E., NAYLOR G. R., STEWART I. O. Second attacks of typhoid fever. J Hyg (Lond) 1953 Jun;51(2):260–267. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400015680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne M., Collins F. M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. I. Extraction of antigens. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):543–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.543-548.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Mukerjee S. Live oral cholera vaccine: report of a trial on human volunteer subjects. Bull World Health Organ. 1969 Apr;40(4):503–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIGERTT W. D. The initial effort to immunize American soldier volunteers with typhoid vaccine. Mil Med. 1959 May;124(5):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong H., Ekdahl M. O. Salmonellosis in calves--the effect of dose rate and other factors on transmission. N Z Vet J. 1965 Jun;13(3):59–64. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1965.33598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


