Abstract
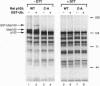
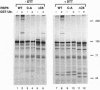
E6-AP is a 100-kDa cellular protein that interacts with the E6 protein of the cancer-associated human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. The E6/E6-AP complex binds to and targets the p53 tumor-suppressor protein for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. E6-AP is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. The amino acid sequence of E6-AP shows similarity to a number of protein sequences over an approximately 350-aa region corresponding to the carboxyl termini of both E6-AP and the E6-AP-related proteins. Of particular note is a conserved cysteine residue within the last 32-34 aa, which in E6-AP is likely to be the site of ubiquitin thioester formation. Two of the E6-AP-related proteins, a rat 100-kDa protein and a yeast 95-kDa protein (RSP5), both of previously unknown function, are shown here to form thioesters with ubiquitin. Mutation of the conserved cysteine residue of these proteins destroys their ability to accept ubiquitin. These data strongly suggest that the rat 100-kDa protein and RSP5, as well as the other E6-AP-related proteins, belong to a class of functionally related E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases, defined by a domain homologous to the E6-AP carboxyl terminus (hect domain).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel B., Wünning I., Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3179–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girod P. A., Carpenter T. B., van Nocker S., Sullivan M. L., Vierstra R. D. Homologs of the essential ubiquitin conjugating enzymes UBC1, 4, and 5 in yeast are encoded by a multigene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1993 Apr;3(4):545–552. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.03040545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G., Goetsch L., Byers B. The Ubc3 (Cdc34) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme is ubiquitinated and phosphorylated in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3022–3029. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Ren K., Dubner R., Iadarola M. J. Cloning of a DNA binding protein that is a tyrosine kinase substrate and recognizes an upstream initiator-like sequence in the promoter of the preprodynorphin gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Jul;24(1-4):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Scheffner M., Huibregtse J., Münger K. Oncoproteins encoded by the cancer-associated human papillomaviruses target the products of the retinoblastoma and p53 tumor suppressor genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:149–155. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. A cellular protein mediates association of p53 with the E6 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus types 16 or 18. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4129–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for E6-AP, a protein that mediates the interaction of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein with p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):775–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Localization of the E6-AP regions that direct human papillomavirus E6 binding, association with p53, and ubiquitination of associated proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4918–4927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Tomooka Y., Noda M. Identification of a set of genes with developmentally down-regulated expression in the mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91747-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield E., Hersperger E., Biggs J., Shearn A. Genetic and molecular analysis of hyperplastic discs, a gene whose product is required for regulation of cell proliferation in Drosophila melanogaster imaginal discs and germ cells. Dev Biol. 1994 Oct;165(2):507–526. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Martin A., Shearn A. Studies of l(3)c43hs1 a polyphasic, temperature-sensitive mutant of Drosophila melanogaster with a variety of imaginal disc defects. Dev Biol. 1977 Feb;55(2):213–232. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D., Rehbein M., Baumeister H., Richter D. Molecular characterization of a novel rat protein structurally related to poly(A) binding proteins and the 70K protein of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1471–1475. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. Identification of a human ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that mediates the E6-AP-dependent ubiquitination of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8797–8801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Huibregtse J. M., Vierstra R. D., Howley P. M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Nuber U., Huibregtse J. M. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1-E2-E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):81–83. doi: 10.1038/373081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Romanczuk H., Münger K., Huibregtse J. M., Mietz J. A., Howley P. M. Functions of human papillomavirus proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1994;186:83–99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78487-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Jentsch S. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBC4 and UBC5 mediate selective degradation of short-lived and abnormal proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):543–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treier M., Seufert W., Jentsch S. Drosophila UbcD1 encodes a highly conserved ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme involved in selective protein degradation. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):367–372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen M., Heinlein R., Jones D., Jentsch S., Candido E. P. The ubc-2 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme involved in selective protein degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1371–1377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]