Abstract
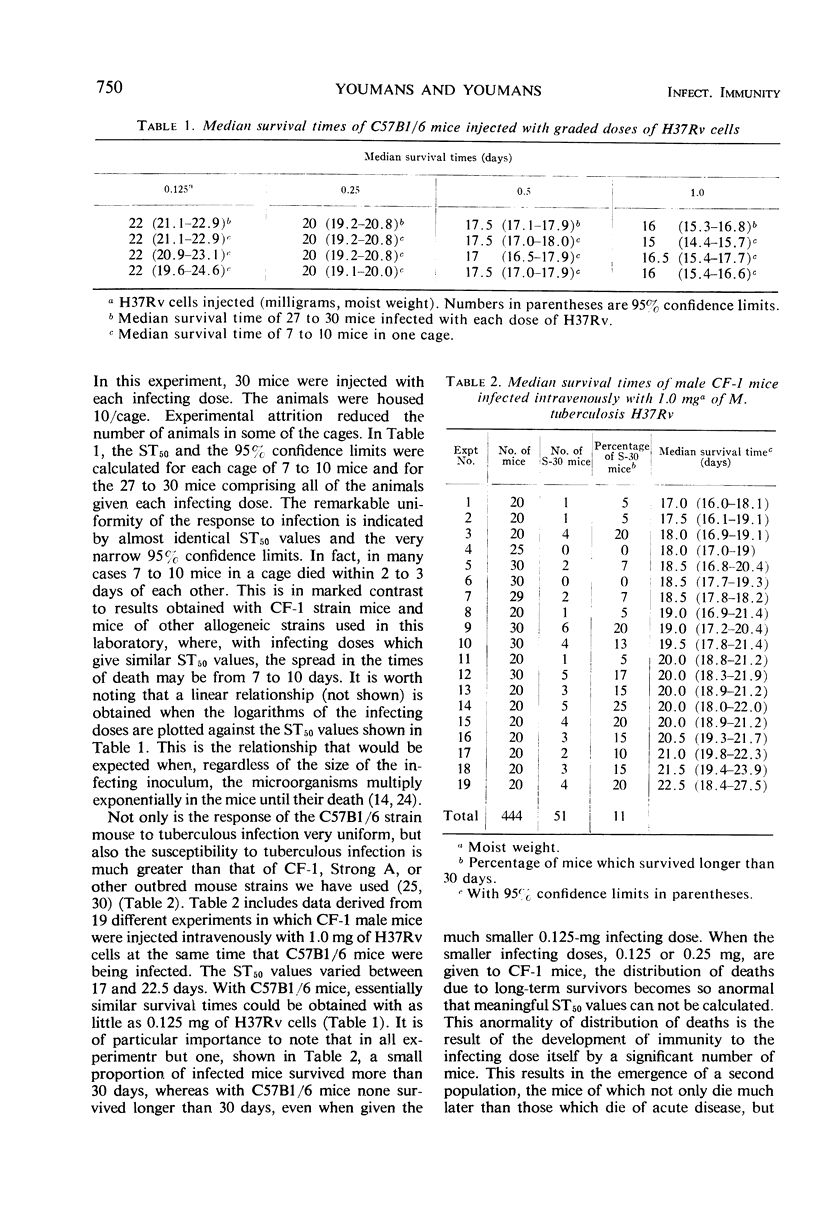
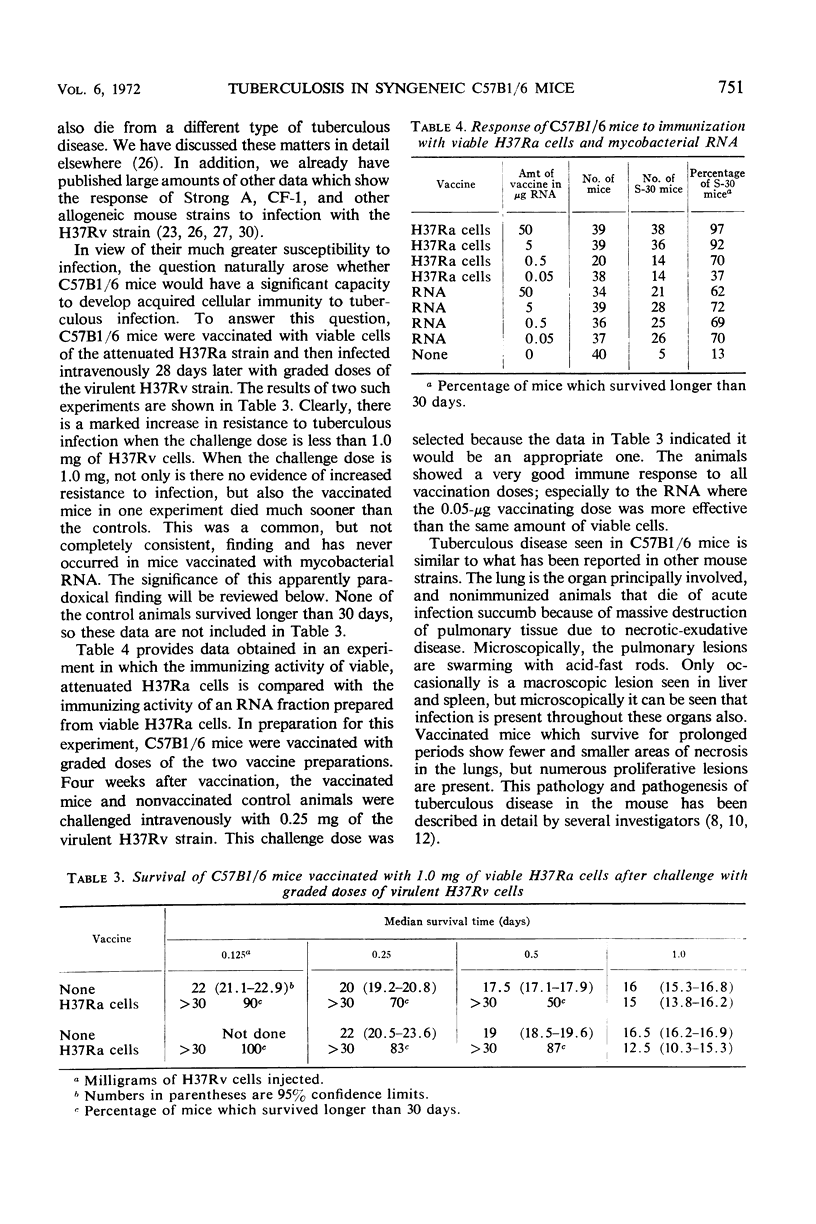
Data are presented which show that the syngeneic C57B1/6 mouse strain is far more susceptible to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv than are the other allogeneic mouse strains used in this laboratory, particularly the Strong A and the CF-1 strains. Not only are the C57B1/6 mice more susceptible to tuberculous infection, but also they respond to infection more uniformly than do the allogeneic strains. C57B1/6 mice develop immunity to challenge with small infecting doses of the virulent H37Rv strain when they are vaccinated with viable cells of the attenuated H37Ra strain and with ribonucleic acid (RNA) preparations isolated from the H37Ra strain. Mice vaccinated with viable cells of the H37Ra strain, however, may die more rapidly than nonvaccinated mice when given a large infecting dose (1.0 mg). This accelerated type of disease is not seen in mice vaccinated with mycobacterial RNA. Since C57B1/6 mice are known to develop tuberculin hypersensitivity more readily than many other mouse strains, the possibility is discussed that the increased susceptibility to tuberculous infection of mice vaccinated with viable cells of the H37Ra strain may be due to a superimposition of a pronounced acute inflammatory response due to tuberculin hypersensitivity upon the infectious process. The several advantages that may be gained in the study of certain host-parasite interactions in tuberculosis by the use of a highly susceptible syngeneic mouse strain such as the C57B1/6 are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HOYT A., MOORE F. J., KNOWLES R. G., SMITH C. R. Sex differences of normal and immunized mice in resistance to experimental tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Apr;75(4):618–623. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S. H., Weiser R. S. Systemic tuberculin sensitivity in mice. I. Factors contributing to active tuberculin shock. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1152–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITCHFIELD J. T., Jr A method for rapid graphic solution of time-per cent effect curves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Dec;97(4):399-408, 3 tab. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER E., JACKSON E. R., WHITESIDE E. S., ALVERSON C. Experimental embolic pulmonary tuberculosis in mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Mar;69(3):419–442. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYKA W., FAHERTY J. F., MALONE L. C., KISER J. S. A histological study of the pathogenesis of tuberculosis in mice experimentally infected with bacilli of human type. Exp Med Surg. 1954;12(3):367–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., YOUMANS G. P. Enumeration of viable tubercle bacilli from the organs of nonimmunized and immunized mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Oct;76(4):616–635. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.76.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORTLEY G., WILKINS J. R. INDEPENDENT-ACTION AND BIRTH-DEATH MODELS IN EXPERIMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:102–141. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.102-141.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E., KIRSANOW E. M. Fate of attenuated tubercle bacilli (BCG) in germ-free and conventional mice. Nature. 1962 Jul 28;195:397–398. doi: 10.1038/195397b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. Response of mice to standard infecting doses of Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. hominis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):238–240. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. The relation between the size of the infecting dose of tubercle bacilli and the survival time of mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1951 Nov;64(5):534–540. doi: 10.1164/art.1951.64.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. The relationship of sex to the susceptibility of normal and immunized mice to tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Nov;80:750–752. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.5.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Factors affecting immunogenic activity of mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic acid preparations. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.42-50.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Immunogenic mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic Acid preparations: chemical and physical characteristics. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):659–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.659-668.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Ribonucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid, and protein content of cells of different ages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the ralationship to immunogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):272–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.272-279.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. Allergenicity of mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic acid preparations in mice and guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):134–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.134-139.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. Recent studies on acquired immunity in tuberculosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;48:129–178. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46163-7_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



