Abstract
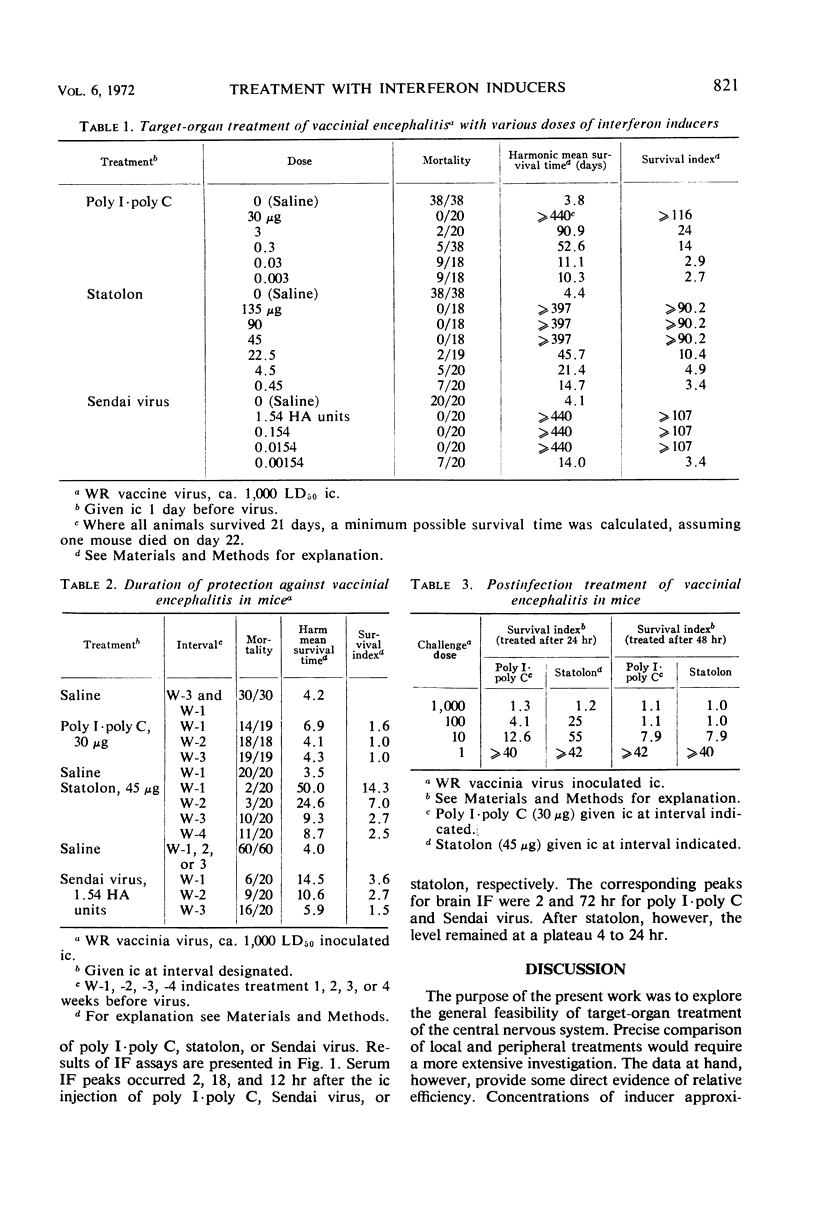
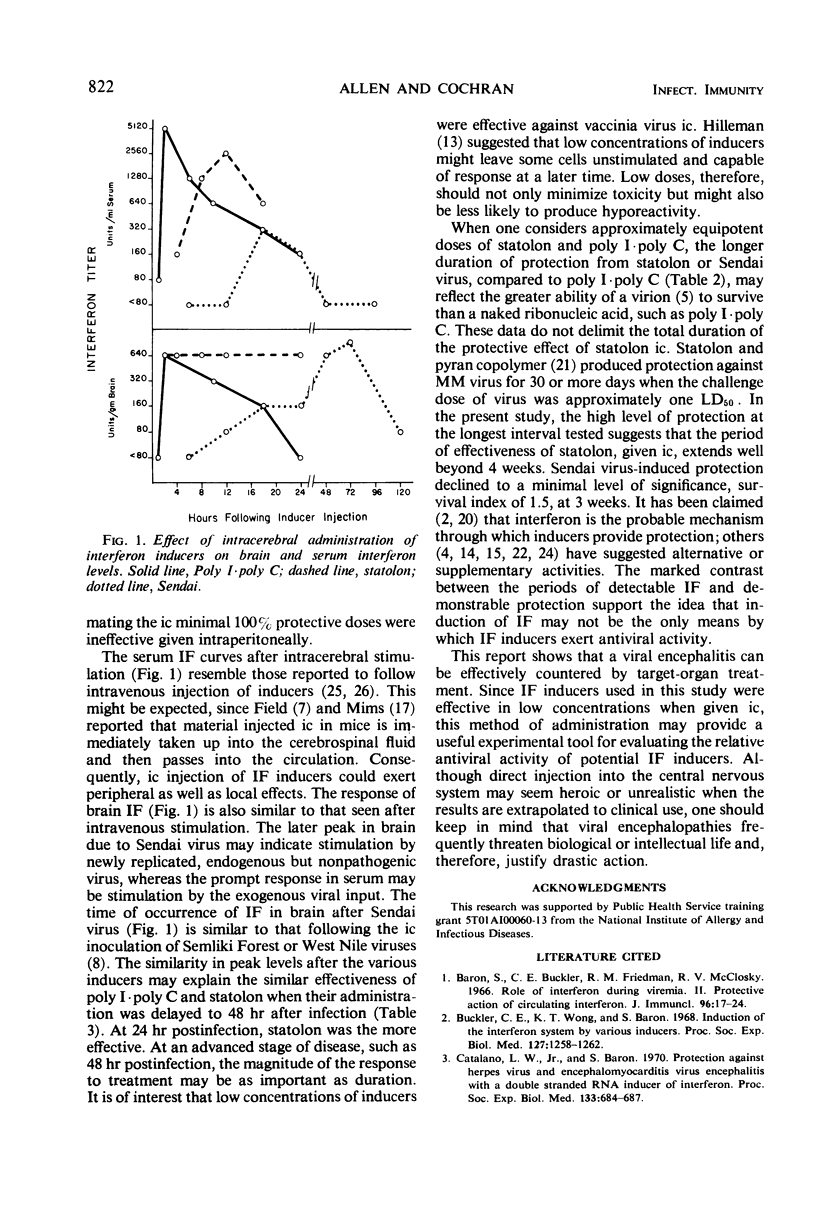
Interferon inducers were used against vaccinial encephalitis to study the target-organ treatment of neurotropic disease and to correlate interferon levels and the antiviral state following such treatment. A 45-μg amount of statolon, 30 μg of polyribinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex (poly I·poly C), or 0.0154 HA unit of Sendai virus given intracerebrally protected 100% of mice challenged the next day with 1,000 median lethal doses (LD50) of vaccinia virus. Significant protection against 1,000 LD50 of vaccinia virus persisted for 1, 4, or 3 weeks after poly I·poly C, statolon, or Sendai virus (154 HA units), respectively. These doses of poly I·poly C and statolon were also used to study postinfection treatment. Mice challenged with 1, 10, 100, or 1,000 LD50 were treated intracerebrally with poly I·poly C or statolon 24 or 48 hr later. Significant increases in survival time were seen in mice challenged with 1 to 100 LD50 of vaccinia virus and treated 24 hr later. At challenges of 10 or 100 LD50, statolon was more effective than poly I·poly C in increasing survival times. When treatment was delayed until 48 hr after infection, significant increases in survival time occurred only when the challenges were in the range of 1 to 10 LD50, with poly I·poly C and statolon being equally effective. Interferon was measured by Finter's dye-uptake method, with L-929 cells and Semliki Forest virus. Poly I·poly C, statolon, or Sendai virus, given intracerebrally to mice, produced serum interferon peaks of 5,120 units/ml at 2 hr, 2,560 units/ml at 12 hr, or 320 units/ml at 18 hr, respectively. Corresponding brain interferon peaks were 640 units/g at 2 hr, 640 units/g at 4 to 24 hr, and 960 units/g at 72 hr.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron S., Buckler C. E., Friedman R. M., McCloskey R. V. Role of interferon during viremia. II. Protective action of circulating interferon. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., Wong K. T., Baron S. Induction of the interferon system by various inducers. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Baron S. Protection against herpes virus and encephalomyocarditis virus encephalitis with a double-stranded RNA inducer of interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):684–687. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L. F., Kleinschmidt W. J. Virus-like particles of a fraction of statolon, a mould product. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):649–650. doi: 10.1038/215649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINTER N. B. A RICH SOURCE OF MOUSE INTERFERON. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1114–1115. doi: 10.1038/2041114b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falabella F. Bleeding mice: a successful technique of cardiac puncture. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Dec;70(6):981–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finter N. B. Interferon as an antiviral agent in vivo: quantitative and temporal aspects of the protection of mice against Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Aug;47(4):361–371. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerone P. J., Hill D. A., Appell L. H., Baron S. Inhibition of respiratory virus infections of mice with aerosols of synthetic double-stranded ribonucleic Acid. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):323–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.323-327.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Double-stranded RNAs (poly I:C) in the prevention of viral infections. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):109–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsberg E., Flikke M. Antiviral activity of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid in the absence of cell-controlled RNA synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1971 Feb;10(2):147–154. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-10-2-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt W. J., Streightoff F. Inhibition of influenza virus and interferon response intranasally with statolon. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):738–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.738-741.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. Intracerebral injections and the growth of viruses in the mouse brain. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:52–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL H. M., CULBERTSON C. G. Action of an antiviral mold filtrate against MEFI poliomyelitis virus in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 May;83(1):161–163. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. H., Baron S. Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis: therapy with synthetic double-stranded RNA. Science. 1968 Nov 15;162(3855):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3855.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer T. W., Lockart R. Z., Jr Interferon required for viral resistance induced by poly I.poly C. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):449–450. doi: 10.1038/226449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. P., Pindak F. F., Giron D. J., Ibarra R. R. Duration of resistance to viral infection following administration of interferon inducers. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1971 Spring;29(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner W., Chan S. P., Chirigos M. A. Stimulation of humoral and cellular antibody formation in mice by poly Ir:Cr. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):334–338. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F. Effect of statolon on Friend virus leukemia in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Mar;124(3):855–858. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhour A. F., Friedman A., Tytell A. A., Hilleman M. R. Hyperpotentiation by synthetic double-stranded RNA of antibody responses to influenza virus vaccine in adjuvant 65. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):809–817. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Hallum J. V. Interferon production in mice by double-stranded synthetic polynucleotides: induction or release? Virology. 1968 May;35(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R. Comparison of interferon production in mice by bacterial endotoxin and statolon. Virology. 1966 Jun;29(2):310–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


