Abstract
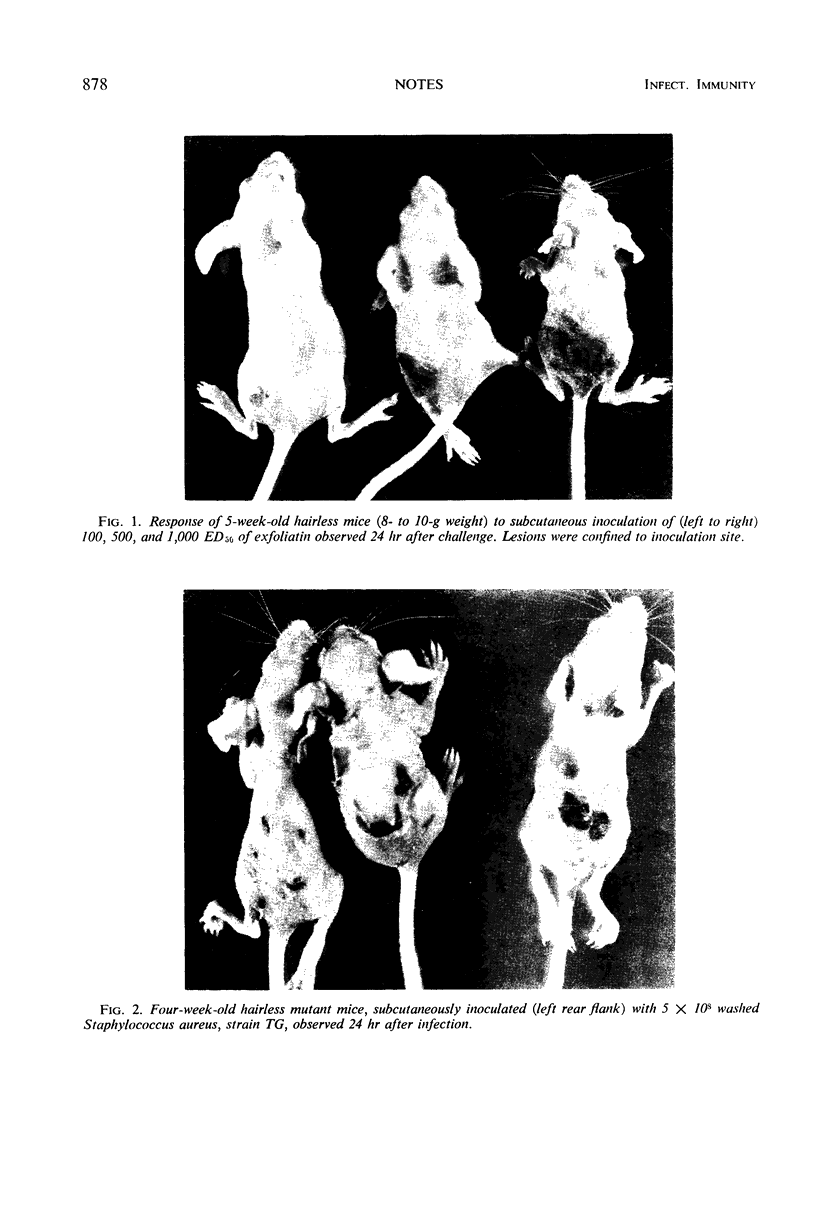
Exfoliatin caused skin loss in hairless mutant mice only while they lacked hair, but older mice were more resistant to this effect than neonates.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott J. P., Kent J., Lyell A., Gemmell C. G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis produced by an extracellular product of Staphylococcus aureus. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Aug;85(2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A., Turner M. D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):129–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]