Abstract
The hemolysis of sheep red blood cells by Rickettsia prowazeki has been characterized. A requirement for the adsorption of the rickettsia to the erythrocyte was indicated. No indication of the production of a soluble hemolysin was observed. Neither adsorption nor hemolysis can proceed at 0 C. The hemolytic process is rapid with a half-time of less than 30 min, and both the rate and extent are proportional to the number of rickettsiae present.
Full text
PDF

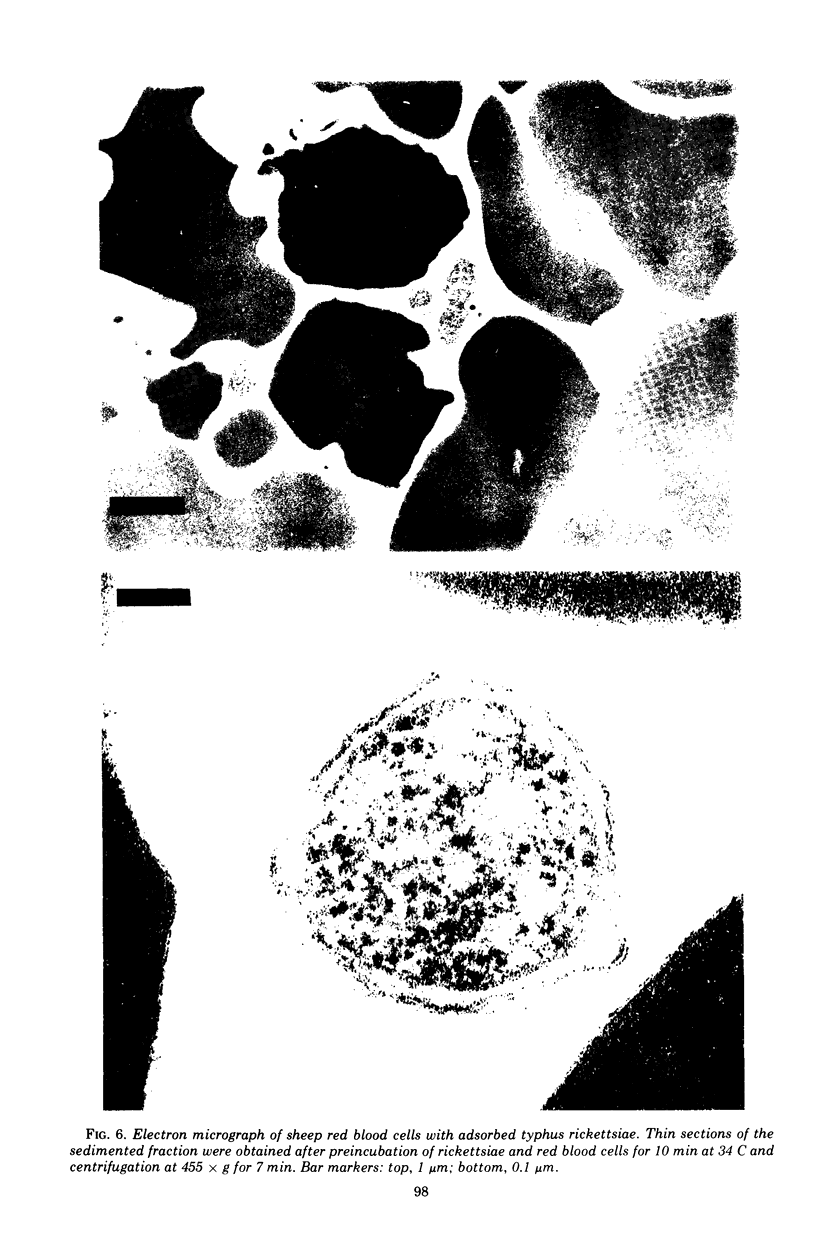

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOVARNICK M. R., ALLEN E. G. Reversible inactivation of the toxicity and hemolytic activity of typhus rickettsiae by starvation. J Bacteriol. 1957 Nov;74(5):637–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.5.637-645.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., ALLEN E. G. Reversible inactivation of typhus Rickettsiae. I. Inactivation by freezing. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):169–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovarnick M. R., Schneider L. ROLE OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE IN THE HEMOLYSIS OF SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES BY TYPHUS RICKETTSIAE. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80(3):344–354. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.344-354.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER J. C., BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., CHANG R. S. M. Observations on the hemolytic properties of typhus rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jun;67(6):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.6.724-730.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C., Greenawalt J. W. Enzymatic properties of the inner and outer membranes of rat liver mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):158–175. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, JACKSON E. B., HAHN F. E., LEY A. C., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. I. The effects of antimicrobial substances and enzyme inhibitors on the oxidation of glutamate by purified rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]