Abstract
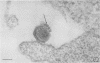
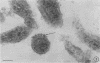
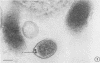
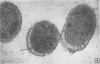
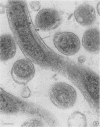
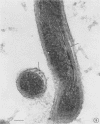
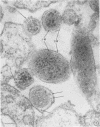
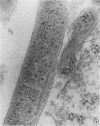
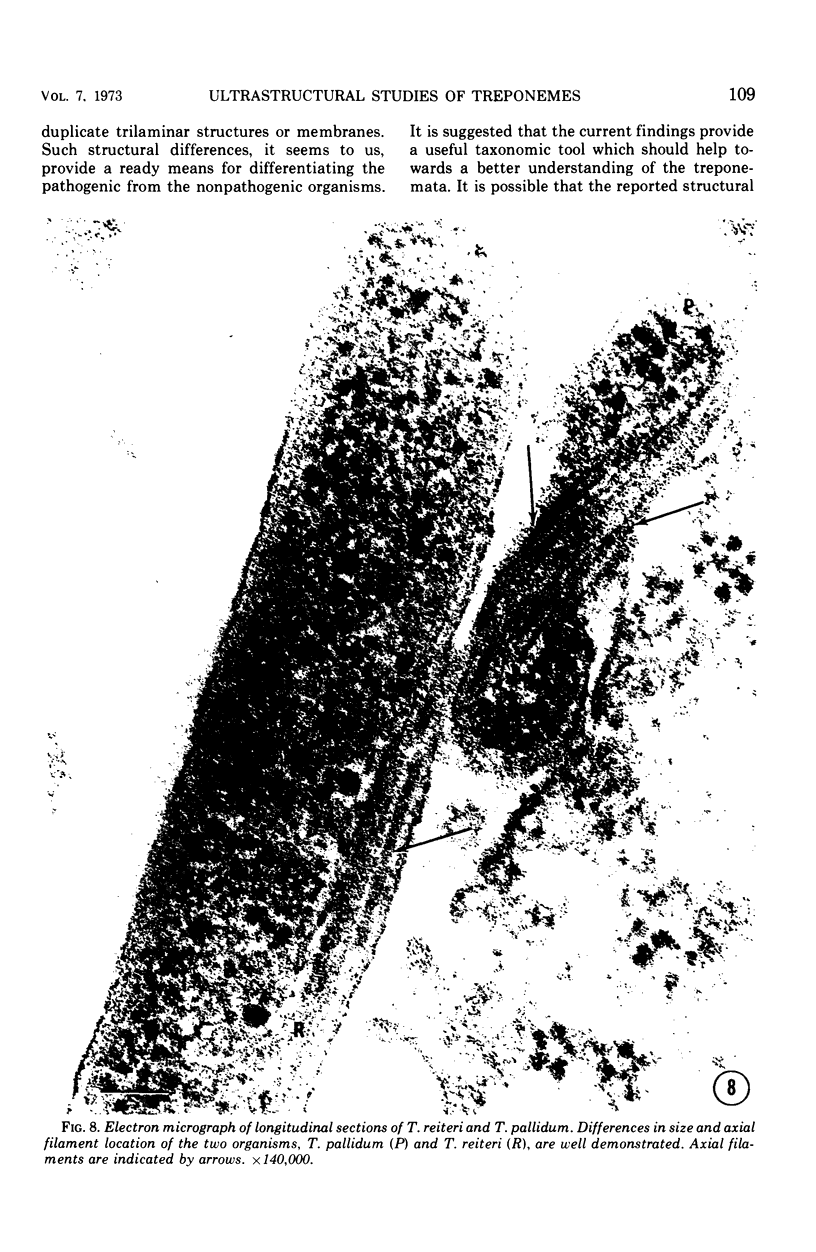
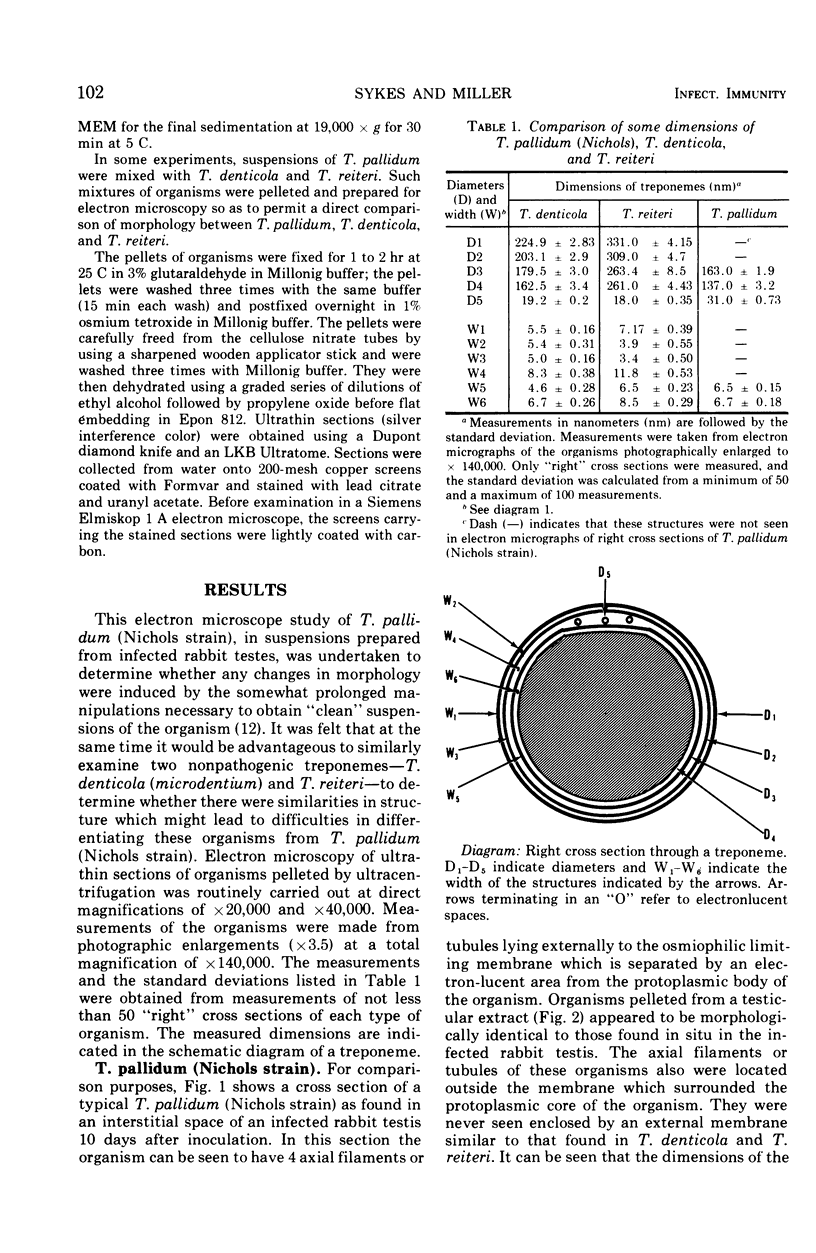
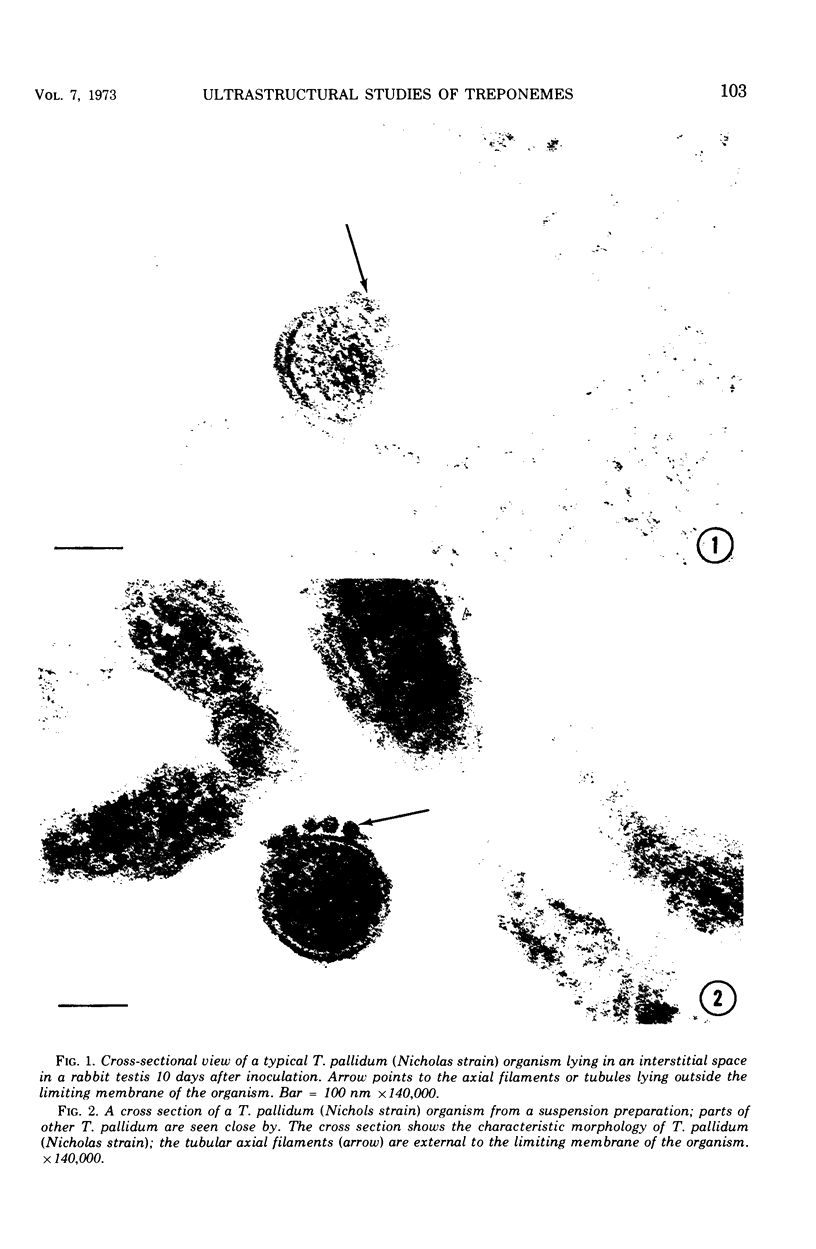
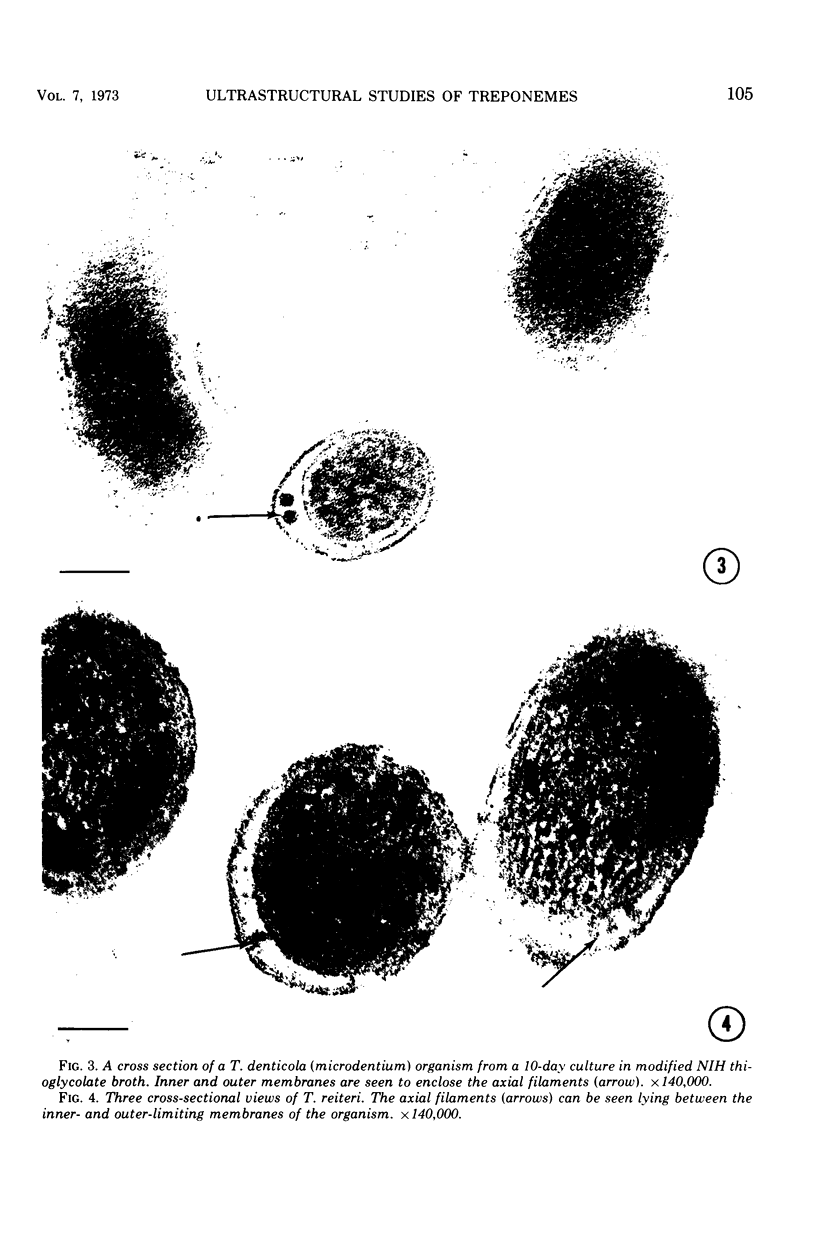
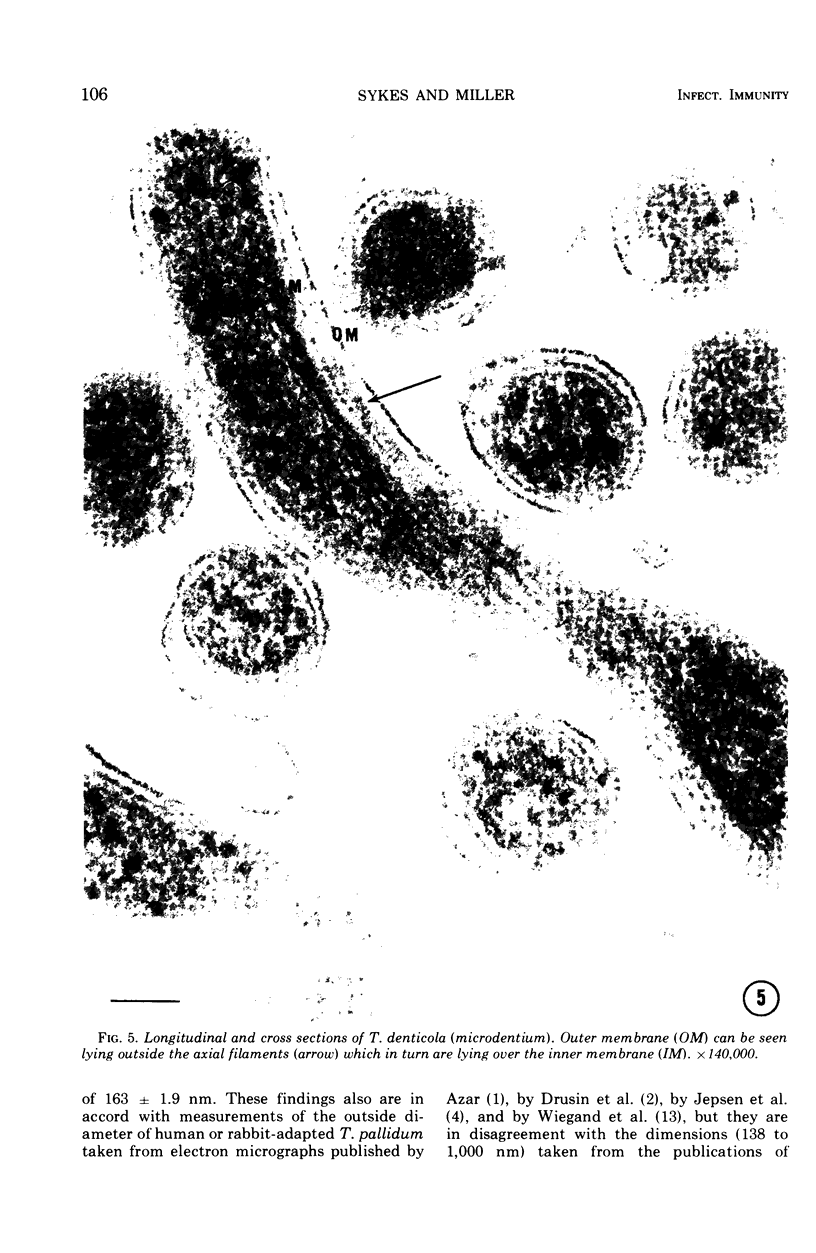
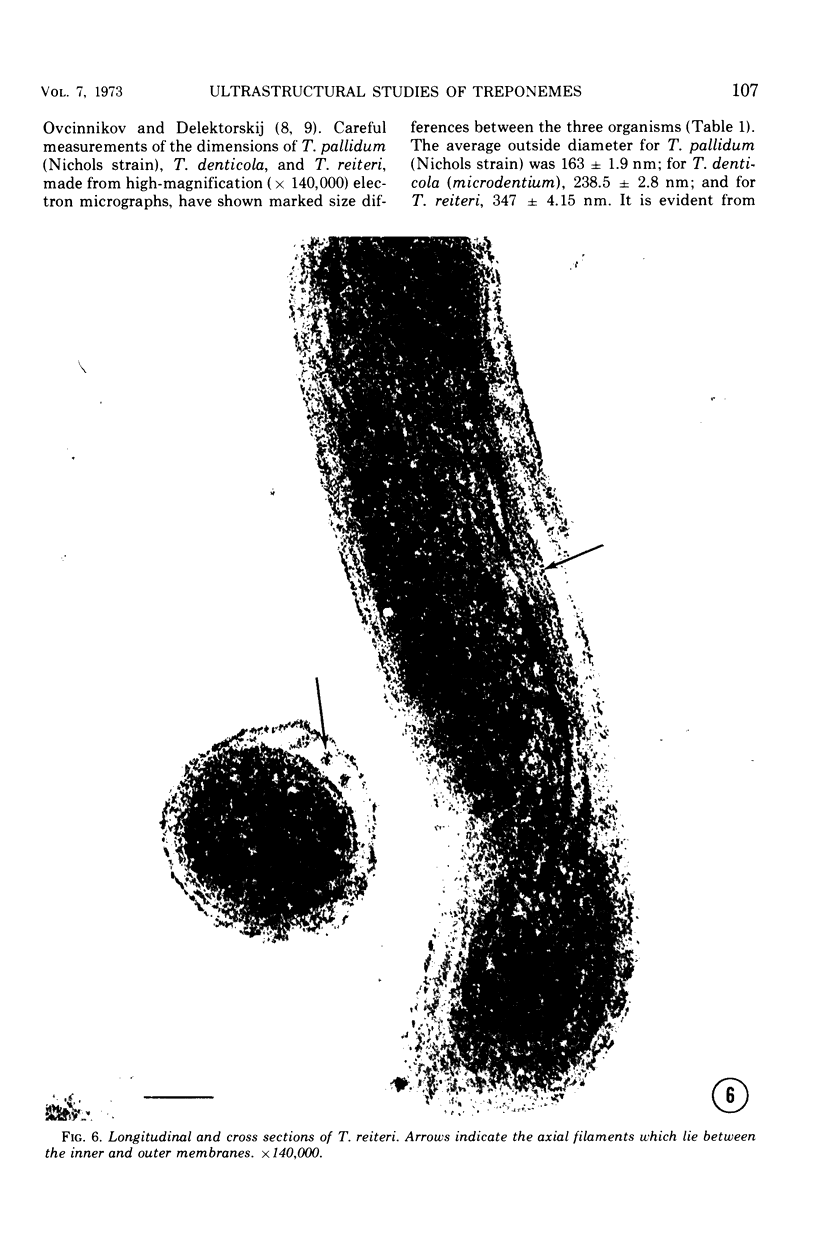
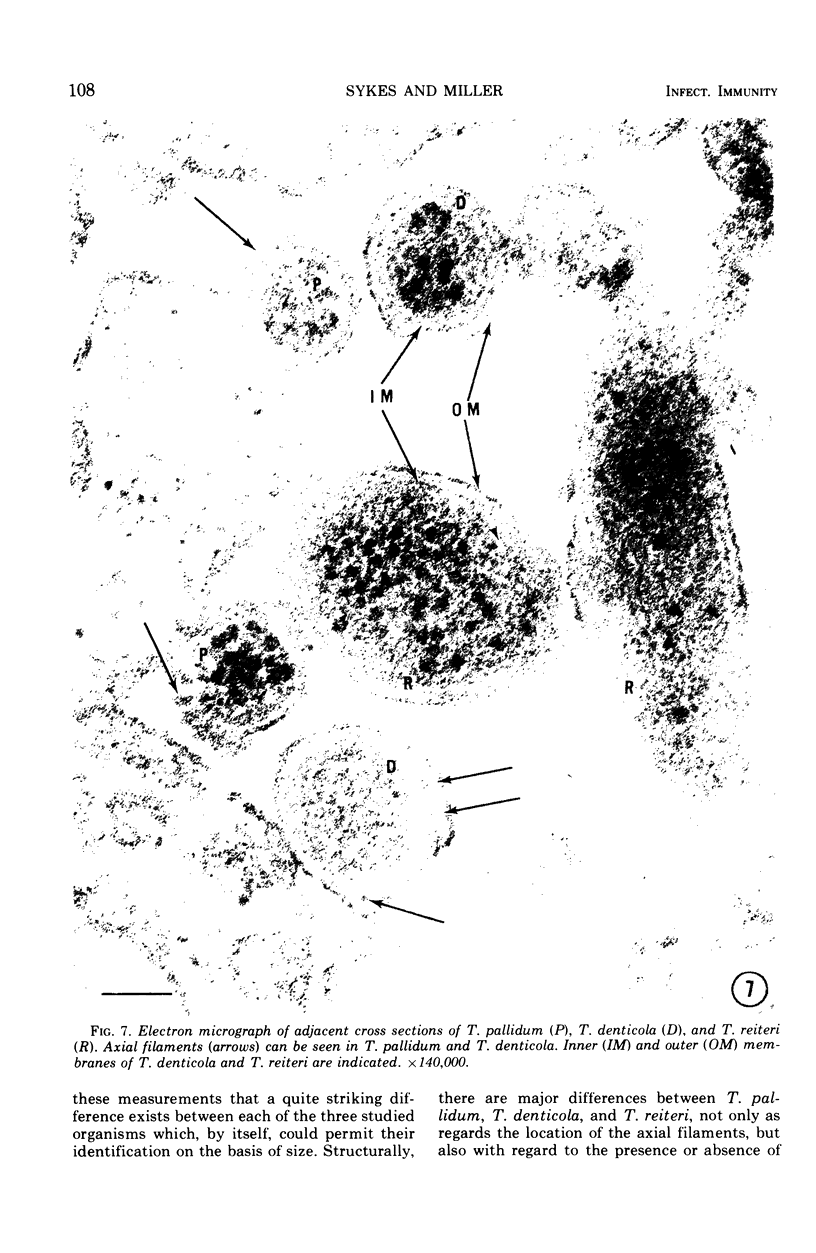
Ultrathin sections of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain), T. denticola (microdentium), and T. reiteri have been studied in the electron microscope to determine the location of the axial filaments and some of the dimensions of these organisms. The axial filaments of T. pallidum (Nichols strain) have been seen to be tubular in cross section with an overall diameter of 21.0 ± 0.73 nm, and an electron-lucent core of 8.0 nm. The filaments were found to lie on the outside of the organism which had only one membranous structure surrounding the protoplasmic core. These findings were in contrast to those obtained for T. denticola and T. reiteri where the axial filaments did not exhibit a hollow core and were located between an outer membrane and an inner membrane surrounding the protoplasmic core. The outside diameter of T. denticola was determined to be 224.9 ± 2.83 nm, and that of T. reiteri as 331.0 ± 4.15 nm, contrasting with T. pallidum (Nichols strain) which had a diameter of 163.0 ± 1.9 nm.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azar H. A., Pham T. D., Kurban A. K. An electron microscopic study of a syphilitic chancre. Engulfment of Treponema pallidum by plasma cells. Arch Pathol. 1970 Aug;90(2):143–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusin L. M., Rouiller G. C., Chapman G. B. Electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum occurring in a human primary lesion. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):951–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.951-955.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T. Electron microscopic observations on the lesions of condyloma latum. Br J Dermatol. 1969 May;81(5):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb14000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen O. B., Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of treponema pallidum Nichols. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(2):241–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTGARTEN M. A., LOESCHE W. J., SOCRANSKY S. S. MORPHOLOGY OF TREPONEMA MICRODENTIUM AS REVEALED BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF ULTRATHIN SECTIONS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:932–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.932-939.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTGARTEN M. A., SOCRANSKY S. S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF AXIAL FIBRILS, OUTER ENVELOPE, AND CELL DIVISION OF CERTAIN ORAL SPIROCHETES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1087–1103. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1087-1103.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauderdale V., Goldman J. N. Serial ultrathin sectioning demonstrating the intracellularity of T. Pallidum. An electron microscopic study. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):87–96. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Current concepts of the morphology and biology of Treponema pallidum based on electron microscopy. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Oct;47(5):315–328. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.5.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Further studies of the morphology of Treponema pallidum under the electron microscope. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Jun;45(2):87–116. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., PILLOT J. [Electron microscope study of the external and internal structure of the Reiter treponema]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Apr;104:496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAIN R. H. Electron microscopic studies of the morphology of pathogenic spirochaetes. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):117–128. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Intracellular location of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in the rabbit testis. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):307–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.307-314.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand S. E., Strobel P. L., Glassman L. H. Electron microscopic anatomy of pathogenic Treponema pallidum. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Apr;58(4):186–204. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12539907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]