Abstract
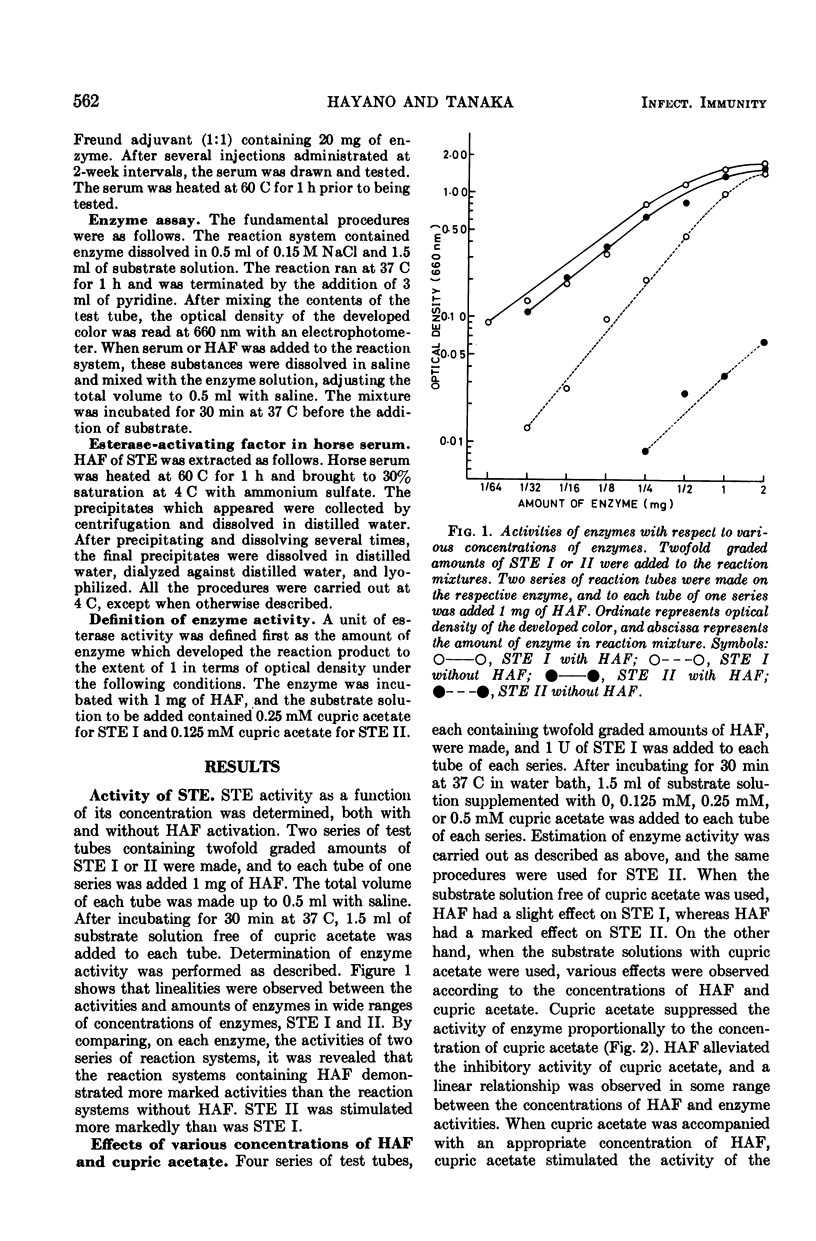
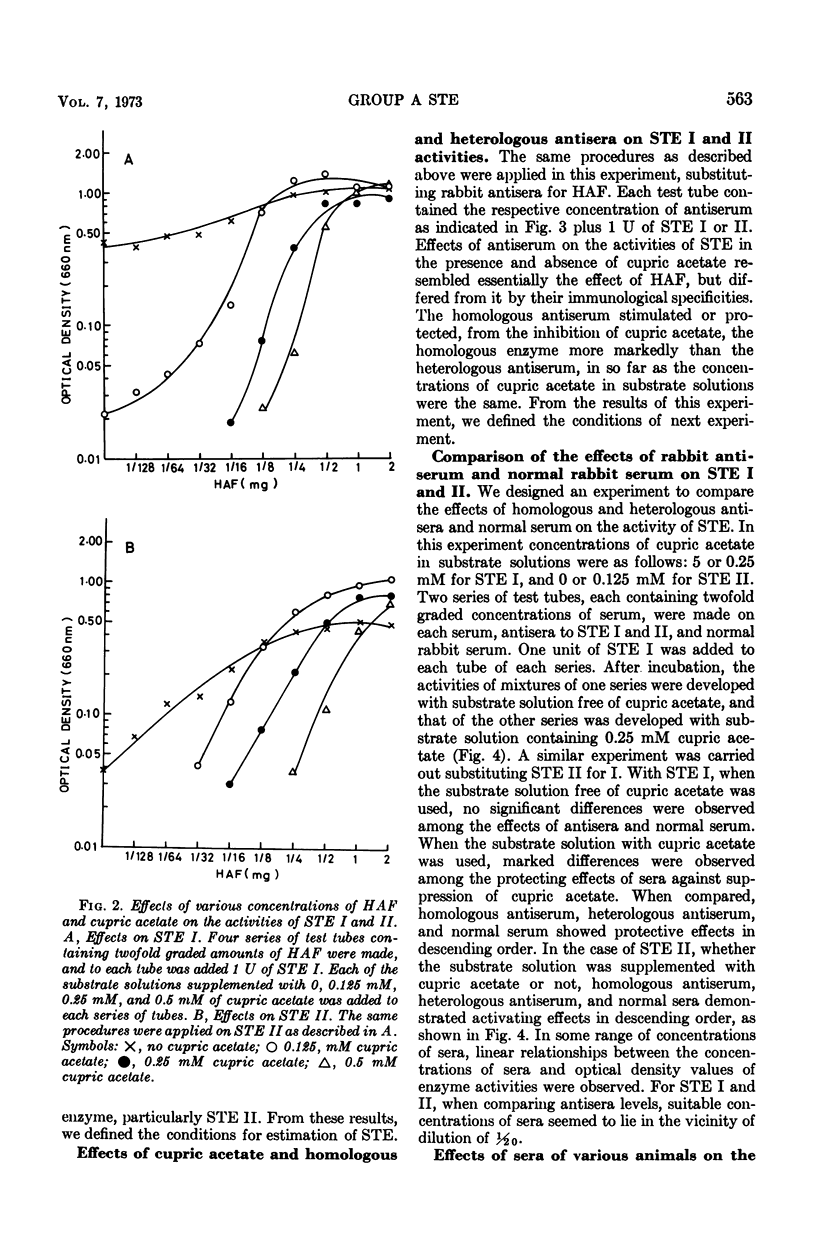
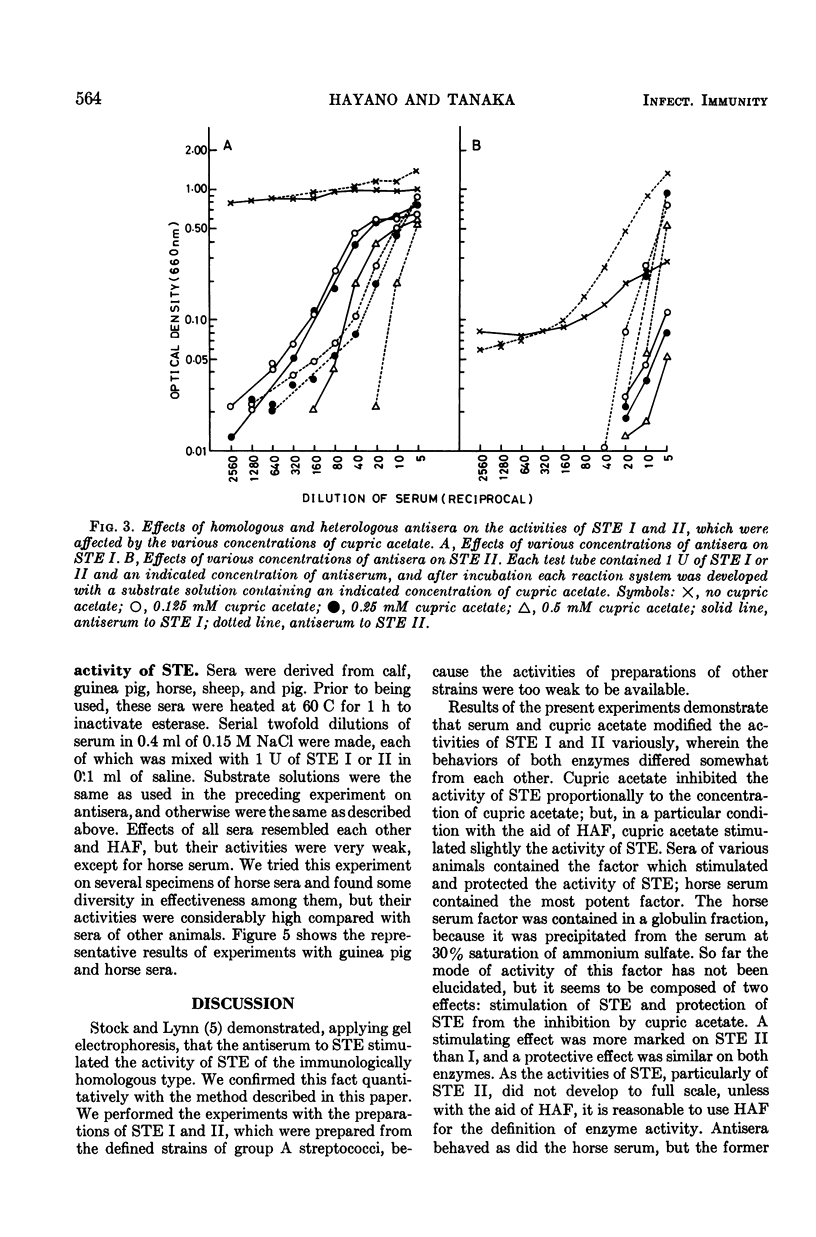
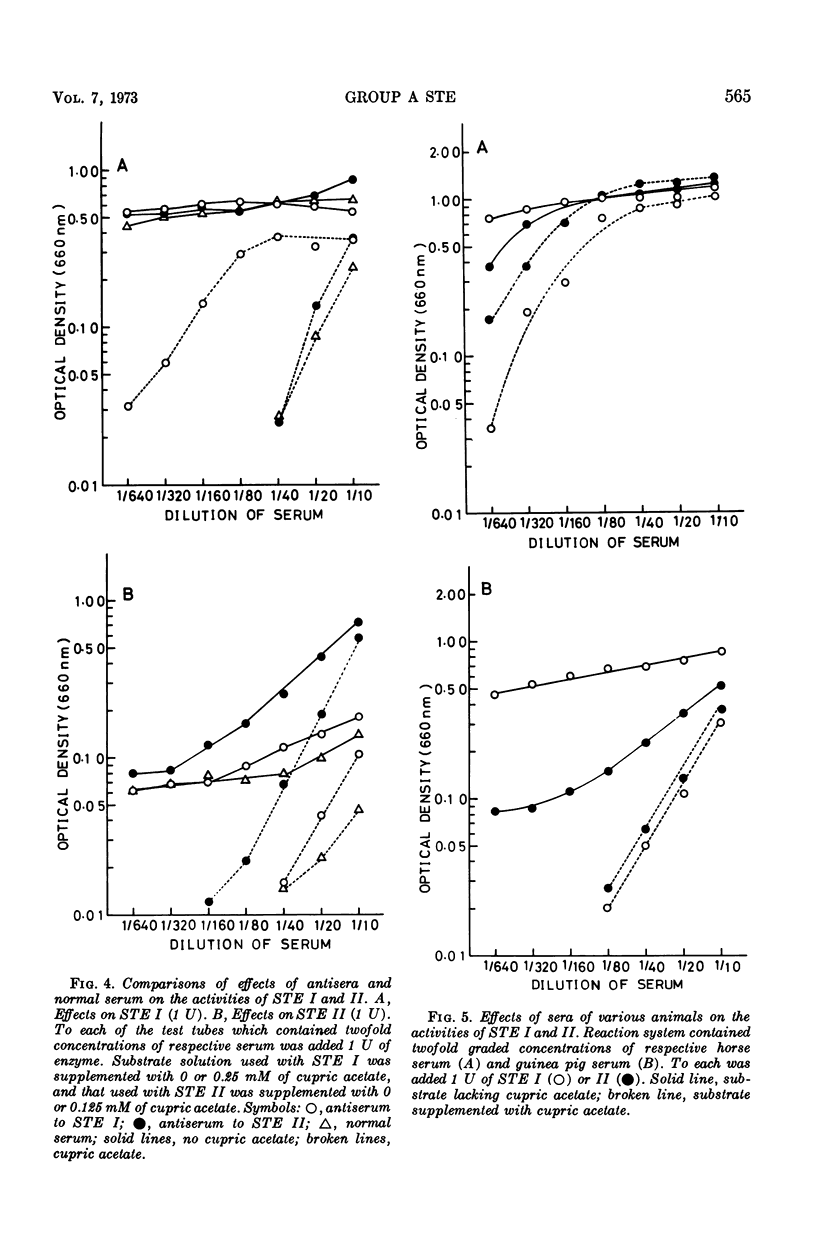
Methods were devised to prepare and estimate quantitatively the extracellular esterases of group A streptococci (STE). Two types of esterase preparations were prepared, corresponding to Stock and Lynn's serotype I (STE I) and II (STE II). The former was prepared from Streptococcus pyogenes strain SS379 (group A, type 40), and the latter from S. pyogenes strain 69882 (group A, type 49). Effects of cupric acetate, sera of various animals, and rabbit antisera to STE I and II on the activities of STE were tested. Cupric acetate added in substrate solution inhibited the activities of STE according to the concentration of cupric acetate. Sera of various animals (calf, guinea pig, horse, sheep, and pig) stimulated the activities of STE and protected them from the inhibitory effect of cupric acetate. Among the sera of various animals, horse serum gave the most potent activating and protecting effect, and was the serum from which the effective factor (horse serum-activating factor, HAF) was extracted by precipitation with ammonium sulfate. STE I was not stimulated by serum or HAF as markedly as STE II, but both enzymes were protected likewise by serum or HAF from the inhibition of cupric acetate. Antibodies to STE I and II were prepared in rabbits. Their effects on STE resembled that of HAF, but differed from the latter in immunological specificity. Activities of STE were stimulated and protected more markedly by homologous antiserum than by heterologous antiserum or normal rabbit serum. Applying suitable conditions, we defined the potency of STE and differentiated antibodies to STE I and II and normal serum quantitatively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celada F., Ellis J., Bodlund K., Rotman B. Antibody-mediated activation of a defective beta-D-galactosidase. II. Immunological relationship between the normal and the defective enzyme. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):751–764. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. B., Bolger C. D., Bridges J. M. Factors influencing the "in vitro" enhancement of L-asparaginase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman M. B., Celada F. Antibody-mediated activation of a defective beta-D-galactosidase extracted from an Escherichia coli mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):660–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCK A. H., URIEL J., GRABAR P. Esterase in extracellular concentrates of group A streptococci and the homologous antibody. Nature. 1961 Nov 4;192:434–435. doi: 10.1038/192434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A. H., Lynn R. J. Extracellular esterases of streptococci and the distribution of specific antibodies in human sera of various age groups. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):859–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


