Abstract
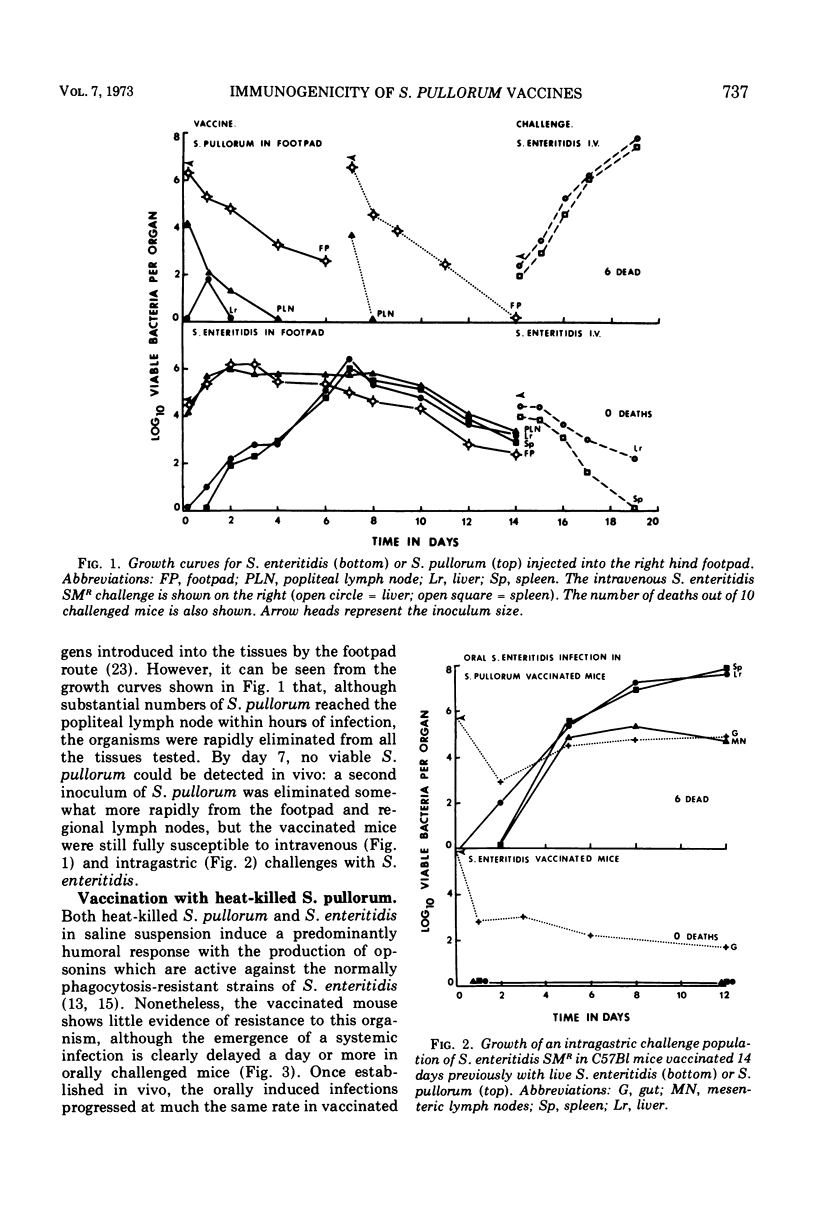
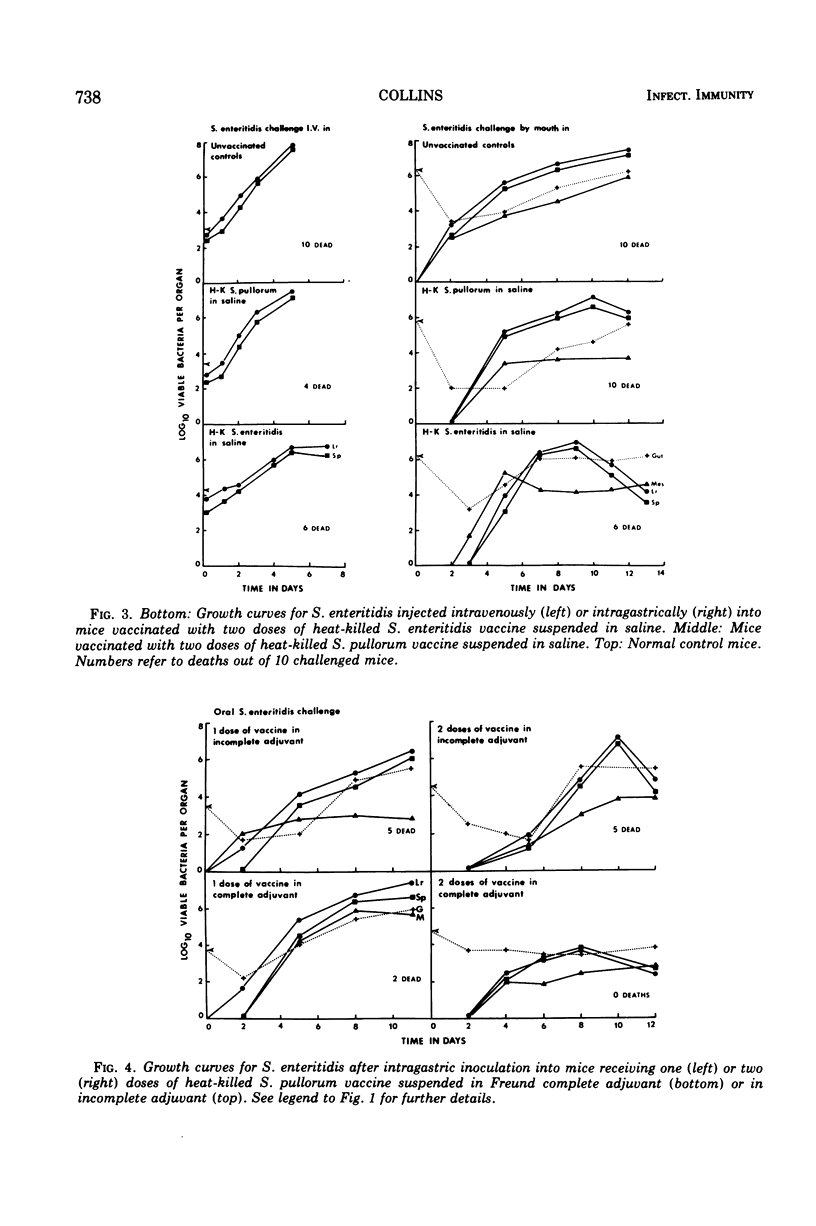
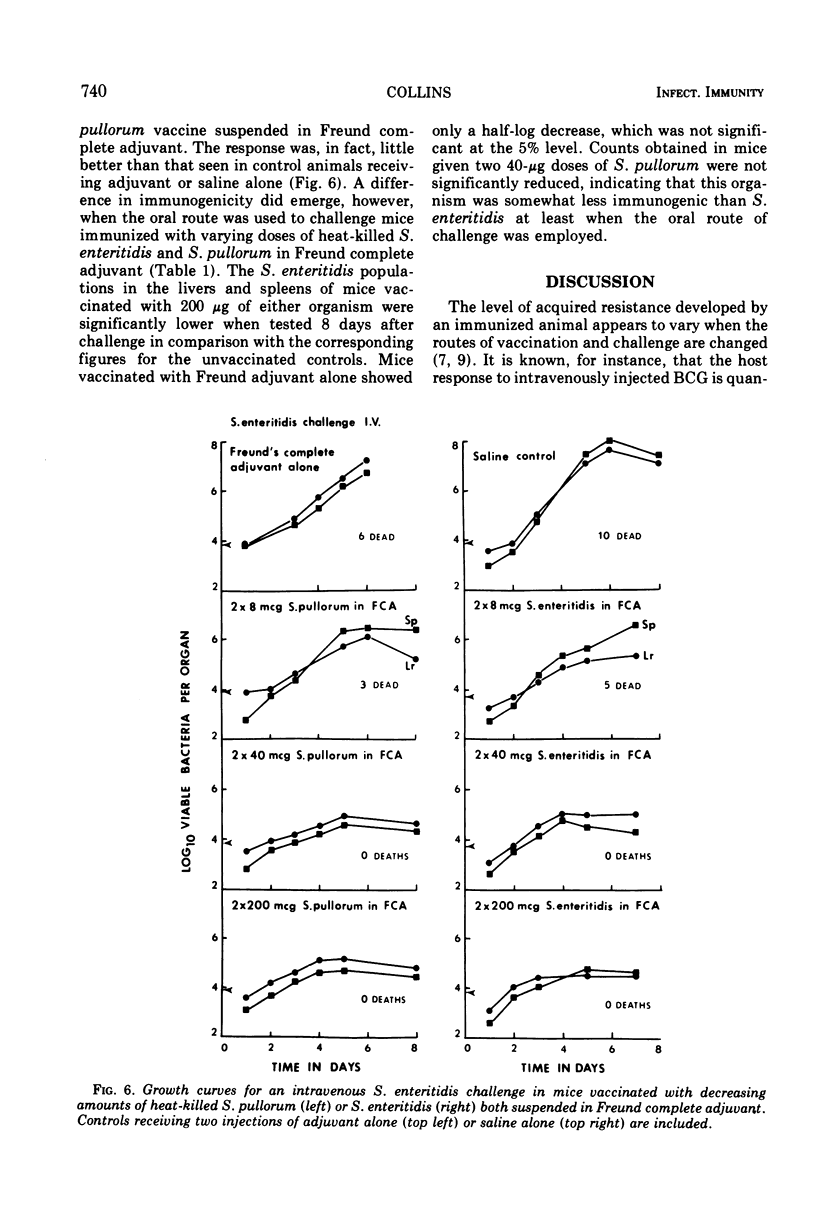
Specific pathogen-free CD-1 and C57Bl mice were infected in a hind footpad with 5 × 104 viable Salmonella enteritidis cells or 107 viable S. pullorum cells. The resulting bacterial growth within the footpad, the draining lymph nodes, and the liver and spleen was followed for 14 days. Mice vaccinated with live S. enteritidis rapidly developed an effective antibacterial resistance to both intravenous and intragastric challenge with S. enteritidis SMR. The viable inoculum of S. pullorum was rapidly eliminated from the normal mouse tissues and failed to induce a detectable anti-Salmonella resistance to parenteral or oral challenge with S. enteritidis. Heat-killed saline suspensions (200 μg, dry wt) of S. enteritidis or S. pullorum were unable to induce an effective antimicrobial resistance against a subsequent virulent Salmonella challenge. However, when the organisms were suspended in Freund complete adjuvant, both vaccines induced an antibacterial resistance to intravenous and intragastric challenge. Reduction of the antigenic dose from 200 to 40 μg did not greatly affect the protective value of the two killed vaccines against an intravenous challenge, but the level of protection observed with two 40-μg doses of S. pullorum was considerably reduced when the animals were infected intragastrically, suggesting that some quantitative differences existed between the sensitizing antigenic contents of the two test organisms.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Barclay W. R., Brehmer W., Goode G., List R. H., Ribi E., Tarmina D. F. Effectiveness of cell walls of Mycobacterium bovis strain BCG administered by various routes and in different adjuvants in protecting mice against airborne infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Feb;99(2):242–248. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Carter P. B. Comparative immunogenicity of heat-killed and living oral Salmonella vaccines. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):451–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.451-458.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of adjuvant on immunogenicity of a heat-killed salmonella vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):69–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice preimmunized with living or ethyl alcohol-killed vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.676-683.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Immunogenicity of various mycobacteria and the corresponding levels of cross-protection developed between species. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):688–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.688-696.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. Delayed hypersensitivity and arthus reactivity in relation to host resistance in salmonella-infected mice. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):830–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. II. Effect of adjuvant on the allergenicity and immunogenicity of heat-killed tubercle bacilli. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):266–275. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mechanisms in antimicrobial immunity. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jul;10(1):58–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Recall of immunity in mice vaccinated with Salmonella enteritidis or Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2014–2021. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2014-2021.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Salmonellosis in orally infected specific pathogen-free C57B1 mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):191–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.191-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Serum mediated killing of three group D salmonellas. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):247–253. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in Experimental Salmonellosis I. Protection Induced by Rough Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.309-315.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. Resistance to reinfection in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):334–343. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO TYPHOID IN MICE AND THE QUESTION OF "CELLULAR IMMUNITY". Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:391–404. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.391-404.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. Resistance to intracellular infection. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):439–445. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S., Mildenhall P. Studies on cytophilic antibodies. 1. The production by mice of macrophage cytophilic antibodies to sheep erythrocytes: relationship to the production of other antibodies and the development of delayed-type hypersensitivity. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):113–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Detection of delayed hypersensitivity in mice injected with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.384-389.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USHIBA D., SAITO K., AKIYAMA T., NAKANO M., SUGIYAMA T., SHIRONO S. Studies on experimental typhoid: bacterial multiplication and host cell response after infection with Salmonella enteritidis in mice immunized with live and killed vaccines. Jpn J Microbiol. 1959 Apr;3:231–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1959.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Delayed hypersensitivity. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jul;46(3):359–419. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiba D. Two types of immunity in experimental typhoid; "cellular immunity" and "humoral immunity". Keio J Med. 1965 Jun;14(2):45–61. doi: 10.2302/kjm.14.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



