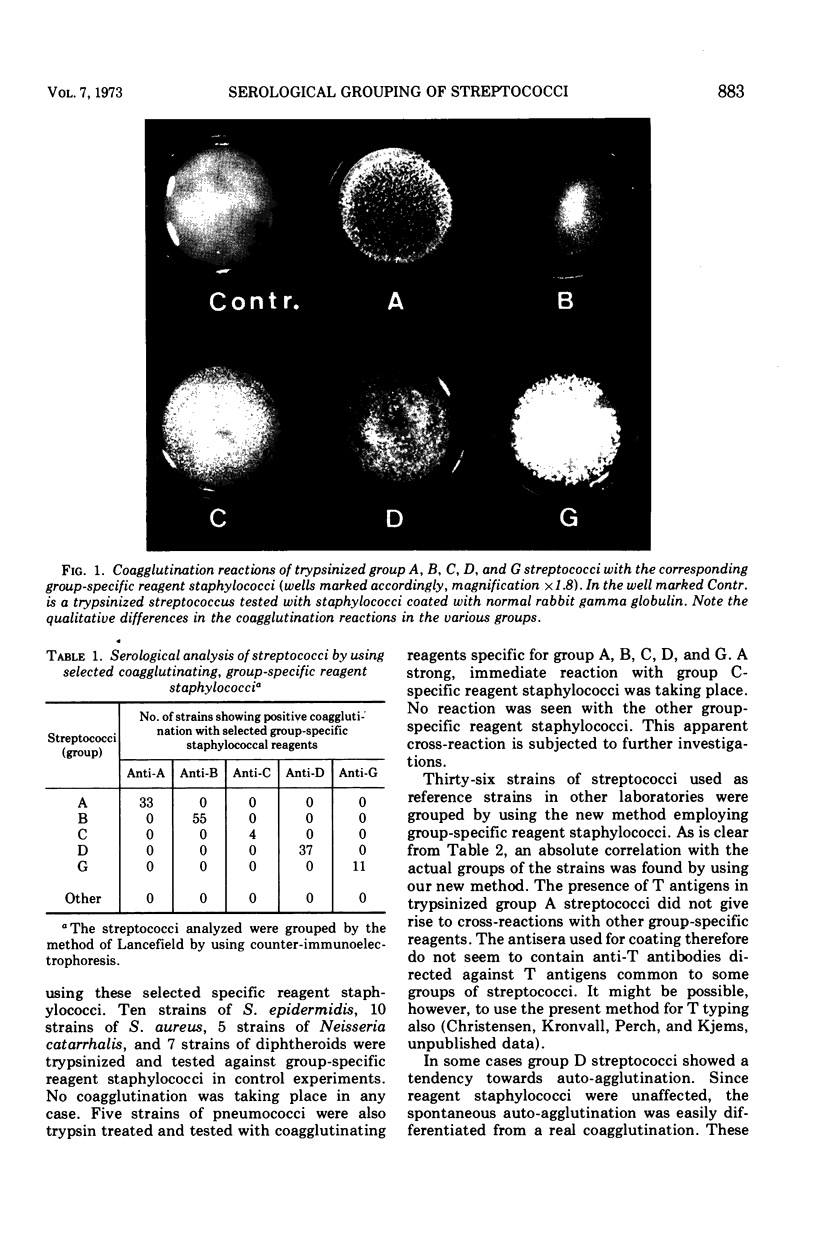
Abstract
A coagglutinating reagent has recently been developed and utilized in capsule typing of pneumococci. The reagent consists of stabilized staphylococci coated with specific antibody via the gamma globulin Fc-protein A reaction thereby orienting the antibody molecules with the antigen-reactive Fab parts outwards. Reagent staphylococci coated with antibodies directed against streptococcal group-specific antigens have been used in the present investigations. Overnight cultures of streptococci were treated with trypsin and then directly tested for coagglutination of selected reagent staphylococci on glass slides. In all, 179 strains of streptococci were analyzed by the method described. The results were compared with grouping by using Lancefield extracts in counter-immunoelectrophoresis and were shown to agree completely. The coagglutination method described proved to be accurate, rapid, and simple.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson S., Holme T., Wadström T. Influence of cultivation conditions on the production of extracellular proteins by Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT S. D. Type and group polysaccharides of group D streptococci. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:621–630. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ederer G. M., Herrmann M. M., Bruce R., Matsen J. M., Chapman S. S. Rapid extraction method with pronase B for grouping beta-hemolytic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):285–288. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.285-288.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. I. An immunochemical study of the causative agent (PM streptococcus). J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):205–212. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franek J., Kubín V., Procházka O. The use of immunofluorescence in grouping of streptococci and in diagnosis of tularemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:12–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Frommel D. Definition of staphylococcal protein A reactivity for human immunoglobulin G fragments. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):124–127. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Grey H. M., Williams R. C., Jr Protein A reactivity with mouse immunoglobulins. Structural relationship between some mouse and human immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1116–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Seal U. S., Finstad J., Williams R. C., Jr Phylogenetic insight into evolution of mammalian Fc fragment of gamma G globulin using staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova M. T., Beauvais E., Brezenski F. T., Litsky W. Fluorescent-antibody techniques for the identification of group D streptococci: direct staining method. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):571–577. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.571-577.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENDAL K. Grouping of hemolytic streptococci belonging to groups A, C, and G; a comparison between the results obtained by precipitation and by slide-agglutination. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(2):127–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D., SLADE H. D. THE CELLULAR LOCATION OF THE STREPTOCOCCAL GROUP D ANTIGEN. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:297–305. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade H. D. Extraction of Cell-Wall Polysaccharide Antigen from Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.667-672.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKEN A. J., ELLIOTT S. D., BADDILEY J. The identity of streptococcal group D antigen with teichoic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 May;31:231–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]