Abstract
Analysis of the partition in a two-polymer phase system of Salmonella typhimurium R mutants with different susceptibility to phagocytosis distinguished between the mutants. Close to 80% of the R mutants least resistant to phagocytosis accumulated in the dextran-rich phase, whereas more phagocytosis-resistant mutants showed higher affinity for the interface and the polyethylene glycol-rich top phase. By growing the uridine diphosphate (pyro)-gal-4-epimeraseless mutant LT2-M1 in the presence of d-galactose for different periods of time, two well-defined peaks were obtained in counter-current distribution analysis with an aqueous two-polymer phase system revealing a heterogeneous population in the culture. One peak was located at a site characteristic of R bacteria, the other at the site of S bacteria. As growth proceeded, more bacteria transferred from the R-type to the S-type peak. Within each peak, a gradual increase in resistance to phagocytosis by rabbit polymorphonuclear cells occurred with increasing length of growth in d-galactose.
Full text
PDF

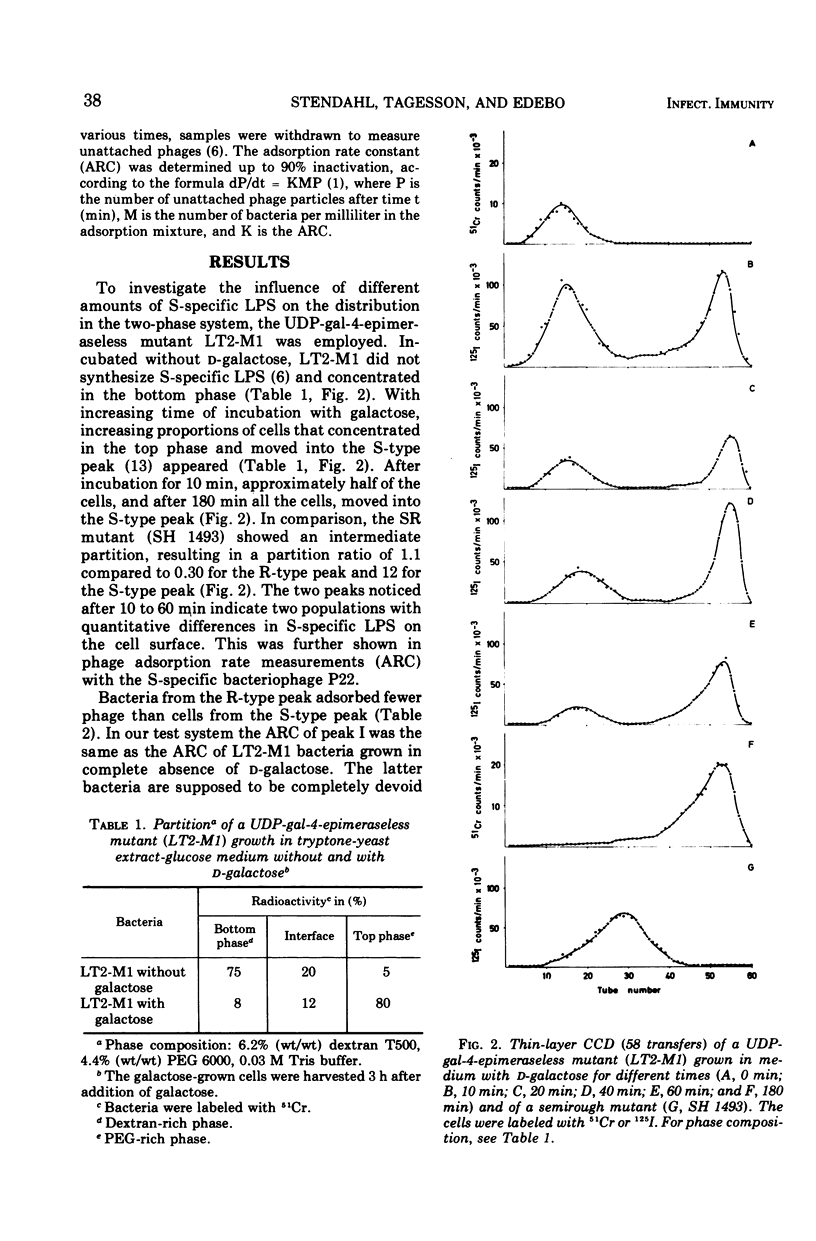
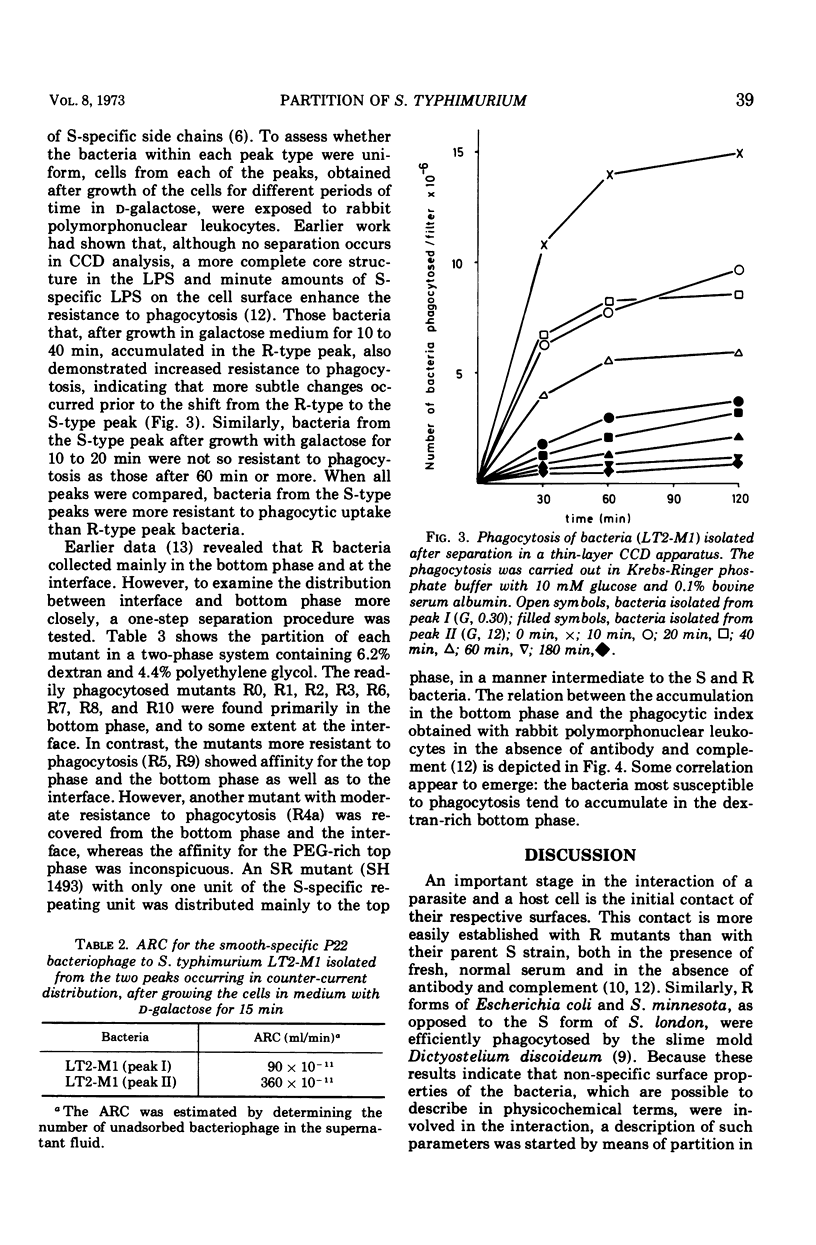
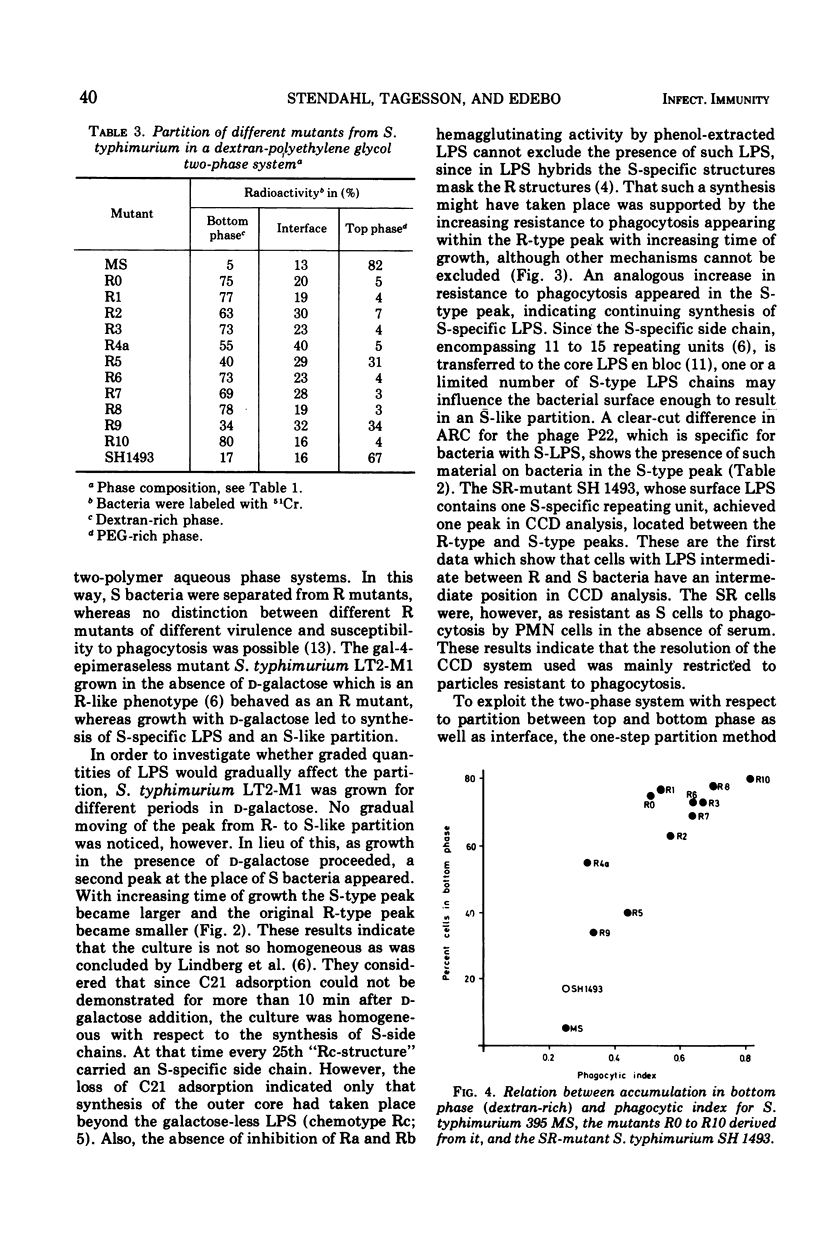

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsson P. A. Partition of cell particles and macromolecules in polymer two-phase systems. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:309–341. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F. Influence of endotoxin (51cr) structure on blood clearance in the absence of specific antibodies. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Feb;7(2):238–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Holme T., Hellerqvist C. G., Svensson S. Bacteriophage receptor development and synthesis of O-specific side chains after addition of D-galactose to the uridine diphosphate-galactose-4-epimeraseless mutant Salmonella typhimurium LT2-M1. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):540–547. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.540-547.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Sarvas M., Mäkelä P. H. Bacteriophage attachment to the somatic antigen of salmonella: effect of o-specific structures in leaky R mutants and s, t1 hybrids. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):88–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.88-97.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Gerisch G., Riedel V. Polysaccharide in vegetativen und aggregationsreifen Amöben von Dictyostelium discoideum. 1. In vivo Degradierung von Bakterien-Lipopolysaccharid. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Nov;2(4):469–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Saito K. The chemical compositions of the cell wall of Salmonella typhimurium affecting the clearance-rate in mouse; influence of specific antibody. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Nov;14(6):451–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Edebo L. Phagocytosis of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by rabbit polymorphonuclear cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Magnusson K. E., Tagesson C., Cunningham R., Edebo L. Characterization of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by counter-current distribution in an aqueous two-polymer phase system. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):573–577. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.573-577.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Contact angles and phagocytosis of non-opsonized bacteria. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Sep;12(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


