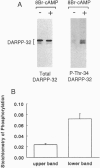
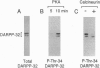Abstract
Although protein phosphatases appear to be highly controlled in intact cells, relatively little is known about the physiological regulation of their activity. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of apparent M(r) 32,000, is phosphorylated in vitro by casein kinase I, casein kinase II, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase on sites phosphorylated in vivo. DARPP-32 phosphorylated on Thr-34 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 and an excellent substrate for calcineurin, a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase. Here we provide evidence, using both purified proteins and brain slices, that phosphorylation of DARPP-32 on Ser-137 by casein kinase I inhibits the dephosphorylation of Thr-34 by calcineurin. This inhibition occurs only when phospho-Ser-137 and phospho-Thr-34 are located on the same DARPP-32 molecule and is not dependent on the mode of activation of calcineurin. The results demonstrate that the inhibition is due to a modification in the properties of the substrate which alters its dephosphorylation rate. Thus, casein kinase I may play a physiological role in striatonigral neurons as a modulator of the regulation of protein phosphatase 1 via DARPP-32.
Full text
PDF
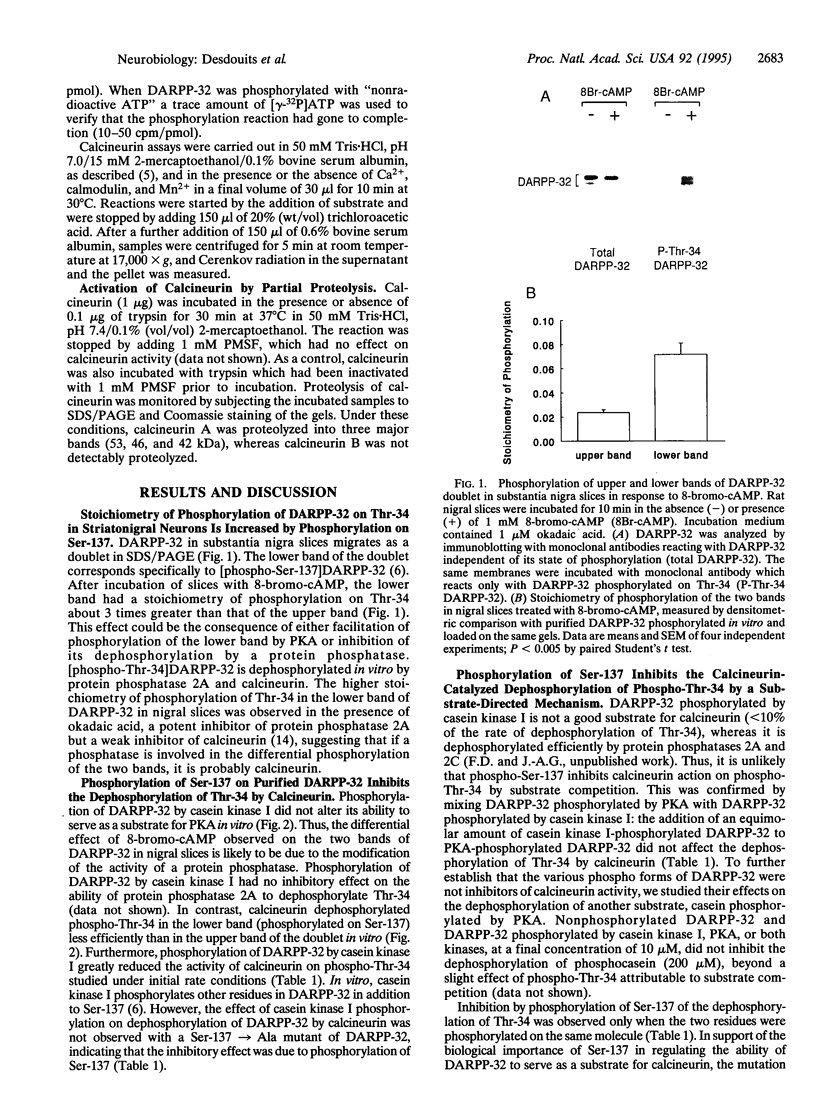

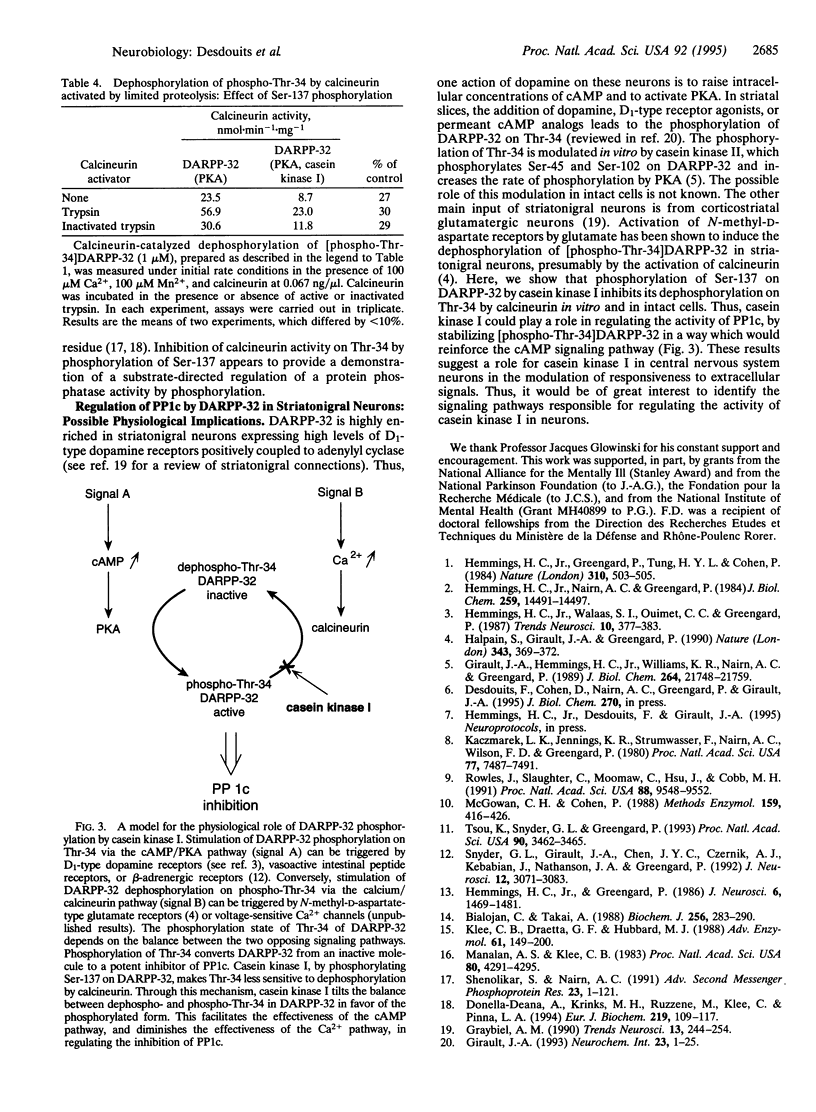
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donella-Deana A., Krinks M. H., Ruzzene M., Klee C., Pinna L. A. Dephosphorylation of phosphopeptides by calcineurin (protein phosphatase 2B). Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):109–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Williams K. R., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32, a dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, by casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21748–21759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A. Protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in mammalian central nervous system. Neurochem Int. 1993 Jul;23(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90139-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90104-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpain S., Girault J. A., Greengard P. Activation of NMDA receptors induces dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 in rat striatal slices. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):369–372. doi: 10.1038/343369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein: regional, tissue, and phylogenetic distribution. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1469–1481. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):503–505. doi: 10.1038/310503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein. II. Comparison of the kinetics of phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and phosphatase inhibitor 1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14491–14497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L. K., Jennings K. R., Strumwasser F., Nairn A. C., Walter U., Wilson F. D., Greengard P. Microinjection of catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase enhances calcium action potentials of bag cell neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7487–7491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Draetta G. F., Hubbard M. J. Calcineurin. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1988;61:149–200. doi: 10.1002/9780470123072.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Activation of calcineurin by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4291–4295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Cohen P. Protein phosphatase-2C from rabbit skeletal muscle and liver: an Mg2+-dependent enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:416–426. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowles J., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. Purification of casein kinase I and isolation of cDNAs encoding multiple casein kinase I-like enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9548–9552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Nairn A. C. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:1–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder G. L., Girault J. A., Chen J. Y., Czernik A. J., Kebabian J. W., Nathanson J. A., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 in rat choroid plexus: regulation by factors other than dopamine. J Neurosci. 1992 Aug;12(8):3071–3083. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-08-03071.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou K., Snyder G. L., Greengard P. Nitric oxide/cGMP pathway stimulates phosphorylation of DARPP-32, a dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, in the substantia nigra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3462–3465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]