Abstract
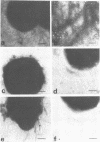
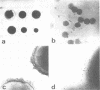
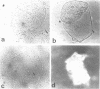
Gonococci of the colonial types that are associated with virulence, types 1 and 2, have pili that enable the bacteria both to attach in vitro to human epithelial cells and to resist phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. These piliated gonococci also agglutinate various mammalian and chicken erythrocytes. Gonococci of an avirulent colonial type, i.e., type 4, have no pili and neither attach to epithelial cells or erythrocytes nor resist phagocytosis. Like the type 4 bacteria, mechanically or enzymatically (trypsin) depiliated type 1 gonococci failed to attach to epithelial cells and erythrocytes and were susceptible to phagocytosis. Pili of types 1 and 2 gonococci were antigenically similar. Both type 1 gonococci and pili isolated from them induced in rabbits antibody that (i) precipitated gonococcal pili in immunodiffusion, (ii) reacted with piliated gonococci as tested by indirect immunofluorescent analysis, (iii) inhibited attachment of piliated gonococci to both human epithelial cells and erythrocytes, and (iv) opsonized piliated gonococci.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P. Fimbriae and adhesive properties in Klebsiella strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:271–286. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P., SMITH I. W., DEMPSTER G., EDMUNDS P. N. Non-flagellar filamentous appendages (fimbriae) and haemagglutinating activity in Bacterium coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):335–348. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Anderson E. S., Campbell I. Fimbriae and adhesive properties in Salmonellae. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):107–138. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY M. J., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenicity of group A streptococci. II. The antiphagocytic effects of the M protein and the capsular gel. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:617–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):437–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN S. P., GREEN R. Methods for the study of surviving leukocytes: A. Preparation of cell suspension. Methods Med Res. 1958;7:136–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. R., FLEMING D. O., WOOD W. B., Jr THE EFFECT OF ACUTE RADIATION INJURY ON PHAGOCYTIC MECHANISMS OF ANTIBACTERIAL DEFENSE. J Immunol. 1963 Jun;90:914–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweedy J. M., Park R. W., Hodgkiss W. Evidence for the presence of fimbriae (pili) on vibrio species. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(2):235–244. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Glynn A. A., Watt P. J. The fate of gonococci in polymorphonuclear leucocytes: an electron microscopic study of the natural disease. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Jun;53(3):289–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. J. The fate of gonococci in polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):501–509. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistreich G. A., Baker R. F. The presence of fimbriae (pili) in three species of Neisseria. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Feb;65(2):167–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]