Abstract
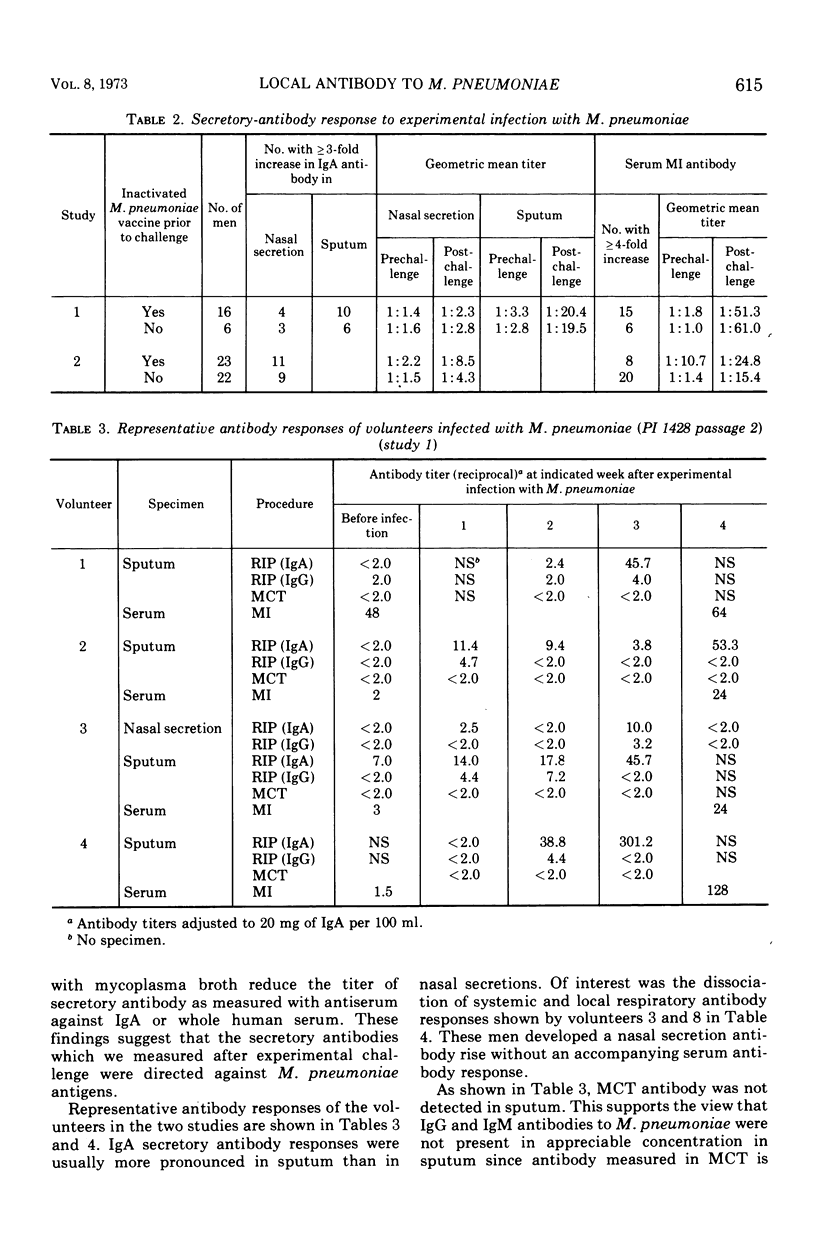
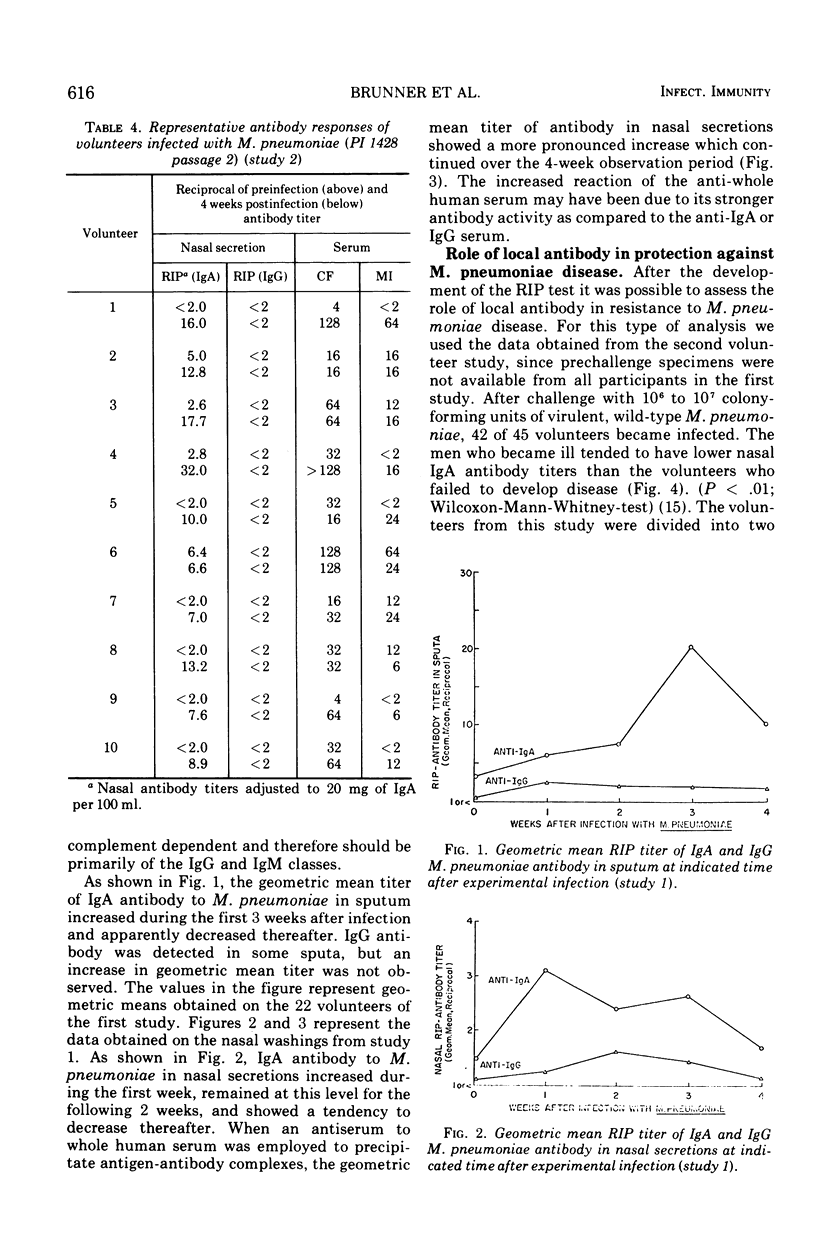
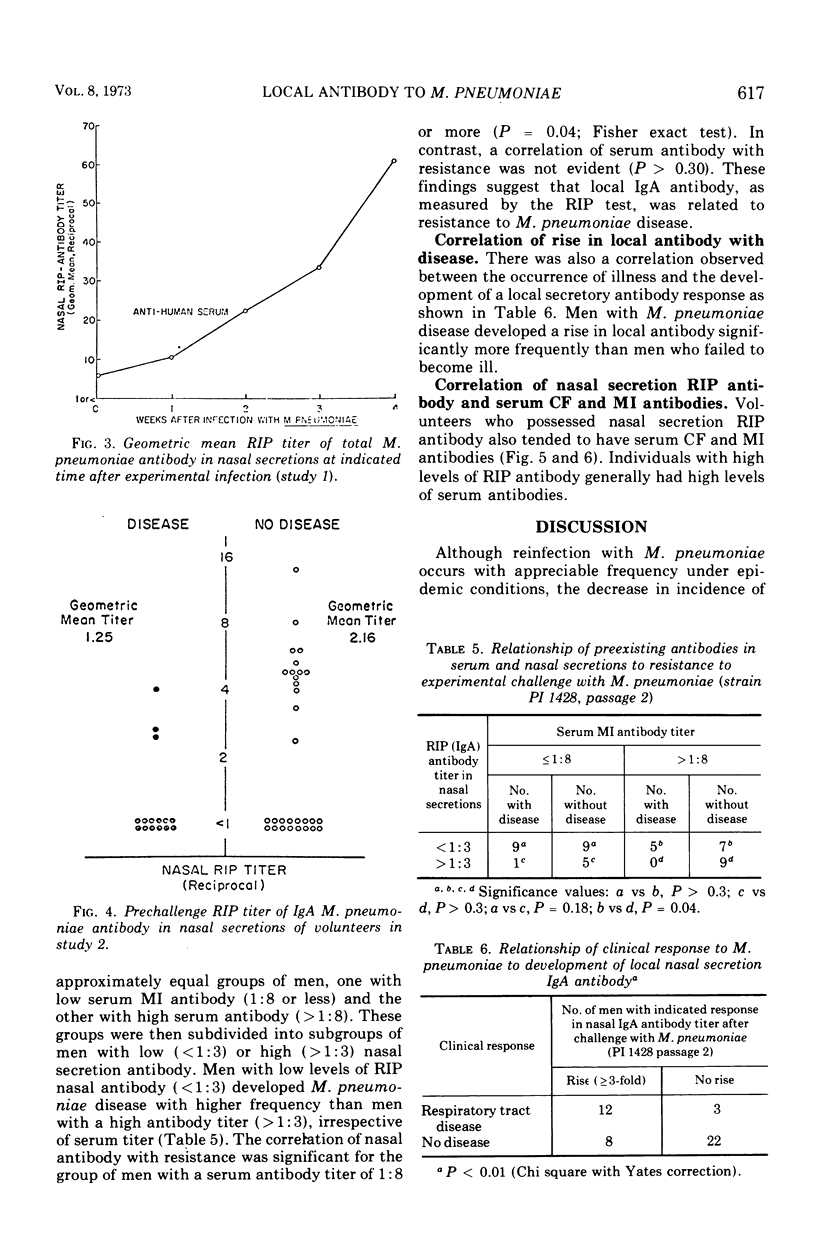
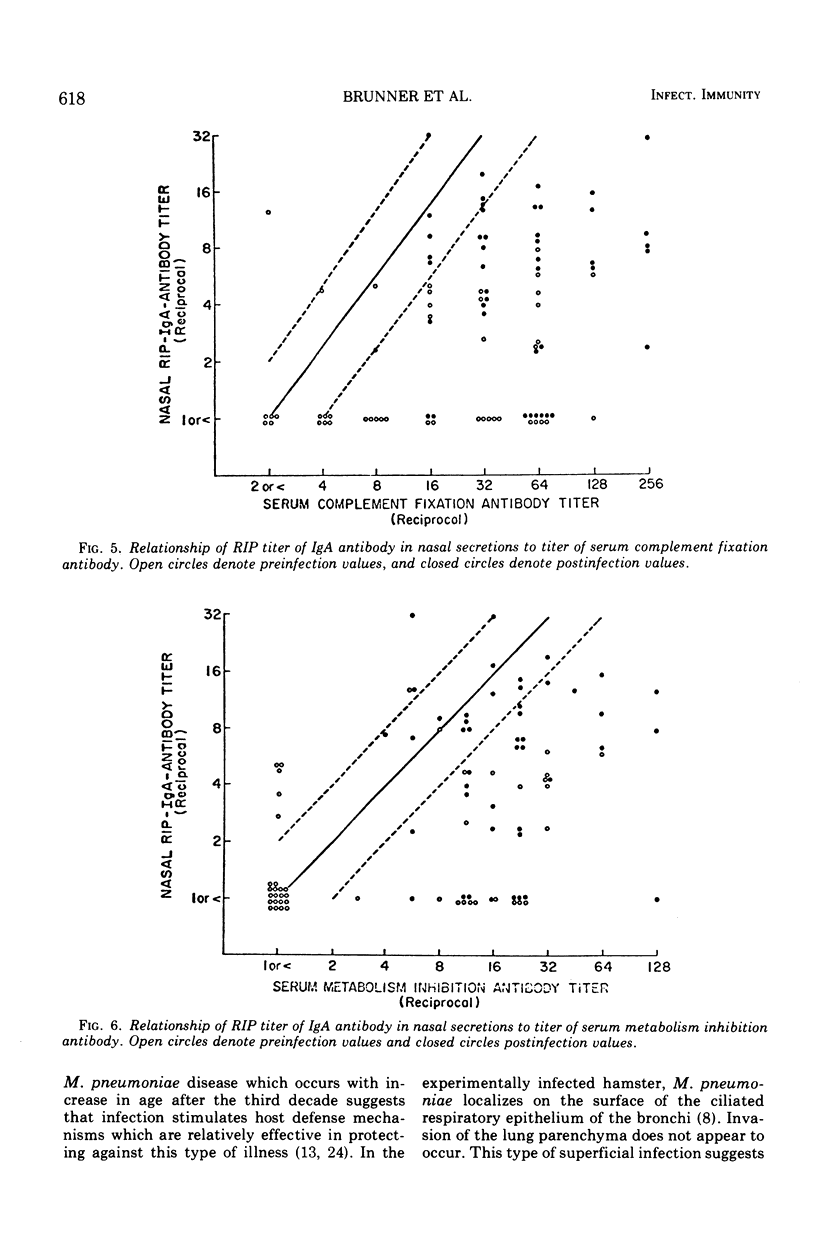
After experimental infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae, 42% of 67 volunteers developed a threefold or greater rise in antibody in nasal secretions as measured by radioimmunoprecipitation. Development of an antibody increase in sputum was detected more often, i.e., in 73% of the volunteers. Each of the antibody increases involved immunoglobulin (Ig) A. Twelve rises in IgG antibody were detected in the specimens which exhibited a rise in IgA antibody. In almost every instance the rise in IgA antibody exceeded that seen with IgG antibody. Analysis of the response to experimental challenge with M. pneumoniae of volunteers with different levels of preexisting respiratory tract IgA antibody suggested that this secretory antibody was related to host resistance to M. pneumoniae disease. Further, respiratory tract IgA antibody appeared to be more directly related to host resistance than was antibody in serum.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELLANTI J. A., ARTENSTEIN M. S., BUESCHER E. L. CHARACTERIZATION OF VIRUS NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODIES IN HUMAN SERUM AND NASAL SECRETIONS. J Immunol. 1965 Mar;94:344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Sterner G. Antibodies against Mycoplasma pneumoniae in bronchial secretions. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;76(4):646–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1969.tb03296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Perey D. Y. Immune mechanisms of mucosal resistance. Med Clin North Am. 1972 Mar;56(2):391–402. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., James W. D., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Measurement of Mycoplasma pneumoniae mycoplasmacidal antibody in human serum. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1491–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Somerson N. L. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: hydrogen peroxide secretion and its possible role in virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):85–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Biologic effects of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and other mycoplasmas from man on hamster tracheal organ culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Dec;132(3):1153–1158. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZEKAS de ST GROTH S., DONNELLEY M. Studies in experimental immunology of influenza. IV. The protective value of active immunization. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 Jan;28(1):61–75. doi: 10.1038/icb.1950.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Bienenstock J. Immunoglobulin-containing cells in lungs of hamsters infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1400–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Clyde W. A. Protective Effect of Vaccines in Experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae Disease. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):559–565. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.559-565.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., McMahan R., Mansy A. M., Grayston J. T. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in an urban area. Five years of surveillance. JAMA. 1970 Nov 30;214(9):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Bellanti J. A., Arrobio J. O., Mills J., Brandt C. D., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Respiratory syncytial virus neutralizing activity in nasal secretions following natural infection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):658–661. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Chanock R. M., Friedewald W. T., Alford R. H. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in volunteers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):471–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Purcell R. H., Bellanti J. A., Chanock R. M. Protective effect of antibody to parainfluenza type 1 virus. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 24;275(21):1145–1152. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611242752101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerson N. L., James W. D., Walls B. E., Chanock R. M. Growth of Mycoplasma pneumoniae on a glass surface. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):384–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., SOMERSON N. L., TURNER H. C., CHANOCK R. M. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS AS SHOWN BY COMPLEMENT-FIXATION AND GEL DIFFUSION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1261–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1261-1273.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


