Abstract
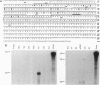
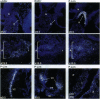
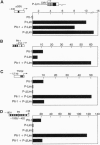
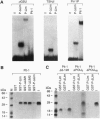
A pituitary LIM homeodomain factor, P-Lim, is expressed as Rathke's pouch forms and as specific pituitary cell phenotypes are established, suggesting functional roles throughout pituitary development. While selectively expressed in both anterior and intermediate pituitary in mature mice, P-Lim is also transiently expressed in the developing ventral neural cord and brainstem. P-Lim binds to and activates the promoter of the alpha-glycoprotein subunit gene, a marker of early pituitary development, and synergizes with Pit-1 in transcriptional activation of genes encoding terminal differentiation markers. The LIM domain of P-Lim specifically interacts with the Pit-1 POU domain and is required for synergistic interactions with Pit-1, but not for basal transcriptional activation events.
Full text
PDF
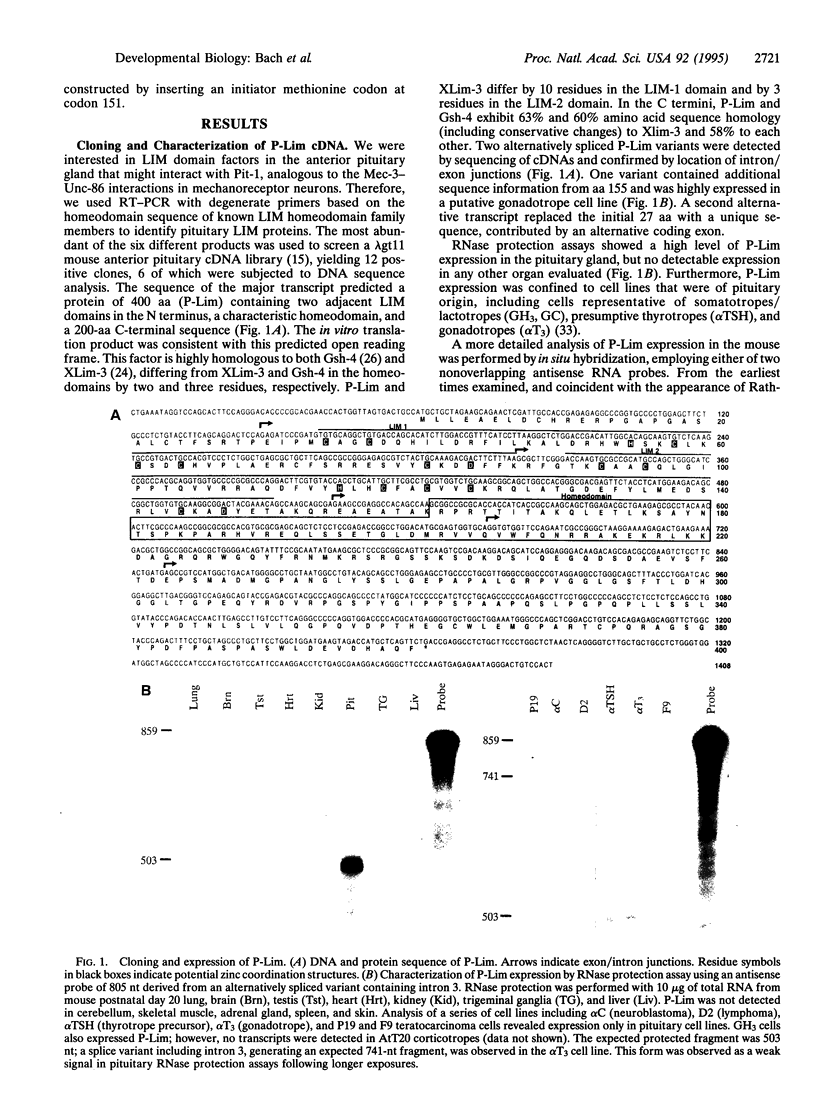

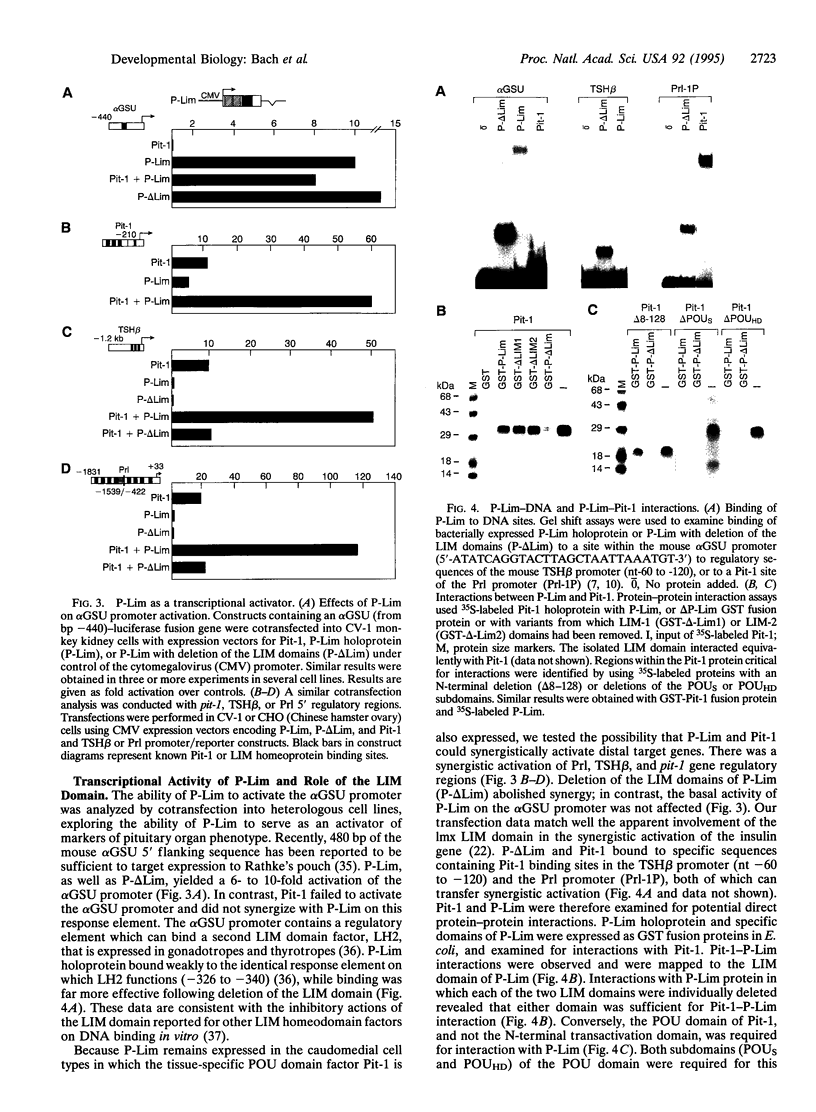

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes J. D., Crosby J. L., Jones C. M., Wright C. V., Hogan B. L. Embryonic expression of Lim-1, the mouse homolog of Xenopus Xlim-1, suggests a role in lateral mesoderm differentiation and neurogenesis. Dev Biol. 1994 Jan;161(1):168–178. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Horvitz H. R., Sulston J. E. Mutations that lead to reiterations in the cell lineages of C. elegans. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90501-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., McGuffin M. E., Pfeifle C., Segal D., Cohen S. M. apterous, a gene required for imaginal disc development in Drosophila encodes a member of the LIM family of developmental regulatory proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):715–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Kalla K., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Cell-specific expression of the prolactin gene in transgenic mice is controlled by synergistic interactions between promoter and enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):959–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein R., Wang X., Song D., Cooke N. E., Liebhaber S. A. The LIM/double zinc-finger motif functions as a protein dimerization domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10655–10659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyd G., Kim S. K., Horvitz H. R. Novel cysteine-rich motif and homeodomain in the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell lineage gene lin-11. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):876–879. doi: 10.1038/344876a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Wang J., Chadwick R. B., Rutter W. J. Synergistic activation of the insulin gene by a LIM-homeo domain protein and a basic helix-loop-helix protein: building a functional insulin minienhancer complex. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2165–2176. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Japón M. A., Rubinstein M., Low M. J. In situ hybridization analysis of anterior pituitary hormone gene expression during fetal mouse development. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Aug;42(8):1117–1125. doi: 10.1177/42.8.8027530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Thor S., Norberg T., Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Insulin gene enhancer binding protein Isl-1 is a member of a novel class of proteins containing both a homeo- and a Cys-His domain. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):879–882. doi: 10.1038/344879a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall S. K., Gordon D. F., Birkmeier T. S., Petrey D., Sarapura V. D., O'Shea K. S., Wood W. M., Lloyd R. V., Ridgway E. C., Camper S. A. Enhancer-mediated high level expression of mouse pituitary glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit transgene in thyrotropes, gonadotropes, and developing pituitary gland. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Oct;8(10):1420–1433. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.10.7531821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. S., Herr W. Ethidium bromide provides a simple tool for identifying genuine DNA-independent protein associations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6958–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Witte D. P., Branford W. W., Aronow B. J., Weinstein M., Kaur S., Wert S., Singh G., Schreiner C. M., Whitsett J. A. Gsh-4 encodes a LIM-type homeodomain, is expressed in the developing central nervous system and is required for early postnatal survival. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2876–2885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. C., Li S., Drolet D. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Pituitary ontogeny of the Snell dwarf mouse reveals Pit-1-independent and Pit-1-dependent origins of the thyrotrope. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):515–522. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin S. M., När A. M., Kalla K. A., Sack R. A., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of a novel zinc finger protein binding a conserved element critical for Pit-1-dependent growth hormone gene expression. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1674–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Chen R., DiMattia G. E., Scully K. M., Kalla K. A., Lin S. C., Yu V. C., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific enhancer confers Pit-1-dependent morphogen inducibility and autoregulation on the pit-1 gene. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):913–932. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., DiMattia G. E., Rosenfeld M. G. Transcriptional mechanisms in anterior pituitary cell differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Oct;4(5):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90138-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberson M. S., Schoderbek W. E., Tremml G., Maurer R. A. Activation of the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit promoter by a LIM-homeodomain transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):2985–2993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., West B. L., Baxter J. D. Synergistic activation of the rat growth hormone promoter by Pit-1 and the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;6(4):656–665. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1584227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeichel K. L., Beckerle M. C. The LIM domain is a modular protein-binding interface. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Barale J. C., Marcinkiewicz M., Mattei M. G., Day R., Chrétien M. The mouse homeoprotein mLIM-3 is expressed early in cells derived from the neuroepithelium and persists in adult pituitary. DNA Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;13(12):1163–1180. doi: 10.1089/dna.1994.13.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinfelder H. J., Hauser P., Nakayama Y., Radovick S., McClaskey J. H., Taylor T., Weintraub B. D., Wondisford F. E. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone regulation of human TSHB expression: role of a pituitary-specific transcription factor (Pit-1/GHF-1) and potential interaction with a thyroid hormone-inhibitory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3130–3134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-García I., Osada H., Forster A., Rabbitts T. H. The cysteine-rich LIM domains inhibit DNA binding by the associated homeodomain in Isl-1. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4243–4250. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-García I., Rabbitts T. H. The LIM domain: a new structural motif found in zinc-finger-like proteins. Trends Genet. 1994 Sep;10(9):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Hayes W. P., Otani H., Dawid I. B. Expression of LIM class homeobox gene Xlim-3 in Xenopus development is limited to neural and neuroendocrine tissues. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):245–256. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Jamrich M., Good P. J., Dawid I. B. The LIM domain-containing homeo box gene Xlim-1 is expressed specifically in the organizer region of Xenopus gastrula embryos. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):356–366. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- This week in science. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):155–155. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5054.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Anterior pituitary development: short tales from dwarf mice. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):527–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90422-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Chalfie M. mec-3, a homeobox-containing gene that specifies differentiation of the touch receptor neurons in C. elegans. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Weiner R. I., Mellon P. L. Cell lines of the pituitary gonadotrope lineage derived by targeted oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):597–603. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Baldassare M., Fisher P., Rathbun G., Oltz E. M., Yancopoulos G. D., Jessell T. M., Alt F. W. LH-2: a LIM/homeodomain gene expressed in developing lymphocytes and neural cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):227–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue D., Tu Y., Chalfie M. Cooperative interactions between the Caenorhabditis elegans homeoproteins UNC-86 and MEC-3. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1324–1328. doi: 10.1126/science.8103239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]