Summary
DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs) are caused by environmental, endogenous, and chemotherapeutic agents and pose a severe threat to genome stability. We use Xenopus egg extracts to recapitulate DPC repair and show that this process is coupled to DNA replication. A DPC on the leading strand template arrests the replisome ahead of the lesion by stalling the CMG helicase. The DPC is then degraded on DNA, yielding a peptide-DNA adduct that is bypassed by CMG. The leading strand subsequently resumes synthesis, stalls again at the adduct, and then extends past it. Bypass of the peptide adduct requires DNA pol ζ. A DPC on the lagging strand template only transiently stalls the replisome, but it too is degraded, allowing Okazaki fragment bypass. Our experiments describe a versatile, proteolysis-based mechanism of S phase DPC repair that avoids replication fork collapse as well as the need to induce double strand breaks in the repair process.
Introduction
Chromosomes contain myriad structural and regulatory proteins that ensure the stability, expression, and duplication of the genome. These proteins sometimes form covalent DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs) through the action of ionizing radiation (IR), UV light, endogenous and exogenous reactive aldehydes, and chemotherapeutics such as nitrogen mustards, cisplatins, and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (azaC) (reviewed in Barker et al., 2005; Ide et al., 2011). Because of their bulky nature, DPCs are predicted to inhibit DNA replication and transcription and thereby interfere with genome integrity. Despite its relevance to human health, DPCs repair is poorly understood.
In bacteria, current evidence suggests that small DPCs (less than 11 kDa) are repaired via nucleotide excision repair (NER), whereas larger DPCs are repaired by homologous recombination (HR) (Ide et al., 2011; Nakano et al., 2007). As seen in bacteria, the eukaryotic NER machinery only incises DPCs smaller than 11 kDa (Baker et al., 2007; Nakano et al., 2009; Novakova et al., 2003; Reardon and Sancar, 2006). To account for the repair of larger DPCs, the proteasome is proposed to reduce the protein to a small peptide that is removed by NER (Baker et al., 2007; de Graaf et al., 2009; Quievryn and Zhitkovich, 2000; Reardon and Sancar, 2006; Reardon et al., 2006). However, other reports concluded that the proteasome and NER are not involved in DPC removal (Nakano et al., 2009; Zecevic et al., 2010). In a distinct model, eukaryotic DPCs are processed via HR, presumably during replication (Ide et al., 2011; Nakano et al., 2009). This idea is based on findings that chicken and mammalian cells deficient in the Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway and HR are sensitive to DPC-inducing agents (Nakano et al., 2009; Orta et al., 2013; Ridpath et al., 2007), although the involvement of HR has been challenged (Rosado et al., 2011). In summary, there is currently no clear consensus on how DPCs are repaired, especially in vertebrate.
The effect of DPCs on DNA replication has been investigated in bacteria and using purified DNA polymerases. In vitro, DPCs block synthesis by DNA polymerases (Chvalova et al., 2007; Novakova et al., 2003; Yeo et al., 2014). In E. coli, DNA methyltransferase-based DPCs induce replication fork stalling (Kuo et al., 2007), presumably by inhibiting the replicative DnaB helicase. We previously showed that the eukaryotic replicative helicase, CMG (a complex of Cdc45, MCM2-7 and GINS; (Ilves et al., 2010)), readily bypasses a biotin-streptavidin roadblock on the lagging strand template but not on the leading strand template (Fu et al., 2011). This result indicates that CMG encircles and translocates on the leading strand template in the 3′ to 5′ direction. Similarly, only a DPC on the leading strand template is predicted to act as a helicase barrier (Ide et al., 2011). However, the functional interplay between DNA replication and DPC repair has not been examined in any organism.
Fanconi anemia is a bone marrow failure syndrome caused by defects in 16 ‘FANC’ proteins best known for their roles in DNA interstrand crosslink (ICL) repair (Kottemann and Smogorzewska, 2013). Importantly, FANC-deficient cells are hypersensitive to formaldehyde (Ridpath et al., 2007; Rosado et al., 2011). Moreover, mice deficient in both FANCD2 and the aldehyde-detoxifying enzyme, ALDH2, phenocopy the symptoms of FA (Garaycoechea et al., 2012; Langevin et al., 2011). These results suggest that endogenous aldehydes cause FA, raising the possibility that the FA pathway helps repair DPCs.
Here, we report that Xenopus egg extracts support efficient repair of a chemically-defined DPC and that this repair is strictly coupled to DNA replication. Collision of the replisome with the DPC on the leading strand template stalls the CMG helicase and triggers DPC proteolysis, reducing the DPC to a short peptide. The peptide adduct is then bypassed, first by the CMG helicase and then by the nascent leading strand. A lagging strand DPC is readily bypassed by CMG but must be destroyed for the completion of lagging strand synthesis. Extension of nascent strands past the peptide adduct requires DNA pol ζ. Our results describe a versatile mechanism of DPC repair that avoid replisome disassembly and double-stranded DNA break formation, two major sources of genome instability.
Results
Replication of a plasmid containing a site-specific DPC
To generate a plasmid containing a site-specific DPC (pDPC), the DNA methyltransferase HpaII (M.HpaII, ∼45 kD) was covalently linked to its recognition site, CCGG, via 5-fluoro-2′-deoxycytosine (Chen et al., 1991) (Figure 1A). M.HpaII was crosslinked to the top or bottom strands of the plasmid, generating pDPCTop and pDPCBot (Figures 1A and S1A). pCTRL (the fluorinated plasmid lacking M.HpaII) and pDPCTop were replicated in nucleus-free Xenopus egg extract (Walter et al., 1998). In this system, a single, complete round of plasmid DNA replication can be monitored via incorporation of [α-32P]dATP. Replication of pCTRL quickly yielded supercoiled daughter molecules (Figure 1B, lanes 1-6) (Walter and Newport, 2000). In contrast, replicated pDPCTop first accumulated as a 50:50 ratio of open circular and supercoiled molecules (Figure 1B, lane 9) before gradual conversion into the supercoiled form (Figure 1B, lanes 10-12). Because M.HpaII is linked to one DNA strand, we postulated that replication of the undamaged strand quickly yielded supercoiled products, while the damaged strand yielded gapped molecules containing the DPC (Figure 1D). Consistent with this interpretation, when replicated DNA was not treated with proteinase K (ProtK) before electrophoresis, the gapped molecules were selectively retarded in the gel, migrating as a smear (Figure 1B, compare lanes 20-22 to 8-10). This smear was converted to supercoiled products by 60 minutes (Figure 1B, lanes 23-24), suggesting that the DPC was removed from DNA by the time the gap was filled in (Figure 1D). Indeed, we detected the presence of a gap surrounding the DPC (Figures S1A and S1B). Interestingly, the gap first increased in size due to 5′ to 3′ resection of nascent lagging strands (Räschle et al., 2008), but disappeared by 60 minutes, when the DPC had also been removed (Figures S1A and S1B). These data show that DPCs are efficiently removed from DNA during replication in Xenopus egg extracts.
Figure 1. Replication of a plasmid containing a site-specific DPC.

(A) Schematic of pDPCTop. (B) pCTRL and pDPCTop were replicated in egg extract in the presence of [α-32P]dATP. Samples were treated with Proteinase K (ProtK), as indicated, and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. OC, open circular; SC, supercoiled. (C) pCTRL and pDPCTop were replicated, digested with FspI, and analyzed by 2-D gel electrophoresis. The lower cartoon illustrates relevant DNA intermediates. Arrows, see main text. (D) Model for how replication of pDPC initially yields 50% open circular (OC) and 50% supercoiled (SC) products.
We next examined whether a DPC stalls DNA replication forks. Replicating pCTRL and pDPCTop were analyzed by 2-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis after linearization with Fsp1 (Figure 1C, left cartoon). After 7 minutes, replicated pCTRL migrated mostly as linear molecules (Figure 1C, red arrow). In contrast, most of the pDPCTop migrated at the apex of a double-Y arc, consistent with fork convergence and stalling at the lesion (Figure 1C, blue arrow). By 15 minutes, when most of the gapped plasmids still retained the DPC (Figure 1B, lane 21), virtually all replication intermediates migrated as linear products (Figure 1C, green arrow). We conclude that converging forks transiently stall at the DPC; after resolution of the two daughter molecules, the DPC is removed and the gap is filled in (Figure 1D).
The adducted strand is replicated after the un-adducted strand
Our data suggest that replication of the adducted strand is delayed compared to the un-adducted strand (Figure 1D). To confirm this, we examined the fate of both nascent strands during replication. pCTRL, pDPCTop, and pDPCBot were replicated, and at different times, nascent strands were digested with NcoI and AatII and separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The overhangs created by NcoI and AatII digestion yield top strand extension products (Top, 412 nt) that are 8 nt shorter than bottom strand extension products (Bot, 420 nt), allowing us to differentiate between replication of the damaged and undamaged strands (Figures 2A and 2B). During replication of pCTRL, Top and Bot extension products accumulated simultaneously, as expected (Figure 2C, upper panel, lanes 1-7). In contrast, with pDPCTop, replication of the damaged (Top) strand was delayed by ∼20 minutes relative to the undamaged (Bot) strand (Figure 2C, upper panel, lanes 8-14). The same result was obtained with pDPCBot, only now the damaged (Bot) strand was replicated after the undamaged (Top) strand (Figure 2C, upper panel, lanes 15-21). In conclusion, the undamaged strand is replicated well before the DPC-containing strand.
Figure 2. Multistep bypass of a DPC.

Depiction of nascent leading strands generated after NcoI digestion of DPCTop (A) and pDPCBot (B). Extension products were monitored with NcoI and AatII digestion. Green hexamer, rightward CMG helicase; N, sequencing primer. (C) pCTRL, pDPCTop, and pDPCBot replication intermediates were digested with NcoI and AatII (upper panel) or NcoI (lower panel), and separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel alongside a sequencing ladder. Nascent strands generated by the rightward fork are indicated in brackets. For lagging strand identification, see Figure legend S2C. Red and grey arrows, extension products of the top (Top) and bottom (Bot) strands (upper panel). Black arrows, location of the DPC in pDPCTop and pDPCBot (bottom panel).
Multistep bypass of a DPC
We next addressed why replication of the DPC-containing strand was delayed relative to the un-adducted strand. When two replication forks converge on a DPC (Figures 1C and 1D), one fork encounters the DPC on the leading strand template whereas the converging fork encounters the same lesion on the lagging strand template (Figure 2A). Given that CMG translocates on the leading strand template (Fu et al., 2011), we suspected that the fork that encounters the DPC on the leading strand template will stall. In contrast, the fork that encounters the DPC on the lagging strand template might quickly bypass the lesion, allowing rapid replication of the un-adducted strand. To test these predictions, we monitored the leading strand of the rightward fork as it encountered a DPC on the leading (Figure 2B) or lagging strand templates (Figure 2A). Nascent strands of pCTRL, pDPCTop and pDPCBot were digested with NcoI, which cleaves ∼150 nt to the left of the DPC (Figures 2A and 2B), and products were separated on a denaturing gel. Replication of pCTRL yielded no ∼150 nt products, reflecting the absence of any fork stalling (Figure 2C, lower panel, lanes 1-7). In contrast, when the fork encountered a DPC on the leading strand template in pDPCBot, nascent leading strands stalled ∼29 to 42 nt from the DPC and persisted there for up to 30 minutes (Figure 2C, lanes 15-19, red bracket). We previously determined that when forks encounter an ICL, the leading strand stalls on average 30 nt from the lesion due to steric hindrance by CMG (Fu et al., 2011; Räschle et al., 2008). The slightly increased distance observed here (∼36 nt) is consistent with the helicase being obstructed by a DPC, which is bulkier than an ICL. We conclude that the DPC causes prolonged CMG stalling. After this initial arrest, nascent leading strands were further extended, stalling again 15 to 24 nt from the DPC (Figure 2C, green bracket; see Discussion for the possible source of these intermediates). Next, the leading strands reached the cross-linked DNA base, where they stalled at the 0, +1 and +2 positions (Figure 2C, blue bracket; Figures S2D and S2E show that the 0 position corresponds to the site of the damaged base). Finally, by 60 minutes, the leading strands bypassed the lesion and accumulated as extension products (Figure 2C, upper panel, lanes 20-21, Bot extension product).
When the rightward fork encountered the DPC on the lagging strand template (pDPCTop, Figure 2A), the outcome was different. Nascent leading strands stalled ∼34-47 nt from the DPC, but much more transiently (Figure 2C, lanes 8-9, orange bracket), before being extended past the lesion (Figure 2C, upper panel, lanes 9-10, Bot extension product). Thus, a DPC on the lagging strand template appears to only briefly delay movement of the CMG helicase. When leftward and rightward forks converging on the same DPC were compared by cutting pDPCTop on the right of the DPC with AatII (Figure S2A) or on the left of the DPC with NcoI (Figure 2A), we observed the same result (Figures S2C and 2C). We conclude that the fork whose helicase travels on the undamaged strand stalls transiently (∼5 minutes) before moving past the lesion and completing replication of the undamaged template (Figure S2F, rightward fork). The helicase traveling on the damaged strand stalls for ∼20-30 minutes (“-29 to -42” species), accounting for delayed replication of the damaged strand (Figure S2F, leftward fork).
The DPC is processed into a short peptide adduct
The fact that the DPC-containing strand is ultimately fully replicated suggested that the DPC is degraded or excised. Importantly, we did not detect any incision on the parental DNA in the vicinity of the DPC (Figure S3A, lanes 6-11). We therefore postulated that the DPC might be degraded on DNA (Figure S2F). If this hypothesis is correct, a peptide adduct might remain on the parental DNA after completion of replication. To address this possibility, we replicated pCTRL or pDPCTop in egg extract for 120 minutes in the absence of radiolabeled nucleotides. The DNA was then digested to excise a 165 nt fragment encompassing the DPC (Figure 3A). The DNA was separated on a denaturing gel, and the top strand was visualized by strand-specific Southern blotting. As expected, pCTRL produced a single, 165 nt band (Figure 3B, lanes 1-2). In contrast, replicated pDPCTop generated the same 165 nt band and a ladder of more slowly migrating bands, indicating that adducts of different sizes remained attached to DNA (Figure 3B, lane 4). When the same samples were treated with ProtK prior to electrophoresis, the slower migrating species collapsed into a single, new band that migrated just above the un-adducted strand (Figure 3B, compare lanes 4 and 10). Importantly, ProtK is predicted to leave a 4-residues peptide of M.HpaII crosslinked to DNA. We infer that the ladder of bands observed in lane 4 corresponds to short peptide adducts of different lengths. These results demonstrate that DPC repair involves reducing the DPC to a series of short DNA-peptide adducts.
Figure 3. The DPC is degraded on DNA.

(A) Strategy to detect adducted parental strands. (B) pCTRL and pDPCTop were replicated without [α-32P]dATP and supplemented with Geminin (Gem.) where indicated. DNA was phenol-chloroform extracted, digested with NcoI and NdeI, and separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The top strand was detected by Southern blotting. Where indicated, samples were treated with Proteinase K (ProtK) prior to phenol-chloroform extraction. Plasmids containing an intact DPC were lost in the organic layer during phenol-chloroform extraction. This was the case in all samples where no replication occurred (lanes 3, 5, and 6), suggesting DPC destruction is replication-dependent. (C) Schematic of assay to monitor DPC proteolysis. b, biotin. (D) pDPCTop containing biotinylated M.HpaII was replicated with [α-32P]dATP. Input DNA (lower autoradiograph) and DNA co-precipitated with streptavidin (upper autoradiograph) were treated with ProtK and analyzed on an agarose gel. OC, open circular; SC, supercoiled. (E) DNA recovered in the pull-down (panel D) was quantified and normalized to the input, and compared to the appearance of Top strand extension product, as in lanes 8-14 of Figure 2C (primary data not shown).
To examine the kinetics of DPC removal, we used a C-terminally biotinylated M.HpaII to generate pDPCTop, which we replicated in egg extract containing [α-32P]dATP. At different times, biotinylated M.HpaII was precipitated using streptavidin beads, and the recovery of radiolabeled DNA was monitored on an agarose gel (Figure 3C). Once the DPC is degraded, DNA can no longer co-precipitate with M.HpaII. As shown in Figure 3D, DNA recovery drastically declined by 30 minutes, indicating completion of DPC processing (top panel, lane 4). Notably, only replication intermediates and gapped, monomeric molecules were co-precipitated, consistent with our earlier conclusion that gapped but not supercoiled molecules contain the DPC (Figure 3D, lanes 1-4). Whereas most DPC processing occurred before 30 minutes (Figure 3E, blue graph), nearly all lesion bypass was completed after this time (Figure 3E, red graph). Strikingly, when DNA replication initiation was blocked with Geminin (Wohlschlegel et al., 2000), the DPC persisted, demonstrating that DPC processing requires DNA replication (Figure S3B). Together, these experiments show that replication forks activate DPC proteolysis, followed by replication bypass.
Bypass of the peptide adduct requires DNA pol ζ
Mutations in Rev1 and Rev7 (a subunit of DNA pol ζ) sensitize chicken cells to formaldehyde (Ridpath et al., 2007), suggesting a role for these TLS polymerases in DPC repair. In support of this idea, immunodepletion of Rev7 from egg extract (Figure 4A) inhibited the conversion of gapped to supercoiled molecules during replication of pDPCBot (Figure 4B, lanes 7-12). Rev7 depletion did not affect DPC destruction (data not shown). Importantly, in the absence of Rev7, leading strands accumulated at the 0, +1, and +2 positions, and extension products of the damaged (Bot) strand were greatly diminished (Figure 4C, lanes 7-12). Due to the difficulty of expressing vertebrate DNA pol ζ, we did not attempt to rescue the effect of Rev7 depletion. Instead, we examined the effect of depleting Rev1, which has a close physical and functional interaction with DNA pol ζ (Guo et al., 2003), including in Xenopus egg extracts (M. Budzowska and J.C.W., unpublished results). Rev1 depletion from egg extract precisely mimicked the effect of Rev7 depletion (data not shown). We conclude that following DPC destruction, a complex containing DNA pol ζ and Rev1 extends the leading strand past the peptide adduct.
Figure 4. DNA pol ζ depletion inhibits DPC bypass.

(A) Mock-depleted and Rev7-depleted egg extracts were blotted with Rev7 and MCM7 antibodies. (B) The extracts from (A) were used for replication of pDPCBot as in Figure 1B (+ProtK). (C) Samples from (B) were analyzed as in Figure 2C.
FANCI-FANCD2 is not essential for DPC bypass
Because Fanconi anemia has been linked to reactive aldehydes (Langevin et al., 2011; Rosado et al., 2011), we explored its connection to DPC repair. As shown in Figure S1C, replication of pDPCTop stimulated ubiquitylation of FANCD2. However, immunodepletion of the FANCI-FANCD2 complex from egg extract had no effect on DPC bypass (Figures S4A and S4B), even though it inhibited ICL repair (Figures S4C and S4D; (Knipscheer et al., 2009)). We conclude that FANCI-FANCD2 does not participate in replication-coupled DPC repair.
Single forks efficiently bypass leading and lagging strand DPCs
During replication of pDPC, two replication forks rapidly converge on the DPC. By contrast, in vivo, where the inter-origin distance is large, one fork is generally expected to collide with a DPC well before a second fork arrives. We therefore wanted to know whether two forks are required to repair a DPC or whether one fork suffices. To address this issue, we created pDPC-LTop and pDPC-LBot in which an array of 48 lac operator (lacO) sites is placed ∼260 nt to the left of top or bottom strand DPCs (Figures 5A and 5B). When bound by the lac repressor (LacI), the lacO array blocked fork progression for up to four hours (Figure S5A, lanes 16-30; a fuller description of this fork barrier will be presented elsewhere, J.C.W and J.M.D, in preparation). In this way, the rightward fork could not reach the lesion, whereas the leftward fork was allowed to encounter the DPC on its leading (Figure 5A) or lagging strand templates (Figure 5B). Strikingly, during replication of both plasmids, the DPC was processed into a peptide adduct, even when LacI was present (Figures S5B, lanes 7-8 and S5C, lanes 9-10). As seen in the absence of LacI (Figure 3D), most of the processing in the presence of LacI occurred between 15 and 30 minutes (Figure 5D, lanes 1-4 and 10-13). Therefore, a single replication fork is sufficient to trigger destruction of a DPC on either template strand.
Figure 5. DPC bypass by a single replication fork.

Depiction of nascent leading strand intermediates generated when DPC-LTop (A) or pDPC-LBot (B) are replicated in the presence of LacI (blue spheres) and then digested with AatII. Digestion with FspI and AatII yields Top extension products that are 4 nt shorter than Bot extension products. In the presence of LacI, Top extension products correspond to leading strands, and Bot extension products to lagging strands. (C) pCTRL-L, pDPC-LTop, and pDPC-LBot were replicated in the presence of buffer or LacI. Samples were digested with FspI and AatII (upper panel) or AatII alone (lower panel), and analyzed on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Colored brackets, nascent strands generated by the leftward fork (lower panel). Arrows, extension products of the Top and Bot strands (upper panel). (D) pDPC-LTop and pDPC-LBot prepared with biotinylated M.HpaII were replicated in the presence of LacI. Samples were analyzed as in Figure 3D. (E) The pull-down recovery of pDPC-LTop in (D) was graphed alongside the -29 to -42 leading strand arrest quantified from Figure S5D. Values were normalized to the maximum peak value. (F) The pull-down recovery of pDPC-LBot in (D) was graphed alongside the -34 to -47 leading strand arrest quantified from Figure S5D.
We next examined the kinetics with which a single fork bypasses leading and lagging strand DPCs. To examine a leading strand DPC, pDPC-LTop was replicated in the presence of LacI, and replication samples were digested with FspI and AatII to distinguish between leading and lagging strand extension products (Figure 5A). As shown in Figure 5C (upper panel, lanes 22-27), although synthesis of the leading strand was delayed relative to the lagging strand, the leading strand was eventually extended past the lesion, as seen for the convergent fork control (Figure 5C, upper panel, lanes 4-9). Conversely, when the DPC was on the lagging strand template in pDPC-LBot (Figure 5B), the leading strand was synthesized rapidly whereas the lagging strand was delayed but ultimately also fully matured (Figure 5C, upper panel, lanes 28-33), as observed for converging forks (Figure 5C, upper panel, lanes 10-15). Thus, single forks efficiently bypass DPCs.
Correlation of CMG bypass with DPC proteolysis
To examine how a single fork bypasses a leading strand DPC, replicating pDPC-LTop was digested with AatII alone (Figure 5A). Upon encounter of the fork with the DPC, the leading strands stalled, approached, and bypassed the lesion (Figure 5C, lanes 22-27, red, green and blue brackets) as seen during fork convergence (Figures 5C, lanes 4-9 and S2C), albeit with slightly slower kinetics. Strikingly, even when there was no converging fork, a significant portion of lagging strands had fully matured between 20 and 30 minutes, while nearly none of the leading strands had extended past the DPC (Figure 5C, upper panel, lanes 23-24). These data can be explained if the CMG helicase bypassed the lesion, thereby allowing the lagging strand to continue growing, even as the leading strand remained stalled at the crosslink. Importantly, the disappearance of CMG's footprint (-29 to -42 bands) (Figure 5C, lanes 22-27, red bracket) closely followed the kinetics of destruction of the DPC (Figures 5D, lanes 1-9 and 5E). These observations suggest that CMG bypasses a leading strand DPC once the DPC is processed into a peptide adduct, allowing growth of the lagging strand past the lesion.
To investigate how a single fork bypasses a lagging strand DPC, we examined pDPC-LBot (Figure 5B). As seen for convergent forks (Figures 5C, lanes 10-11 and S2C), nascent leading strands of the leftward fork paused ∼34 to 47 nt from the lesion (Figure 5C, lanes 28-29, orange bracket). By 20 minutes, most of the nascent leading strands had bypassed the lesion and accumulated as fully replicated products (Figure 5C, upper panel, lane 29). At that time, the majority of DPCs were not degraded (Figure 5D, lane 12). In fact, disappearance of the CMG footprint (-34 to -47 bands) (Figure 5C, lanes 28-33, orange bracket) preceded DPC destruction by ∼5 minutes (Figures 5D, lanes 10-18 and 5F). We conclude that when CMG encounters a DPC on the lagging strand template, it stalls transiently but quickly unwinds past the lesion. Thus, helicase bypass appears to occur before the DPC is destroyed by proteolysis.
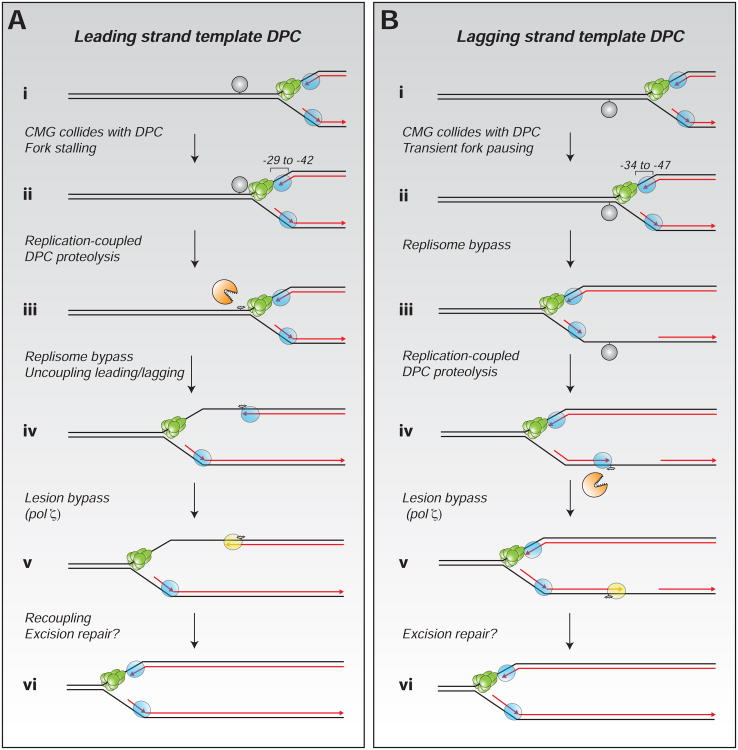
Our data thus far indicate that a single fork is able to bypass leading and lagging strand DPCs (Figures 7A and 7B). In the former case, once the DPC is reduced to a peptide adduct, the helicase and the lagging strand can progress while the leading strand stalls at the peptide, resulting in transient uncoupling of leading and lagging strand synthesis (Figure 7A). For lagging strand DPCs, the helicase and leading strand appear to bypass the DPC independently of its destruction (Figure 7B).
Figure 7. Model for DPC repair in Xenopus egg extracts.
Repair of a DPC on the leading (A) or lagging strand templates (B). See Discussion for details. Black lines, parental DNA; red lines, nascent strands; in green, CMG helicase; in blue, replicative polymerases; in yellow, TLS polymerase; in grey, DPC.
DPC processing is essential for efficient lesion bypass
Our model predicts that failure to destroy a DPC on the leading strand template should inhibit CMG bypass. In contrast, blocking the destruction of a DPC on the lagging strand template should not significantly delay CMG bypass, but rather block completion of the lagging strand. To test these predictions, we sought to inhibit the destruction of M.HpaII by perturbing the ubiquitin system. Two different drugs that inhibited the proteasome (Figures S6A and S6C, top panels) had no evident effect on DPC repair (Figures S6B and S6D). As an alternative approach, we added ubiquitin-vinyl-sulfone (Ub-VS), a deubiquitylating enzyme (DUB) inhibitor that blocks ubiquitin recycling and thereby leads to the depletion of free ubiquitin (Figure S6E) (Dimova et al., 2012). pDPC-LTop and pDPC-LBot were replicated in the presence of LacI in egg extracts that were pre-incubated with buffer, Ub-VS, or Ub-VS and free ubiquitin. Although Ub-VS treatment did not inhibit DNA replication, it dramatically inhibited M.HpaII destruction on both leading and lagging strand templates (Figure 6A, lanes 7-12 and 25-30). Addition of free ubiquitin restored M.HpaII destruction (Figure 6A, lanes 13-18 and 31-36). Therefore, M.HpaII destruction requires the presence of free ubiquitin but apparently not DUB or proteasome activity.
Figure 6. DPC processing is essential for efficient replicative DPC bypass.

(A) pDPC-LTop and pDPC-LBot were replicated in the presence of LacI and buffer (+Buffer), 13 μM Ub-VS (+Ub-VS) or 13 μM Ub-VS and 80 μM ubiquitin (+Ub-VS +Ub.). Samples were analyzed as in Figure 3D. (B) Samples from (A) were analyzed as in Figure 5C. (C) Quantification of the -29 to -42 species of pDPC-LTop from panel (B). Values were normalized to the maximum peak value of the buffer control. (D) -34 to -47 species of pDPC-LBot from panel (B) were quantified as in (C).
To address how lesion bypass is affected when the DPC is not destroyed, nascent strands from each reaction were analyzed following AatII digestion (as depicted in Figures 5A and B). When a leading strand DPC was stabilized with Ub-VS, the disappearance of the -29 to -42 nt leading strand products was delayed for up to 90 minutes, indicating prolonged CMG stalling at the DPC (Figures 6B, compare lanes 1-6 and 7-12, red bracket and 6C). This effect was largely reversed by co-addition of free ubiquitin (Figures 6B, lanes 13-18, red bracket and 6C). Thus, efficient CMG bypass of a leading strand template DPC requires the proteolytic processing of the DPC into a peptide adduct. Although CMG bypass appeared to be severely inhibited, leading strands still approached the lesion over time (Figure 6B, lanes 7-12, blue bracket). By three hours, virtually all of the nascent leading strands had advanced from the -29 position to the cross-linked base, accumulating at the 0 position (Figure 6B, lane 12, blue bracket), even though the DPC was still intact (Figure 6A, lane 12). This approach of the leading strands to the lesion correlated with full maturation of lagging strands past the DPC (Figure 6B, upper panel, lanes 7-12). This surprising observation suggests that a replication fork can bypass an intact DPC on the leading strand template, albeit with slower kinetics than when the DPC is degraded into a peptide. We ruled out the possibility that lagging strand maturation was due to origin firing between the replication fork barrier and the DPC (Figures S6F and S6H). In the Discussion, we propose models that can explain replication fork bypass of an intact DPC.
In further agreement with our predictions, stabilizing the lagging strand DPC did not significantly prolong CMG stalling at the lesion (Figures 6B, lanes 19-30, orange bracket and 6D). This result implies that once the replication fork has moved past the lesion, a growing Okazaki fragment collides with the intact DPC. To examine the fate of this maturing Okazaki fragment, we digested replication samples to the left of the DPC with BssHII (Figure S6G). As shown in Figure S6H, nascent lagging strands approached the 0 position with similar kinetics in the presence and absence of Ub-VS (compare lanes 25-30 with lanes 19-24), consistent with unhindered bypass of the intact DPC by CMG. Interestingly, in the presence of Ub-VS, lagging strands persisted at the 0 position for up to three hours and never advanced to the +1 and +2 positions (Figure S6H, lanes 25-30, 0 position). The same phenomenon was observed when leading strands collided with a stable DPC (Figure 6B, lanes 7-12). Together, these data suggest that a DNA polymerase is able to approach the base to which the intact DPC is attached, and insert a nucleotide across from it. However, advance to the +1 and +2 positions might be impossible due to steric hindrance by the DPC. Consistent with this view, TLS polymerases can bypass short peptide DNA-adducts in vitro, but not larger DPCs (Yamanaka et al., 2010; Yeo et al., 2014). Alternatively, or in addition, ubiquitin-depletion might inhibit recruitment of TLS polymerases (Goodman and Woodgate, 2013). We conclude that DPC degradation is dependent on ubiquitin and that a persistent DPC on the leading but not the lagging strand inhibits progression of the replication fork.
Discussion
Here, we show that Xenopus egg extracts support DNA-protein crosslink (DPC) repair. Our system involves a chemically defined and sequence-specific DPC, and repair is measured directly, by conversion of the DPC to a peptide adduct and generation of supercoiled DNA products. Using this approach, we show that DPC repair requires DNA replication, and we elucidate how the two processes are coupled. A leading strand DPC must be degraded to a peptide to allow efficient bypass of the CMG helicase, consistent with CMG translocation on the leading strand template (Figure 7A, i-iv). Following CMG bypass of a leading strand DPC, the growing leading strand is extended to the adducted base, where it stalls (Figure 7A, iv). Concurrently, the lagging strand continues growing past the DPC, providing a clear instance of replicative uncoupling in vertebrates (Figure 7A, iv-v). Finally, DNA pol z allows the leading strand to bypass the peptide adduct (Figure 7A, v). In contrast, a DPC on the lagging strand template only transiently stalls the replisome (Figure 7B, i-iii), but it too is degraded to a peptide, allowing Okazaki fragment bypass (Figure 7B, iii-v). Although egg extracts do not support removal of the peptide adduct, this reaction might occur in vivo via excision repair (Figures 7A and 7B, vi). Our results describe the first comprehensive model of replication-coupled DPC repair, implications of which are discussed below.
Replication-dependent proteolysis of a DPC
It has been postulated that replication fork collision with DPCs provides a sensing mechanism that triggers DPC repair (Kuo et al., 2007; Nakano et al., 2007; Reardon et al., 2006). Our experiments provide the first direct support for this model as they establish the existence of a replication-dependent protease that reduces DPCs to small DNA-peptide adducts. Notably, inhibition of proteasome activity in egg extracts had no significant effect on DPC repair, suggesting this process is proteasome-independent (although we cannot formally rule out a role for residual proteasome activity). In contrast, ubiquitin depletion inhibited DPC repair. The role of ubiquitin is presently unclear, but we speculate that DPCs might be ubiquitylated prior to destruction by the replication-dependent protease. A potential candidate for this protease is the p97 cofactor Spartan/DVC1, which has homology to yeast Wss1 (Mosbech et al., 2012). Wss1 was recently shown to remove trapped topoisomerase I complexes and to confer resistance to formaldehyde, probably by removing DPCs (Stingele et al., 2014). Intriguingly, Wss1 destroys a wide variety of different DNA binding proteins in a DNA-dependent manner. Analogously, the replication-dependent protease in egg extract appears to employ a general recognition strategy, given its ability to degrade a bacterial methyltransferase. These parallels raise the possibility that Spartan/DVC1 functions in replication-dependent DPC repair. However, we have not been able to generate useful Spartan/DVC1 antibodies to test this idea.
Two mechanisms of leading strand DPC bypass?
Our data suggest that a DNA replication fork can bypass a DPC on the leading strand template by at least two mechanisms. In the primary mechanism, DPC proteolysis allows CMG to pass over the lesion (now a peptide) and continue unwinding DNA. In support of this model, the disappearance of CMG's footprint (-29 to -42 arrest) was closely correlated with DPC degradation (Figure 5E). In addition, when DPC destruction was blocked by Ub-VS, the CMG footprint persisted for up to 2 hours (Figure 6C). Consistent with this mechanism, a purified MCM helicase can translocate past ∼30 amino acid but not ∼45 amino acid peptide adducts (Nakano et al., 2013). Interestingly, after the -29 to -42 CMG footprint disappears, a new population appears that is stalled at the -11 to -24 positions (Figures 6B, green bracket). We speculate that these species might reflect slow unwinding by CMG of the DNA containing the peptide adduct.
Strikingly, in the presence of Ub-VS, all of the leading strands ultimately approached the adducted base by 3 hours, and lagging strands fully matured past the lesion (Figure 6B). Therefore, even when DPC proteolysis is blocked, the fork can eventually bypass the lesion. We can imagine at least two mechanisms for this secondary, proteolysis-independent DPC bypass. First, CMG unwinds past the intact DPC by transiently opening its ring (Figure S7A), as proposed for the viral T antigen helicase (Yardimci et al., 2012). Alternatively, a 5′ to 3′ DNA helicase might load onto the lagging strand template and translocate past the DPC (Figure S7B). Interestingly, the -11 to -24 leading strand species normally seen during DPC bypass are absent in the presence of Ub-VS (Figure 6B, compare lanes 1-6 and 7-12, green bracket). One interpretation is that CMG ring-opening allows the helicase to pass over the DPC without stalling. Alternatively, the 5′ to 3′ helicase invoked above might displace CMG as it unwinds past the DPC (Figure S7B). Whatever the precise details, proteolysis-dependent and proteolysis-independent mechanisms of DPC bypass appear to be mechanistically distinct.
The mechanism of TLS during DPC repair
We show that during bypass of a leading or lagging strand DPC, the nascent strand does not arrest immediately before the adducted base (-1 position). Instead, 0, +1, and +2 products accumulate. This finding demonstrates that the insertion of a nucleotide across from the adducted base (by a replicative or TLS polymerase) is not rate-limiting. In our DPC substrate, the crosslinked cytosine is predicted to be flipped out of the double helix, generating an abasic-like site (Klimasauskas et al., 1994). Importantly, both pol ε and pol δ are able to insert nucleotides opposite abasic sites (Haracska et al., 2001; Sabouri and Johansson, 2009). Pol ε and pol δ might also be able to extend the leading strand to the +1 and +2 positions. Once the adduct blocks further synthesis, the nascent strand is extended past the lesion by a complex containing DNA pol ζ and Rev1. In yeast cells lacking Wss1, Rev3-dependent mutagenesis is reduced (Stingele et al., 2014), consistent with our observation that DPC destruction and TLS are coupled. Given the heterogeneity in the chemistry of DPCs, it is likely that different TLS polymerases will be employed to bypass different types of DPCs.
Implications for Fanconi anemia
The synthetic sickness between FANC mutations and mutations affecting reactive aldehyde metabolism suggested that the biological function of the FA pathway might be to repair DPCs. We found that unlike ICL repair, DPC repair does not require FANCI-FANCD2. In hindsight, this observation is not unexpected. We showed previously that FANCI-FANCD2 promotes incision of replication forks that have stalled at an ICL, leading to ICL unhooking and lesion bypass (Klein Douwel et al.; Knipscheer et al., 2009; Zhang and Walter, 2014) (Figure S4E). In contrast, the DPC repair pathway we describe here does not involve the incision of parental DNA strands, obviating the need for FANCI-FANCD2. A reasonable conclusion is that ICLs are in fact the DNA lesions that drive FA, as widely believed. Consistent with this view, formaldehyde is known to cause ICLs (Huang and Hopkins, 1993). However, we cannot rule out the possibility that the repair of some aldehyde-induced DPCs requires incisions and therefore involves the FA pathway.
Proteolytic versus HR repair of DPCs
Some mammalian studies find a role for HR in DPC repair (Nakano et al., 2009; Ridpath et al., 2007). In yeast, Wss1 and Rad52 exhibit non-epistasis with regard to formaldehyde sensitivity, suggesting that DPC proteolysis and HR represent distinct means of removing DPCs in S phase (Stingele et al., 2014). Consistent with this view, our experiments show that replication-dependent DPC repair in vertebrates proceeds without the formation of double-stranded DNA breaks, which pose a major threat to genome stability. We propose that replication-dependent proteolysis represents the preferred pathway of DPC repair and that HR participates in the bypass of rare DPCs that cannot be degraded.
Experimental Procedures
Preparation of DNA constructs
To generate pDPCTop and pDPCBot, we cloned 5′-CCTCAGCATCCGGTACCTCAGC-3′ between the EcoRI and NdeI sites of pUC.HSO (Wold et al., 1987) to generate pHY10 (Yardimci et al., 2012). We then inserted a 5-fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine (Cfluo)-modified oligonucleotide (Biosynthesis, Lewisville, TX) into either strand. pHY10 was either nicked with Nt.BbvCI and annealed/ligated to 5′-TCAGCATCCfluoGGTACC-3′ to modify the top strand, or nicked with Nb.BbvCI and annealed/ligated to 5′-TGAGGTACCfluoGGATGC-3′ to modify the bottom strand. Modified DNA was gel-purified and mixed with M.HpaII-His6 or M.HpaII-biotin-His6 in reaction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM EDTA) supplemented with 100 μM S-adenosylmethionine (NEB, Ipswich, MA) for 12 hours at 37 °C. To make pCTRL, the plasmid containing the fluorinated cytosine on the top strand was used in an identical reaction without M.HpaII.
Protein expression and purification
To purify M.HpaII-biotin-His6 (biotinylated M.HpaII), pHpaII-Avitag-His6 and an expression plasmid for BirA biotin ligase, pBirAcm (Avidity, Denver, CO), were co-transformed into T7 Express Competent E. coli (NEB). During induction, the culture was supplemented with biotin and His-tagged, biotinylated M.HpaII was purified over Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). M.HpaII-His6 (unbiotinylated M.HpaII) was purified as described above omitting the addition of biotin during induction.
Xenopus egg extracts and replication
For DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts (Lebofsky et al., 2009; Walter et al., 1998), plasmid DNA was incubated in a high-speed supernatant (HSS) of egg cytoplasm for 30 min (7.5 ng/μl final concentration) prior to addition of 2 volumes of nucleoplasmic egg extract (NPE).
Nascent strand analysis
Nascent strand analysis was performed as previously described (Räschle et al., 2008). Briefly, purified DNA was digested with the indicated restriction enzymes followed by addition of 0.5 volumes of Gel Loading Dye II (Denaturing PAGE) (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA). DNA fragments were subsequently separated on 5% or 7% denaturing polyacrylamide gels, transferred to filter paper, dried, and visualized using a phosphorimager. The sequencing ladders were generated with the indicated primers using Cycle Sequencing kit (USB Corporation, Cleveland, OH, USA). Radioactive signal was quantified using ImageJ (NIH, USA).
Primer N: 5′-CATGGGGCGGAGAATGGG-3′;
Primer A: 5′-CTAAGAAACCATTATTATCATGACATTAACC-3′.
Antibodies
The following antibodies were described previously: FANCD2 (Räschle et al., 2008), MCM7 (Walter and Newport, 2000), Rev7 (Räschle et al., 2008) and CDT1 (Arias and Walter, 2005). p-Chk1 (S345) and ubiquitin antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling (#2341) (Danvers, MA, USA) and Santa Cruz (SC-8017), respectively. FANCI antibody was raised against full length FANCI expressed in insect cells and was shown to recognize and immunoprecipitate the FANCI protein in Xenopus egg extracts (data not shown).
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Cell-free repair of a DNA-protein crosslink (DPC)
DPC repair is coupled to DNA replication
Replication triggers DPC proteolysis, yielding a DNA-peptide adduct
Bypass of the peptide adduct requires DNA pol ζ
Acknowledgments
We thank O.D. Schärer, P.M. Burgers, R. Scully, N. Rhind, N. Tretyakova, and the members of the Walter laboratory for feedback on the manuscript. We thank K.J Marians, T. Bernhardt, B. Kay, and New England Biolabs for plasmids, Thomas Graham for Ulp1 protease and help with the purification of LacI, and Jieqiong Zhang for generation of the FANCI antibody. J.P.D was supported by the Department of Defense Bone Marrow Research Program Postdoctoral Traineeship Award W81XWH-13-1-0049. J.C.W was supported by NIH grant GM62267. J.C.W is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
Author Contributions: J.M.D generated and characterized the lac repressor replication fork barrier; H.Y purified M.HpaII-biotin; J.P.D and J.C.W designed and analyzed the experiments; J.P.D performed the experiments; J.P.D and J.C.W prepared the manuscript.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- Arias EE, Walter JC. Replication-dependent destruction of Cdt1 limits DNA replication to a single round per cell cycle in Xenopus egg extracts. Genes Dev. 2005;19:114–126. doi: 10.1101/gad.1255805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker DJ, Wuenschell G, Xia L, Termini J, Bates SE, Riggs AD, O'Connor TR. Nucleotide Excision Repair Eliminates Unique DNA-Protein Cross-links from Mammalian Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007;282:22592–22604. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702856200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker S, Weinfeld M, Murray D. DNA-protein crosslinks: their induction, repair, and biological consequences. Mutat Res. 2005;589:111–135. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2004.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L, MacMillan AM, Chang W, Ezaz-Nikpay K, Lane WS, Verdine GL. Direct identification of the active-site nucleophile in a DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1991;30:11018–11025. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chvalova K, Brabec V, Kasparkova J. Mechanism of the formation of DNA-protein cross-links by antitumor cisplatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:1812–1821. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf B, Clore A, McCullough AK. Cellular pathways for DNA repair and damage tolerance of formaldehyde-induced DNA-protein crosslinks. DNA Repair. 2009;8:1207–1214. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimova NV, Hathaway NA, Lee BH, Kirkpatrick DS, Berkowitz ML, Gygi SP, Finley D, King RW. APC/C-mediated multiple monoubiquitylation provides an alternative degradation signal for cyclin B1. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:168–176. doi: 10.1038/ncb2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu YV, Yardimci H, Long DT, Guainazzi A, Bermudez VP, Hurwitz J, van Oijen A, Schärer OD, Walter JC, Ho247 TV. Selective Bypass of a Lagging Strand Roadblock by the Eukaryotic Replicative DNA Helicase. Cell. 2011;146:931–941. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garaycoechea JI, Crossan GP, Langevin F, Daly M, Arends MJ, Patel KJ. Genotoxic consequences of endogenous aldehydes on mouse haematopoietic stem cell function. Nature. 2012;489:571–575. doi: 10.1038/nature11368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman MF, Woodgate R. Translesion DNA polymerases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a010363. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo C, Fischhaber PL, Luk-Paszyc MJ, Masuda Y, Zhou J, Kamiya K, Kisker C, Friedberg EC. Mouse Rev1 protein interacts with multiple DNA polymerases involved in translesion DNA synthesis. The EMBO Journal. 2003;22:6621–6630. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haracska L, Unk I, Johnson RE, Johansson E, Burgers PM, Prakash S, Prakash L. Roles of yeast DNA polymerases delta and zeta and of Rev1 in the bypass of abasic sites. Genes Dev. 2001;15:945–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.882301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H, Hopkins PB. DNA interstrand cross-linking by formaldehyde: nucleotide sequence preference and covalent structure of the predominant cross-link formed in synthetic oligonucleotides. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115:9402–9408. [Google Scholar]
- Ide H, Shoulkamy MI, Nakano T, Miyamoto-Matsubara M, Salem AMH. Repair and biochemical effects of DNA-protein crosslinks. Mutat Res. 2011;711:113–122. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilves I, Petojevic T, Pesavento JJ, Botchan MR. Activation of the MCM2-7 helicase by association with Cdc45 and GINS proteins. Mol Cell. 2010;37:247–258. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein Douwel D, Boonen RACM, Long DT, Szypowska AA, Räschle M, Walter JC, Knipscheer P. XPF-ERCC1 Acts in Unhooking DNA Interstrand Crosslinks in Cooperation with FANCD2 and FANCP/SLX4. Mol Cell. 54:460–471. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimasauskas S, Kumar S, Roberts RJ, Cheng X. HhaI methyltransferase flips its target base out of the DNA helix. Cell. 1994;76:357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipscheer P, Raschle M, Smogorzewska A, Enoiu M, Ho TV, Scharer OD, Elledge SJ, Walter JC. The Fanconi Anemia Pathway Promotes Replication-Dependent DNA Interstrand Cross-Link Repair. Science. 2009;326:1698–1701. doi: 10.1126/science.1182372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kottemann MC, Smogorzewska A. Fanconi anaemia and the repair of Watson and Crick DNA crosslinks. Nature. 2013;493:356–363. doi: 10.1038/nature11863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo HK, Griffith JD, Kreuzer KN. 5-Azacytidine Induced Methyltransferase-DNA Adducts Block DNA Replication In vivo. Cancer Research. 2007;67:8248–8254. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langevin F, Crossan GP, Rosado IV, Arends MJ, Patel KJ. Fancd2 counteracts the toxic effects of naturally produced aldehydes in mice. Nature. 2011;475:53–58. doi: 10.1038/nature10192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebofsky R, Takahashi T, Walter JC. DNA replication in nucleus-free Xenopus egg extracts. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;521:229–252. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-815-7_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbech A, Gibbs-Seymour I, Kagias K, Thorslund T, Beli P, Povlsen L, Nielsen SV, Smedegaard S, Sedgwick G, Lukas C, et al. DVC1 (C1orf124) is a DNA damage– targeting p97 adaptor that promotes ubiquitin-dependent responses to replication blocks. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2012;19:1084–1092. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T, Katafuchi A, Matsubara M, Terato H, Tsuboi T, Masuda T, Tatsumoto T, Pack SP, Makino K, Croteau DL, et al. Homologous Recombination but Not Nucleotide Excision Repair Plays a Pivotal Role in Tolerance of DNA-Protein Cross-links in Mammalian Cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:27065–27076. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.019174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T, Miyamoto-Matsubara M, Shoulkamy MI, Salem AMH, Pack SP, Ishimi Y, Ide H. Translocation and Stability of Replicative DNA Helicases upon Encountering DNA-Protein Cross-links. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2013;288:4649–4658. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.419358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T, Morishita S, Katafuchi A, Matsubara M, Horikawa Y, Terato H, Salem AMH, Izumi S, Pack SP, Makino K, et al. Nucleotide Excision Repair and Homologous Recombination Systems Commit Differentially to the Repair of DNA-Protein Crosslinks. Mol Cell. 2007;28:147–158. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novakova O, Kasparkova J, Malina J, Natile G, Brabec V. DNA-protein cross-linking by trans-[PtCl(2)(E-iminoether)(2)]. A concept for activation of the trans geometry in platinum antitumor complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:6450–6460. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orta ML, Calderon-Montano JM, Dominguez I, Pastor N, Burgos-Moron E, Lopez-Lazaro M, Cortes F, Mateos S, Helleday T. 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine causes replication lesions that require Fanconi anemia-dependent homologous recombination for repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:5827–5836. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quievryn G, Zhitkovich A. Loss of DNA-protein crosslinks from formaldehyde-exposed cells occurs through spontaneous hydrolysis and an active repair process linked to proteosome function. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:1573–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räschle M, Knipscheer P, Enoiu M, Angelov T, Sun J, Griffith JD, Ellenberger TE, Schärer OD, Walter JC. Mechanism of Replication-Coupled DNA Interstrand Crosslink Repair. Cell. 2008;134:969–980. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon JT, Sancar A. Repair of DNA-polypeptide crosslinks by human excision nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:4056–4061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600538103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon JT, Cheng Y, Sancar A. Repair of DNA-protein cross-links in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:1366–1370. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.13.2892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridpath JR, Nakamura A, Tano K, Luke AM, Sonoda E, Arakawa H, Buerstedde JM, Gillespie DAF, Sale JE, Yamazoe M, et al. Cells Deficient in the FANC/BRCA Pathway Are Hypersensitive to Plasma Levels of Formaldehyde. Cancer Research. 2007;67:11117–11122. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosado IV, Langevin F, Crossan GP, Takata M, Patel KJ. Formaldehyde catabolism is essential in cells deficient for the Fanconi anemia DNA-repair pathway. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2011;18:1432–1434. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabouri N, Johansson E. Translesion synthesis of abasic sites by yeast DNA polymerase epsilon. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009;284:31555–31563. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.043927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingele J, Schwarz MS, Bloemeke N, Wolf PG, Jentsch S. A DNA-Dependent Protease Involved in DNA-Protein Crosslink Repair. Cell. 2014;158:327–338. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J, Newport J. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication: origin unwinding and sequential chromatin association of Cdc45, RPA, and DNA polymerase alpha. Mol Cell. 2000;5:617–627. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J, Sun L, Newport J. Regulated chromosomal DNA replication in the absence of a nucleus. Mol Cell. 1998;1:519–529. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlschlegel JA, Dwyer BT, Dhar SK, Cvetic C, Walter JC, Dutta A. Inhibition of eukaryotic DNA replication by geminin binding to Cdt1. Science. 2000;290:2309–2312. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold MS, Li JJ, Kelly TJ. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka K, Minko IG, Takata KI, Kolbanovskiy A, Kozekov ID, Wood RD, Rizzo CJ, Lloyd RS. Novel Enzymatic Function of DNA Polymerase ν in Translesion DNA Synthesis Past Major Groove DNA-Peptide and DNA-DNA Cross-Links. Chem Res Toxicol. 2010;23:689–695. doi: 10.1021/tx900449u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardimci H, Wang X, Loveland AB, Tappin I, Rudner DZ, Hurwitz J, van Oijen AM, Walter JC. Bypass of a protein barrier by a replicative DNA helicase. Nature. 2012;492:205–209. doi: 10.1038/nature11730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeo JE, Wickramaratne S, Khatwani S, Wang YC, Vervacke J, Distefano MD, Tretyakova NY. Synthesis of Site-Specific DNA-Protein Conjugates and Their Effects on DNA Replication. ACS Chem Biol. 2014 doi: 10.1021/cb5001795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zecevic A, Hagan E, Reynolds M, Poage G, Johnston T, Zhitkovich A. XPA impacts formation but not proteasome-sensitive repair of DNA-protein cross-links induced by chromate. Mutagenesis. 2010;25:381–388. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geq017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Walter JC. Mechanism and regulation of incisions during DNA interstrand cross-link repair. DNA Repair. 2014;19:135–142. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.