Abstract
Rhamnomannans from several isolates of Sporothrix schenckii and Ceratocystis species were compared. No major differences emerged in the analysis of the carbohydrate composition of polysaccharides from either species. Methylation analysis for the identification of the glycosidic linkages present in the polysaccharides showed that they all were very similar with minor differences being observed among strains and between polysaccharides obtained at 25 and 37 C. Partially methylated derivatives were identified by gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Their proportions suggest that polysaccharides from S. schenckii and C. stenoceras have a general structure similar to that of C. ulmi: a (1 → 6)-linked α-d-mannopyranosyl main chain substituted in the 3-positions by α-l-rhamnopyranosyl and in many cases by α-l-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)-l-rhamnopyranosyl side chains. Differences among polysaccharides resided in the proportions of the dirhamnosyl side chains and of 4-O-substituted and 2, 4-di-O-substituted mannose units. Increased proportions of dirhamnosyl side chains were observed in the polysaccharides from S. schenckii strains and from a pathogenic variant of C. stenoceras grown at 25 C. Proton magnetic resonance spectra (H-1 region) of the rhamnomannans showed that S. schenckii strains could be placed in two different groups similar but not identical to any Ceratocystis species. These spectra were very close to those of the polysaccharides from the C. clavata and C. ambrosia groups of Ceratocystis species.
Full text
PDF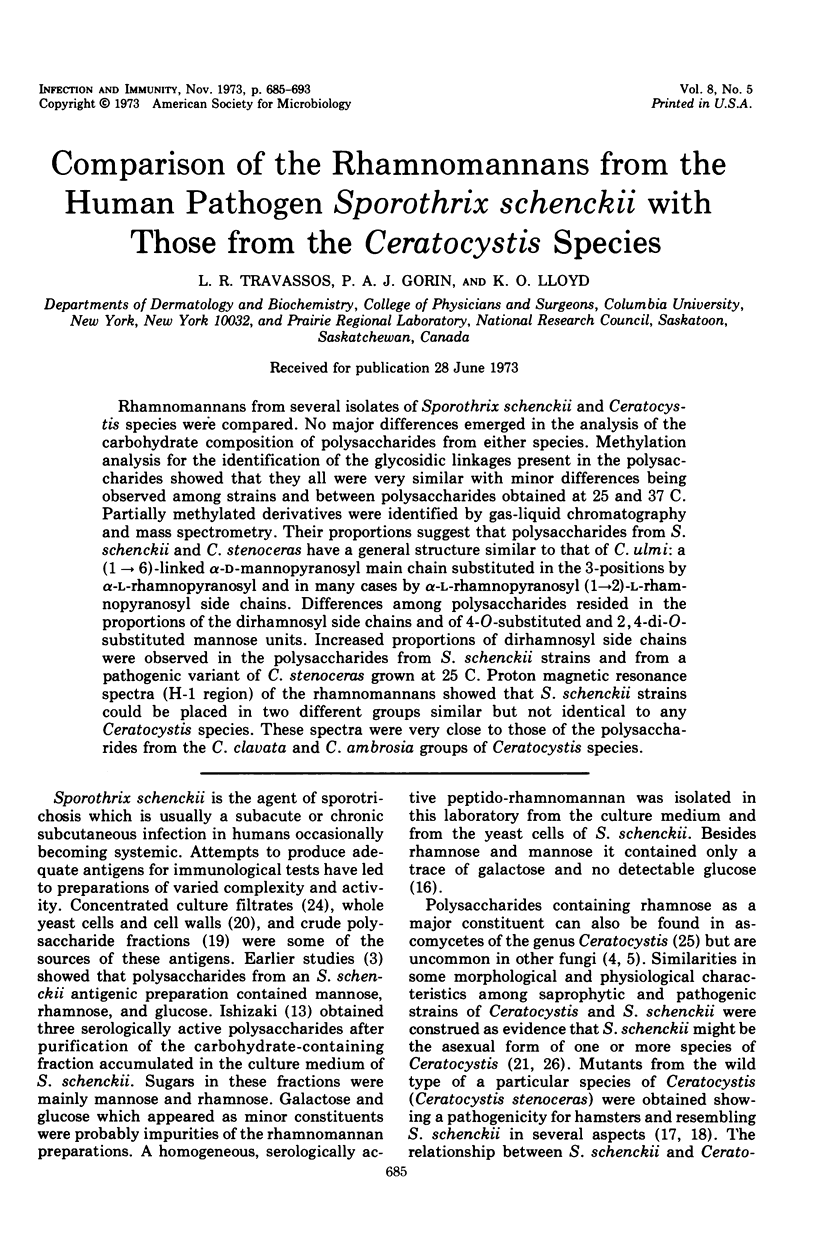




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrieu S., Biguet J., Massamba S. Etude immunologique comparee de Sporothrix schenckii et des souches saprophytes voisines. Sabouraudia. 1971 Nov;9(3):206–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartnicki-Garcia S. Cell wall chemistry, morphogenesis, and taxonomy of fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:87–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin P. A., Spencer J. F. Structural chemistry of fungal polysaccharides. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1968;23:367–417. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanetsuna F., Carbonell L. M., Azuma I., Yamamura Y. Biochemical studies on the thermal dimorphism of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):208–218. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.208-218.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Bitoon M. A. Isolation and purification of a peptido-rhamnomannan from the yeast form of Sporothrix schenckii. Structural and immunochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):663–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O. Isolation, characterization, and partial structure of peptido galactomannans from the yeast form of Cladosporium werneckii. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3446–3453. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariat F. Adaptation de Ceratocystis à la vie parasitaire chez l'animal--étude de l'aquisition d'un pouvoir pathogene comparable à celui de Sporothrix schenckii. Sabouraudia. 1971 Nov;9(3):191–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicot J., Mariat F. Caractères morphologique et position systématique de Sporothrix schenckii, agent de la sporotrichose humaine. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1973 Jan 31;49(1):53–65. doi: 10.1007/BF02057447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. S., Jr Biologic properties of skin test antigens of yeast form Sporotrichum schenckii. J Infect Dis. 1968 Apr;118(2):173–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIFFMAN G., KABAT E. A., THOMPSON W. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON BLOOD GROUPS. XXX. CLEAVAGE OF A, B, AND H BLOOD-GROUP SUBSTANCES BY ALKALI. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:113–120. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDAU J. D., Jr, LAMAR L. M., HAIRSTON M. A., Jr CUTANEOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY TO SPOROTRICHIN IN LOUISIANA. JAMA. 1964 Apr 27;188:371–373. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060300033007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. J. A comparison of some Ceratocystis species with Sporothrix schenckii. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1970 Dec 29;42(3):233–240. doi: 10.1007/BF02051951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



