Abstract
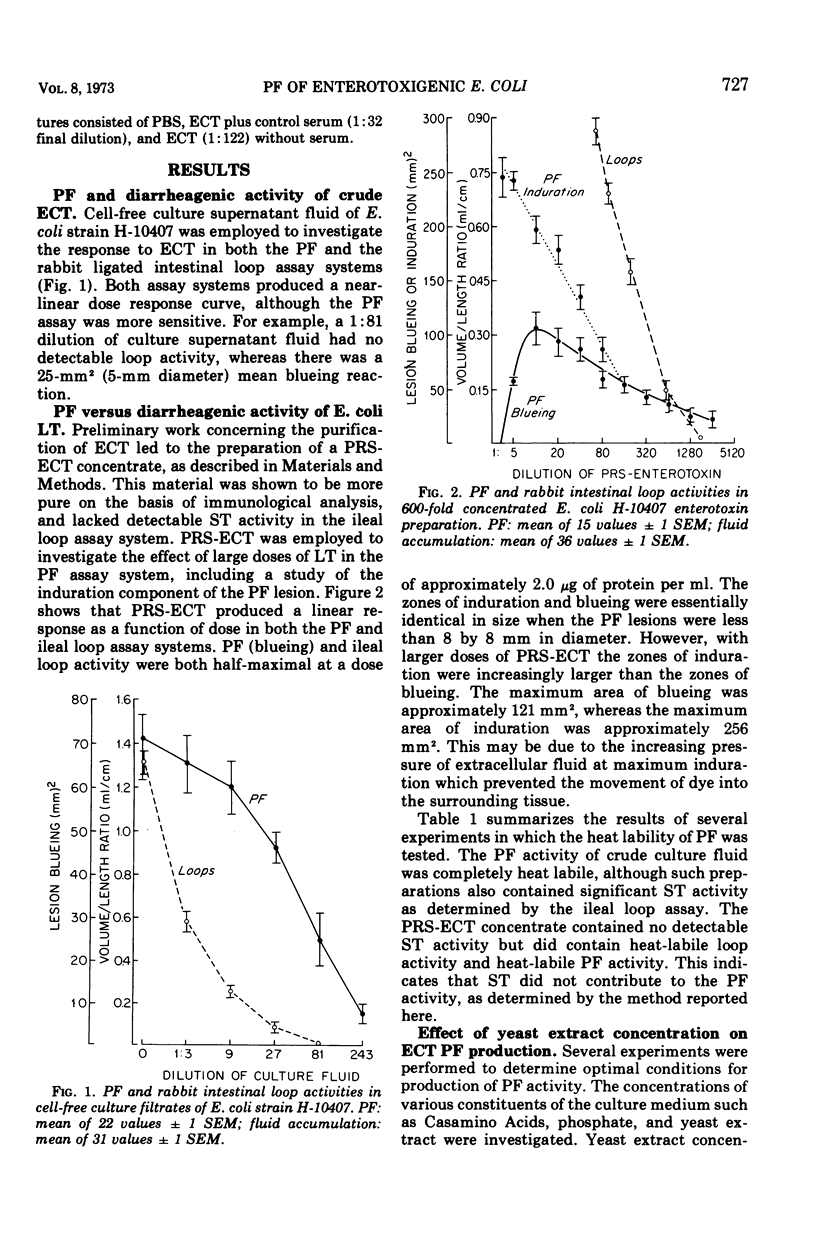
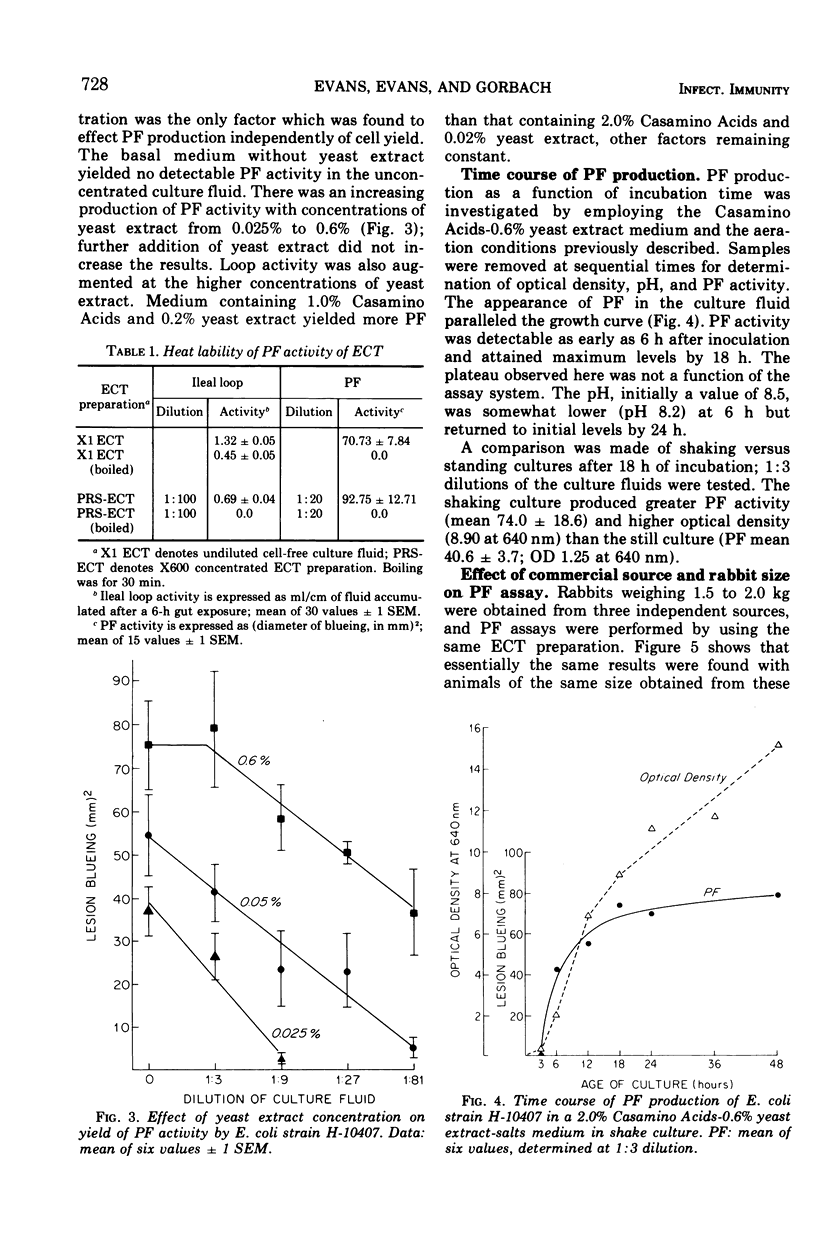
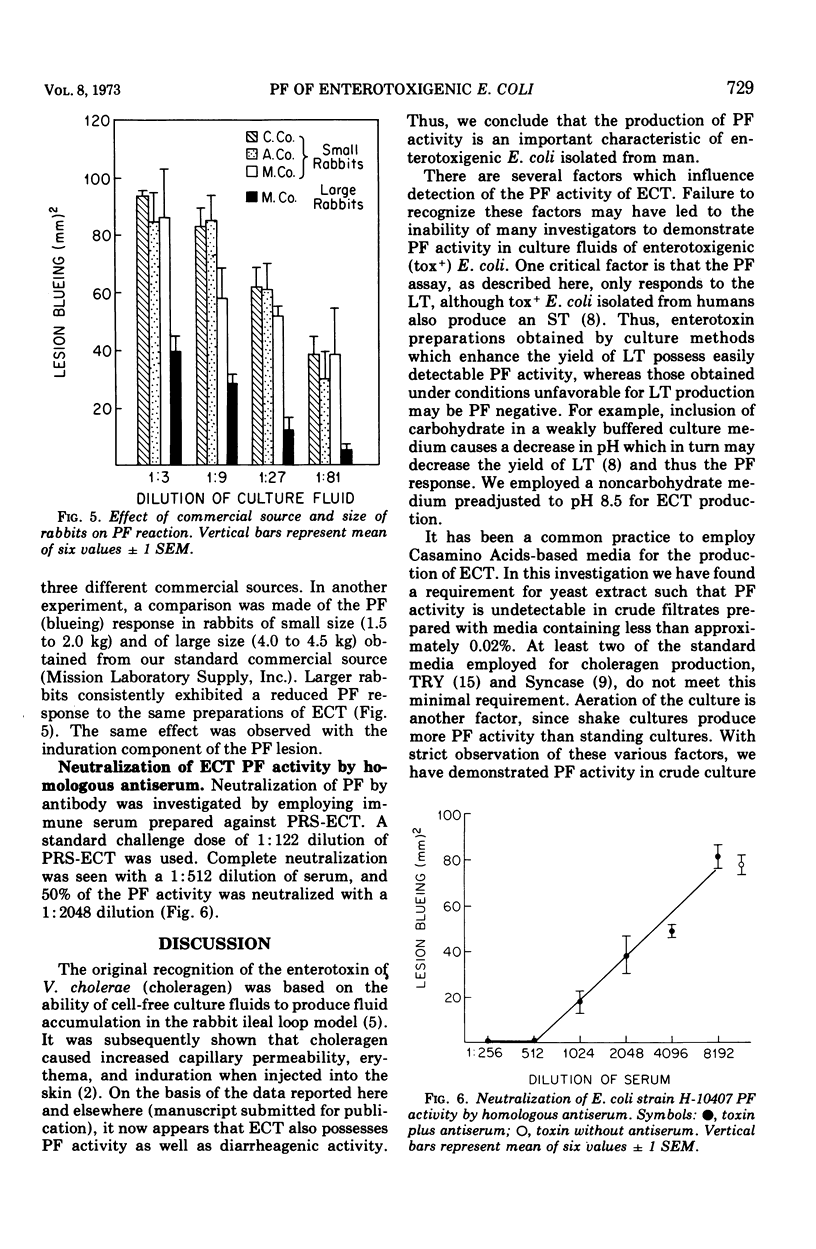
Enterotoxin preparations derived from Escherichia coli strain H-10407 were shown to contain vascular permeability factor (PF) activity as well as diarrheagenic activity. Intradermal injection of E. coli enterotoxin (ECT) caused localized induration and permeability of small blood vessels of the skin to intravenously administered Evans blue dye. The PF assay described here demonstrated a linear dose response and was at least as sensitive as the adult rabbit ileal loop assay for detecting ECT. E. coli PF activity was heat labile and was neutralized by homologous antiserum. PF production was enhanced by the addition of yeast extract (up to 0.6%) to a Casamino Acids-salts medium. PF activity was detectable as early as 6 h in aerated (shake) cultures in the Casamino Acids-yeast extract-salts medium, pH 8.5, maximal at 18 h and essentially unchanged at 48 h. The skin test (PF) assay for ECT has numerous advantages over current assay methods which involve gastrointestinal challenge of experimental animals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpenter C. C. Cholera and other enterotoxin-related diarrheal diseases. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):551–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., GHOSE M. L., SEN A. Activities of bacteria-free preparations from Vibrio cholerae. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:373–380. doi: 10.1002/path.1700790219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkin S., Gorbach S. L. Studies on enterotoxin from Escherichia coli associated with acute diarrhea in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Chatterjee B. D., Jacobs B., Sack R. B. Acute undifferentiated human diarrhea in the tropics. I. Alterations in intestinal micrflora. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):881–889. doi: 10.1172/JCI106560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Aziz K. M. Serological evidence for the identity of the vascular permeability factor and ileal loop toxin of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):243–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R. C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):378–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerman F. J., Formal S. B., Falkow S. Plasmid-associated enterotoxin production in a strain of Escherichia coli isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):622–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.622-624.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



