Abstract
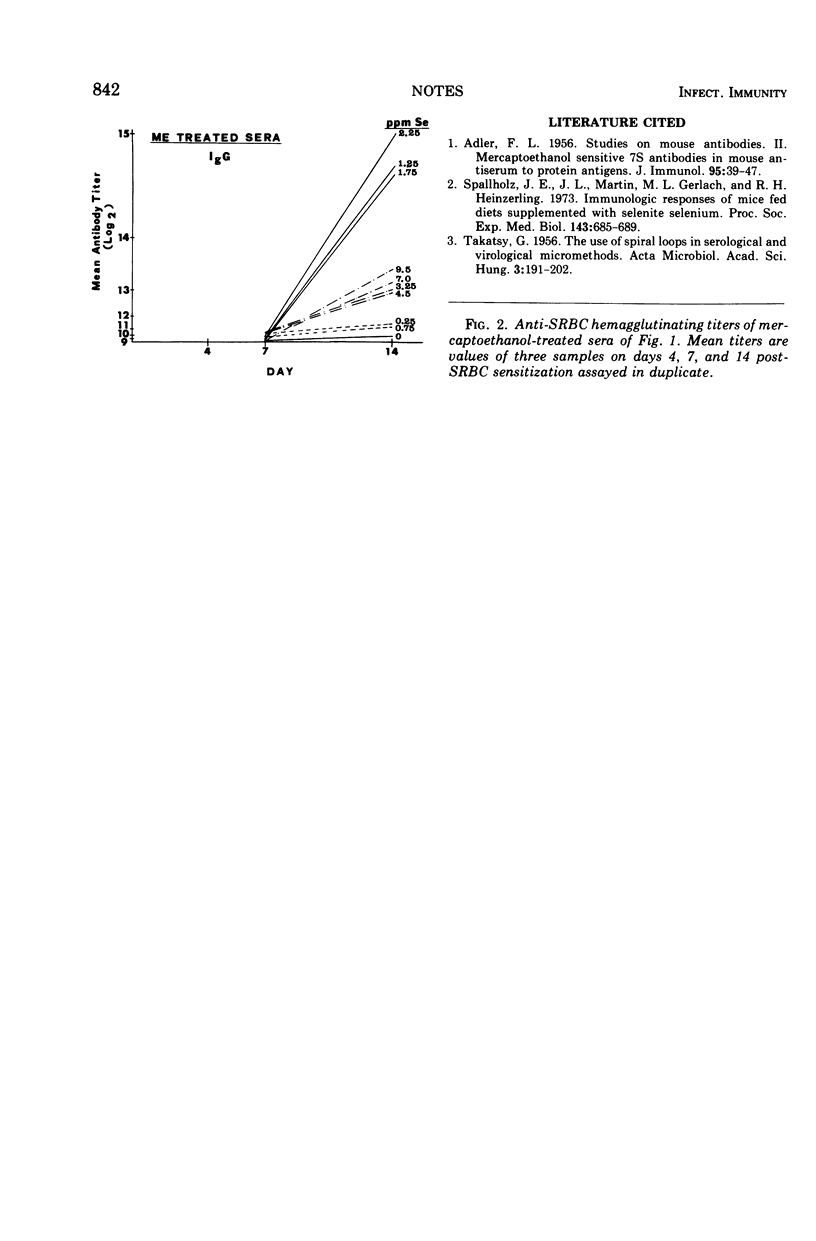
Mice fed diets supplemented with selenium (sodium selenite) immunologically respond to the sheep red blood cell antigen by producing enhanced immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibody titers.
Full text
PDF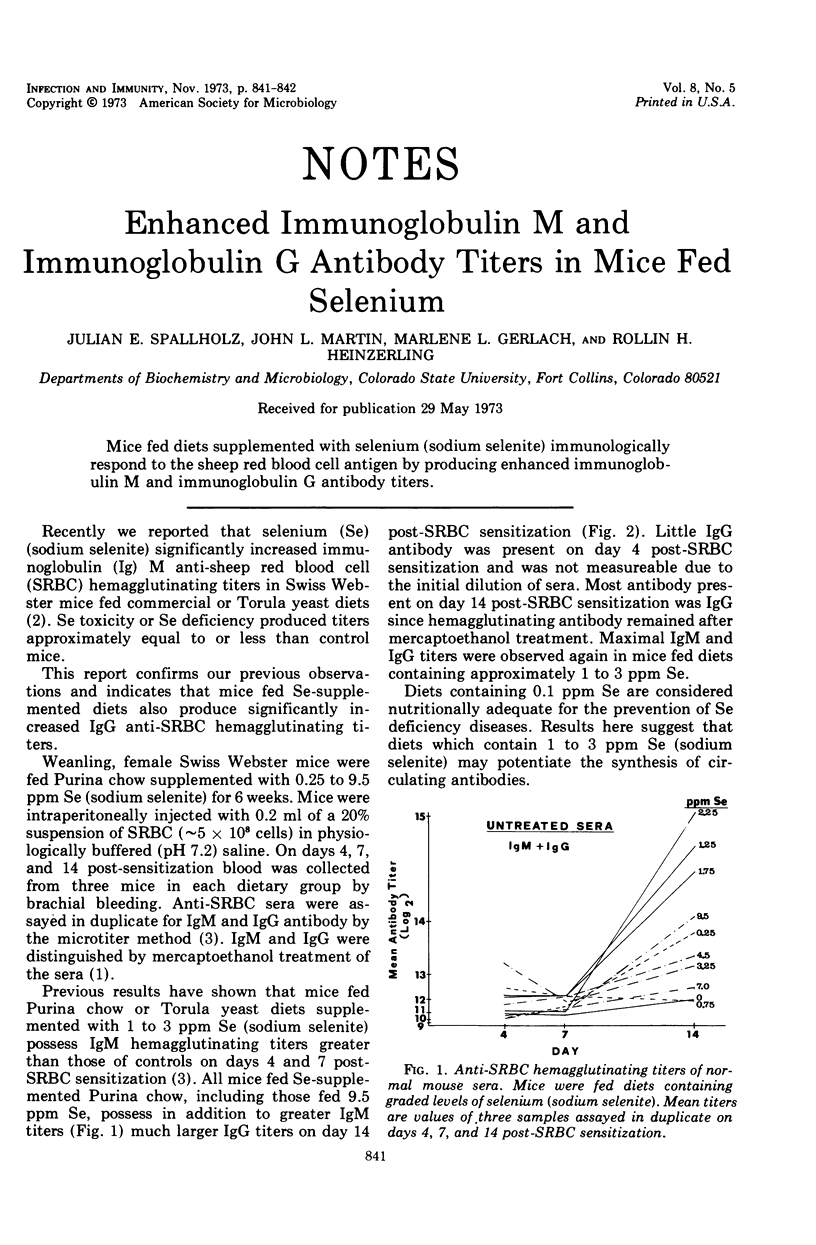
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER F. L. STUDIES ON MOUSE ANTIBODIES. II. MERCAPTOETHANOL-SENSITIVE 7 S ANTIBODIES IN MOUSE ANTISERA TO PROTEIN ANTIGENS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spallholz J. E., Martin J. L., Gerlach M. L., Heinzerling R. H. Immunologic responses of mice fed diets supplemented with selenite selenium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jul;143(3):685–689. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKATSY G. The use of spiral loops in serological and virological micro-methods. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



