Abstract
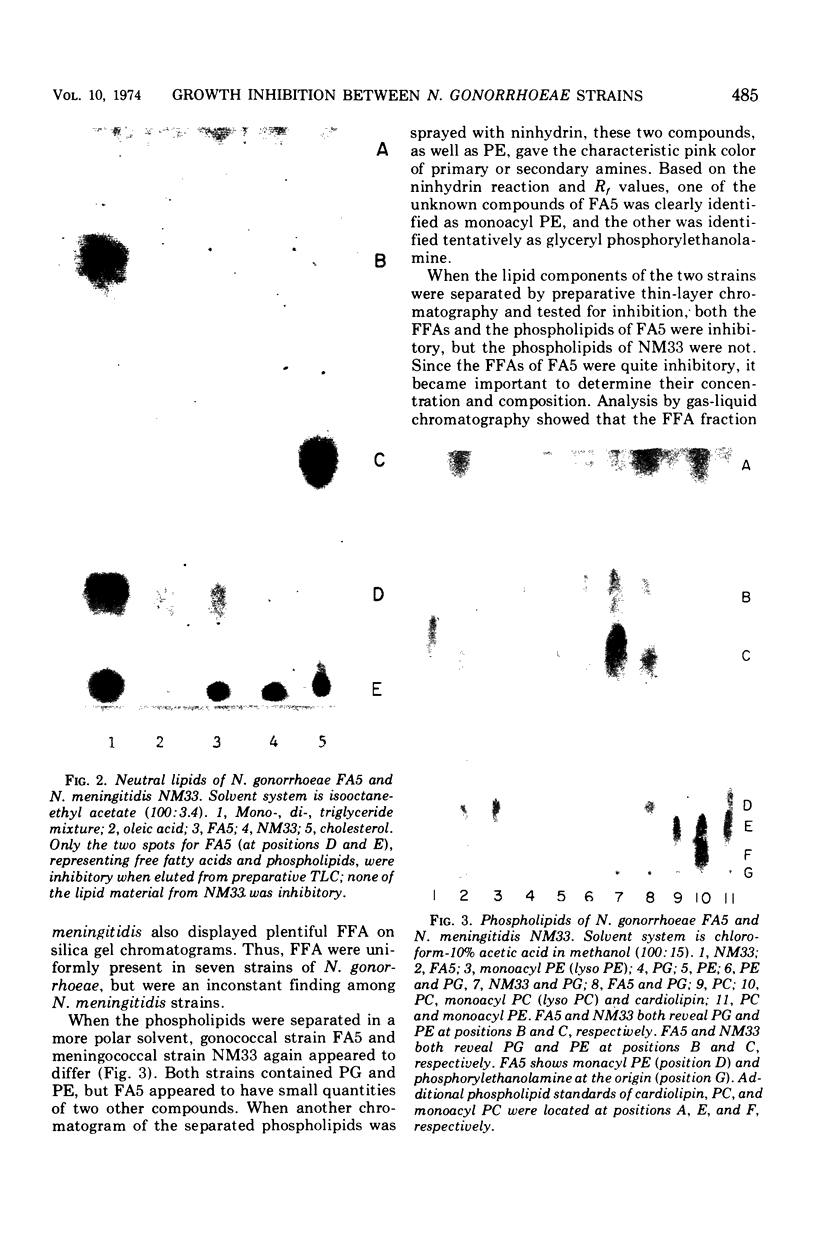
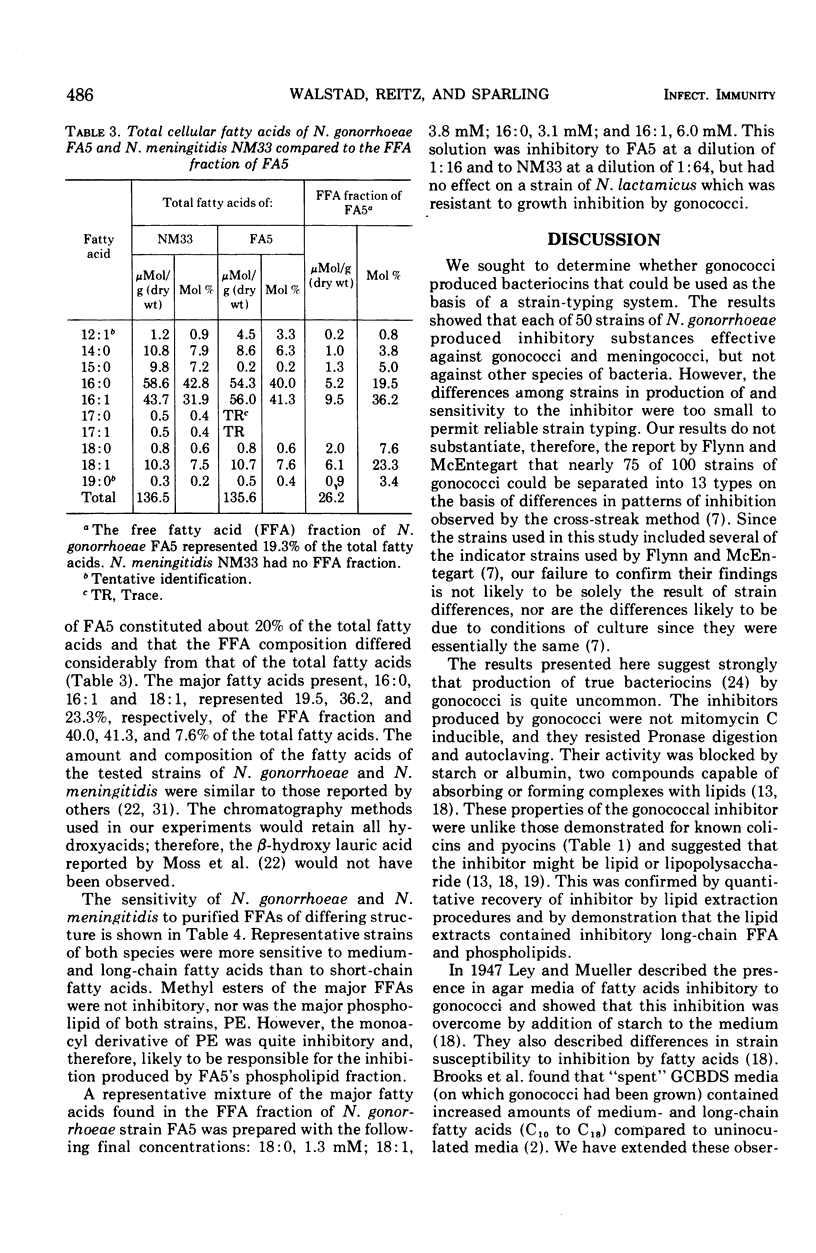
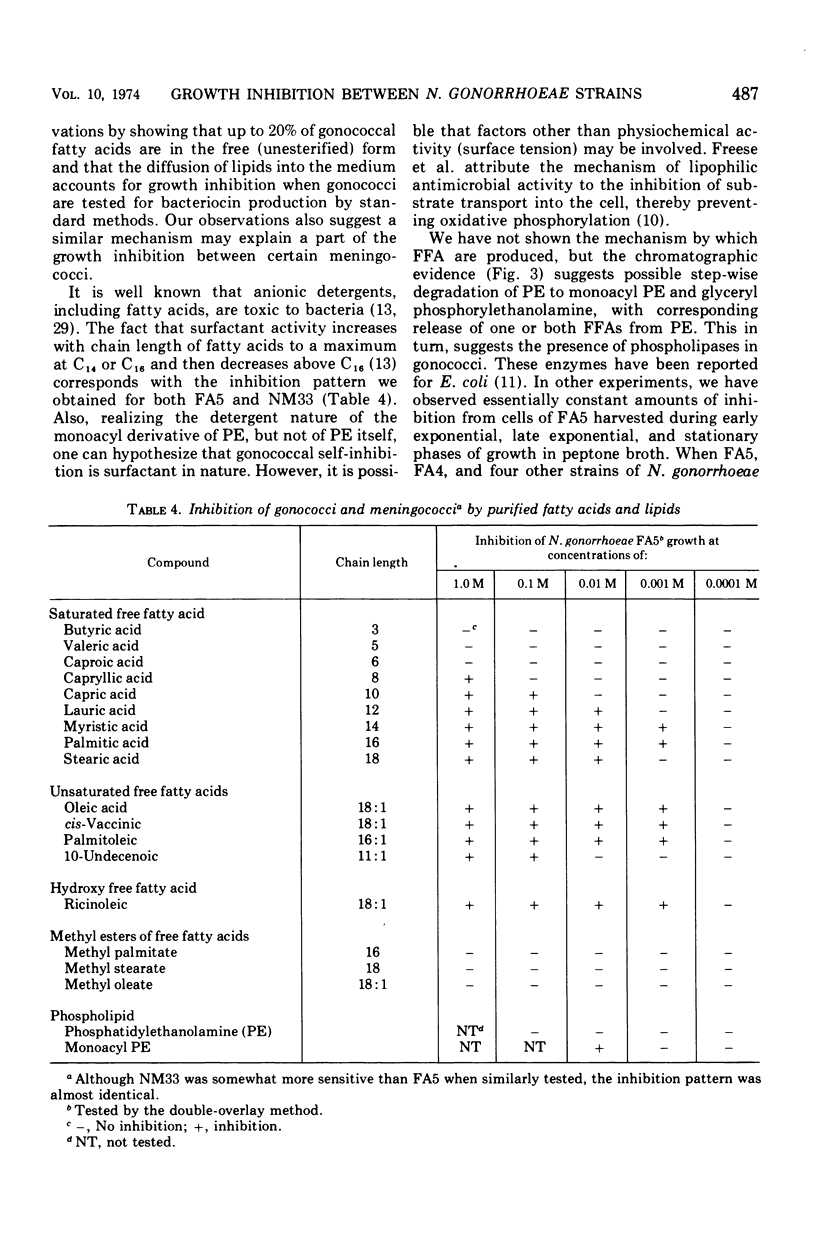
Each of 50 tested strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae produced growth-inhibitory substances that were active against most strains of gonococci or meningococci, but not against species other than the Neisseria. There were quantitative differences among different strains in production of the inhibitor and sensitivity to it, but not of sufficient magnitude to permit routine strain typing. The inhibitor was associated with the cell pellet (crude cell envelope) and was not inducible with mitomycin C. Inhibitory activity was thermostable and resisted alkali and proteolytic enzymes. The inhibitor was quantitatively recovered from whole cells by chloroform-methanol extraction. Separation of total gonococcal lipids by silica gel chromatography revealed inhibitory activity in both the free fatty acid and the phospholipid fractions. The major phospholipid, phosphatidylethanolamine, had no inhibitory activity, but monoacyl phosphatidylethanolamine, a minor phospholipid, was quite inhibitory. It is likely that the “bacteriocin” of N. gonorrhoeae strains results from the degradation of phosphatidylethanolamine to inhibitory long-chain free fatty acids and monoacyl phosphatidylethanolamine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Thacker L., Turner E. M. Analysis by gas chromatography of fatty acids found in whole cultural extracts of Neisseria species. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Apr;17(4):531–543. doi: 10.1139/m71-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Herman L. G. Epidemiological fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the production of and sensitivity of pyocin and bacteriophage. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):760–765. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.760-765.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J., McEntegart M. G. Bacteriocins from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and their possible role in epidemiological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):60–61. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Sheu C. W., Galliers E. Function of lipophilic acids as antimicrobial food additives. Nature. 1973 Feb 2;241(5388):321–325. doi: 10.1038/241321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARBUS J., DELUCA H. F., LOOMANS M. E., STRONG F. M. The rapid incorporation of phosphate into mitochondrial lipids. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman H. N. SURFACE ACTIVE AGENTS AND THEIR APPLICATION IN BACTERIOLOGY. Bacteriol Rev. 1948 Jun;12(2):105–148. doi: 10.1128/br.12.2.105-148.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson R. I. Typing the gonococcus. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 11;3(5714):107–107. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5714.107-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Turner E. M., Callaway C., Lee L., Martin J. E. Particulate Fractions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):624–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.624-632.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T. Bacteriocin production by strains of Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1696–1699. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1696-1699.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley H. L., Jr, Mueller J. H. On the Isolation from Agar of an Inhibitor for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1946 Oct;52(4):453–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.4.453-460.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A. Antibodies in human sera against antigens in gonococci, demonstrated by a passive haemolysis test. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;67(1):102–110. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.67.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A., Kristoffersen T., Hofstad T. Immunochemical investigations on neisseria gonorrhoeae endotoxin. 2. Serological multispecificity and other properties of phenol-water preparations. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Farshy D. C., Lambert M. A., Thayer J. D. Cellular fatty acids of pathogenic Neisseria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.63-68.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. F., LANDS W. E. Positional specificites in phospholipid hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz R. C. Phosphatidyl choline species in Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;260(4):654–665. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Bacterial growth and the cell envelope. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):194–214. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.194-214.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu C. W., Freese E. Lipopolysaccharide layer protection of gram-negative bacteria against inhibition by long-chain fatty acids. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.869-875.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. A., KELLOGG D. S., Jr NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE IDENTIFICATION IN DIRECT SMEARS BY A FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY-COUNTERSTAIN METHOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:171–174. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.171-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAKAWA T., UETA N. GASCHROMATOGRAPHIC STUDIES OF MICROBIAL COMPONENTS. I. CARBOHYDRATE AND FATTY ACID CONSTITUTION OF NEISSERIA. Jpn J Exp Med. 1964 Dec;34:361–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






