Abstract
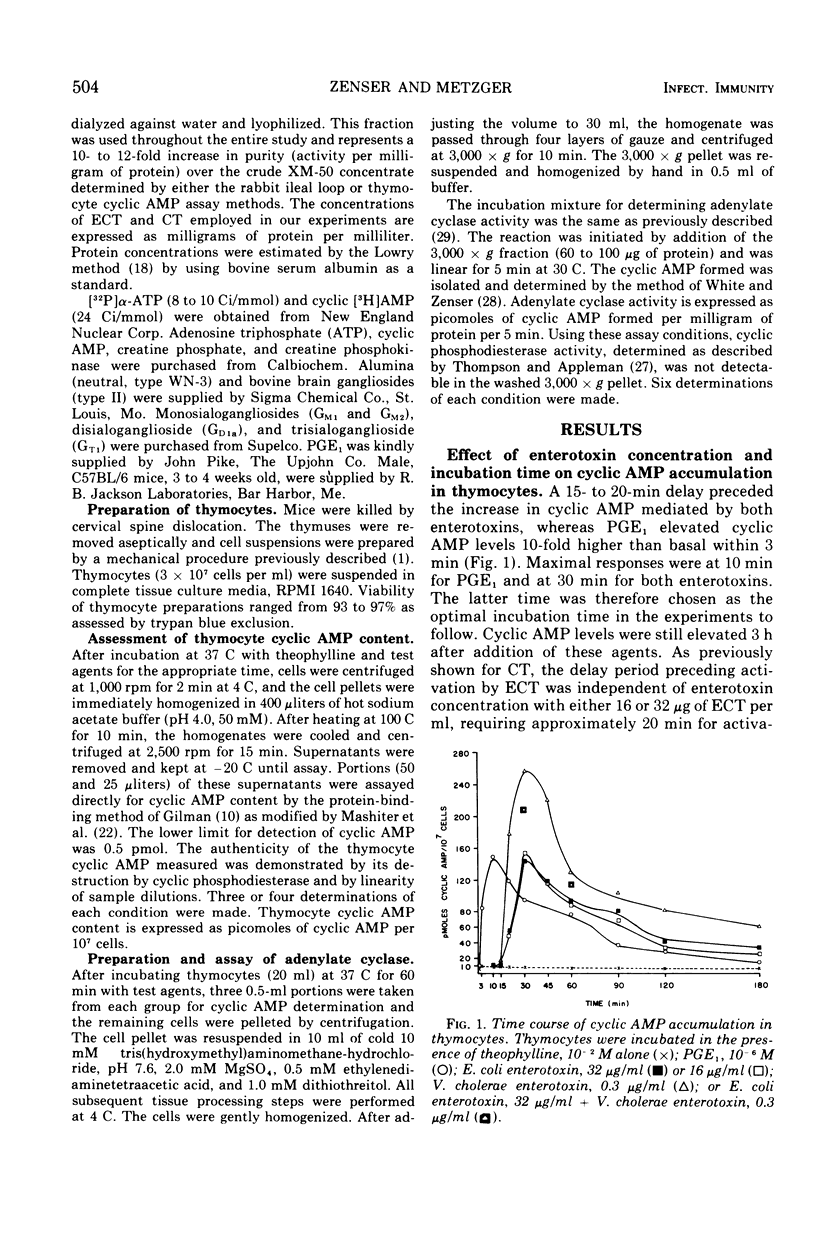
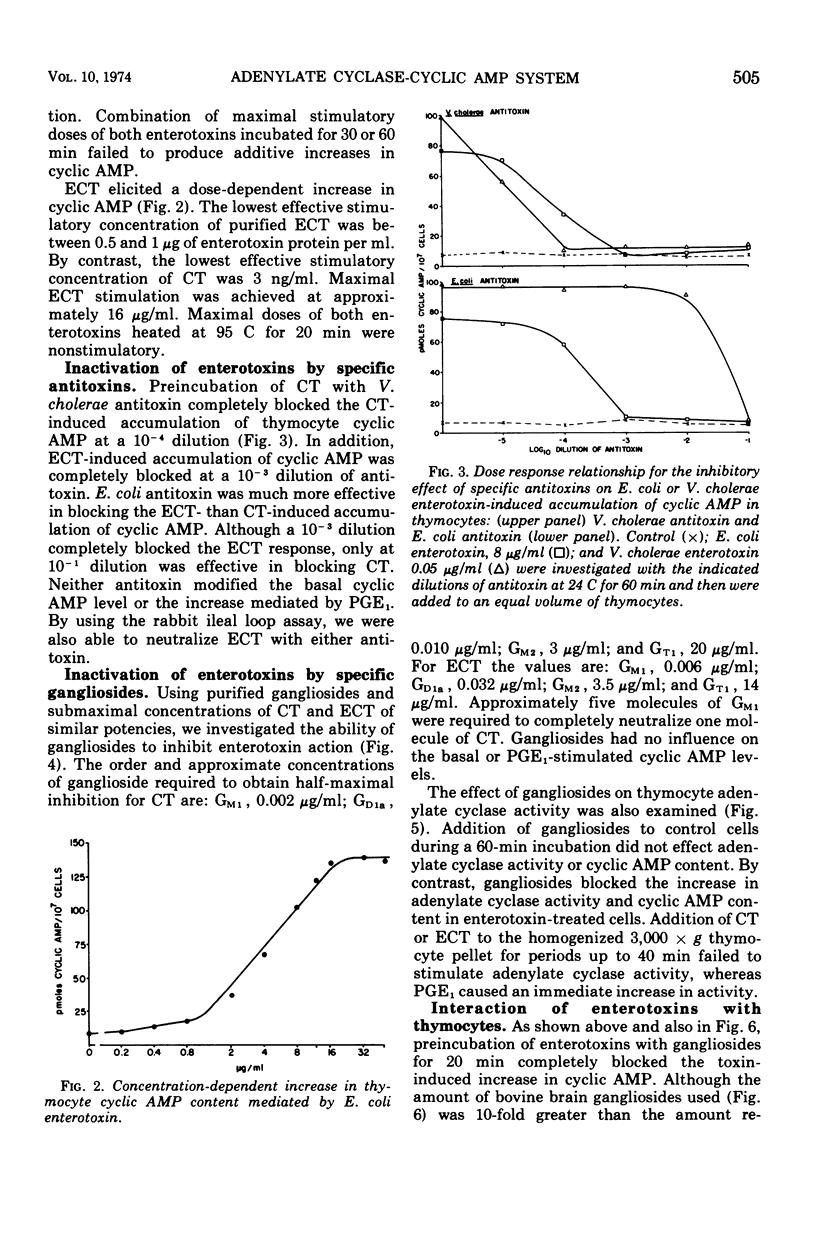
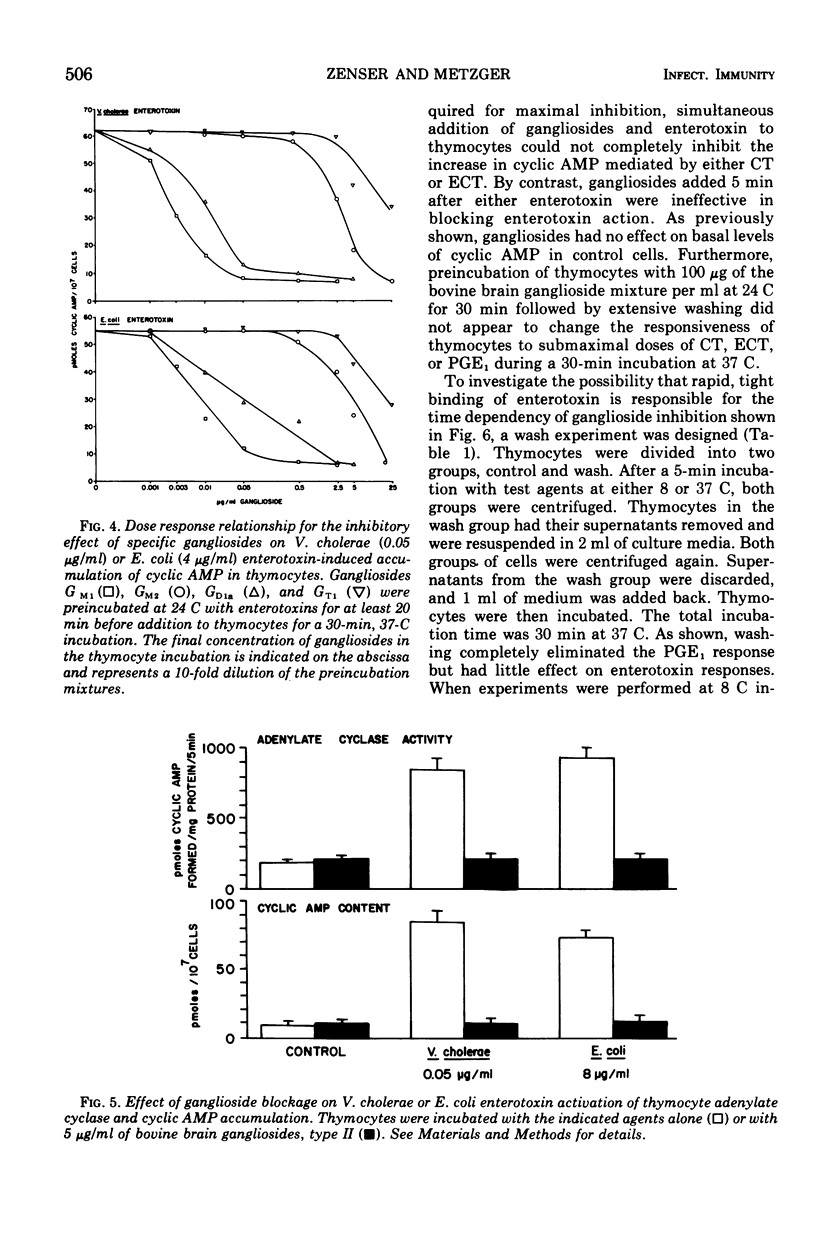
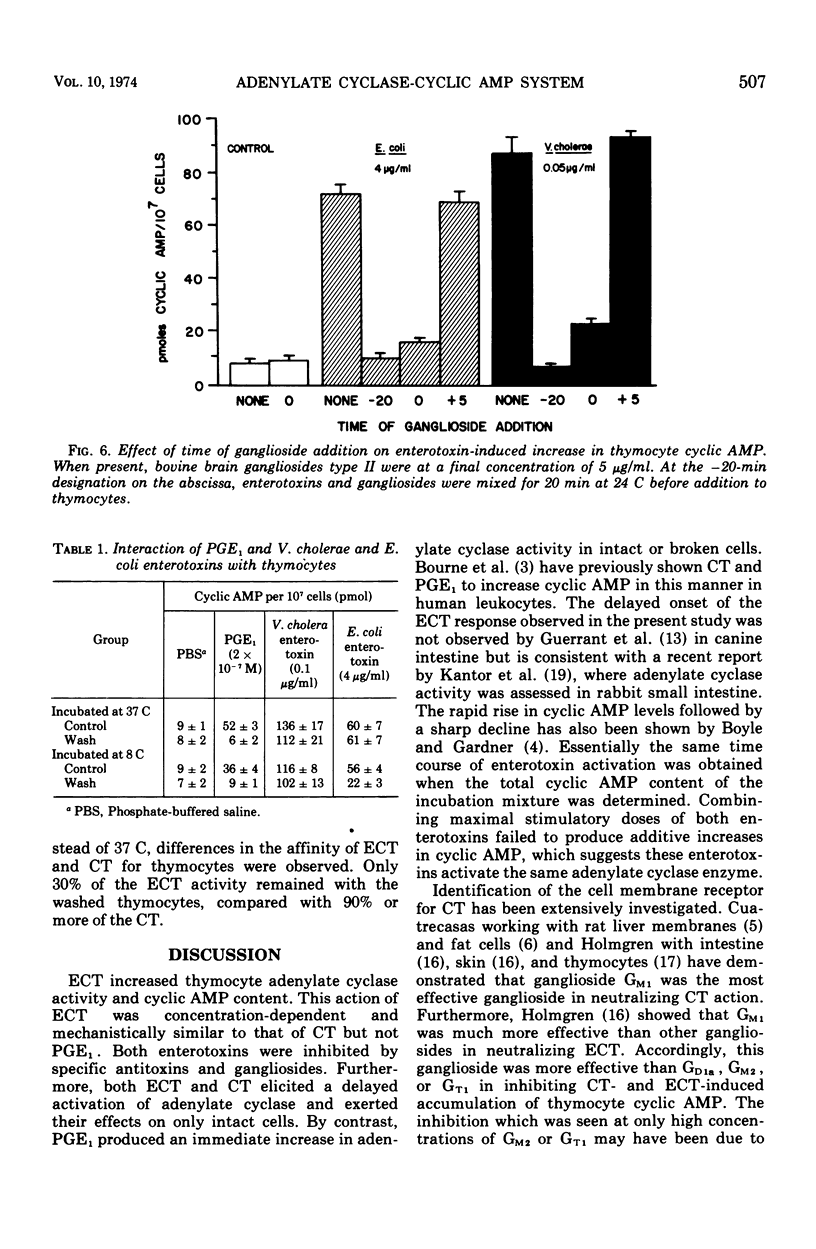
Mouse thymocytes were used to compare mechanisms by which Vibrio cholerae and heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxins activate the adenylate cyclase-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) system. Both enterotoxins had their time-delayed increase in cyclic AMP neutralized by antisera to V. cholerae or E. coli enterotoxin, blocked by low concentrations of ganglioside GM1, and destroyed by prior heating. Enterotoxin activation of adenylate cyclase was similarly affected. By contrast, prostaglandin E1-mediated increases in cyclic AMP were not affected by specific antitoxins or gangliosides. Combination of maximal stimulatory doses of both enterotoxins did not produce additive increases in cyclic AMP. Wash experiments suggested that both enterotoxins bind rapidly and tightly to thymocytes at 37 C. However, lowering the incubation temperature to 8 C reduced the affinity of E. coli enterotoxin but not cholera toxin for thymocytes. Results suggest that heat-labile E. coli enterotoxin and cholera enterotoxin may activate the same adenylate cyclase enzyme by similar mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler W. H., Takiguchi T., Marsh B., Smith R. T. Cellular recognition by mouse lymphocytes in vitro. I. Definition of a new technique and results of stimulation by phytohemagglutinin and specific antigens. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1049–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. Adenyl cyclase in fat cells. II. Hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3477–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lehrer R. I., Lichtenstein L. M., Weissmann G., Zurier R. Effects of cholera enterotoxin on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and neutrophil function. Comparison with other compounds which stimulate leukocyte adenyl cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):698–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI107231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. M., Gardner J. D. Sequence of events mediating the effect of cholera toxin on rat thymocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1149–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI107653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Khurana C. M. Toxigenic Escherichia coli: a cause of infantile diarrhea in Chicago. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 19;287(16):791–795. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210192871603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Miller O. V. Specific prostaglandin E1 and A1 binding sites in rat adipocyte plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 16;323(4):560–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Ganguly U., Casper A. G., Moore E. J., Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C. Effect of Escherichia coli on fluid transport across canine small bowel. Mechanism and time-course with enterotoxin and whole bacterial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1707–1714. doi: 10.1172/JCI107352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Relationships among heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindholm L., Lönnroth I. Interaction of cholera toxin and toxin derivatives with lymphocytes. I. Binding properties and interference with lectin-induced cellular stimulation. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):801–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Tao P., Gorbach S. L. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin: comparison of strains from an infant and an adult with diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Gershon E., Henderson A. Effects of prostaglandins and cholera enterotoxin on intestinal mucosal cyclic AMP accumulation. Evidence against an essential role for prostaglandins in the action of toxin. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):941–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI107635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashiter K., Mashiter G. D., Hauger R. L., Field J. B. Effects of cholera and E. coli enterotoxins on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels and intermediary metabolism in the thyroid. Endocrinology. 1973 Feb;92(2):541–549. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-2-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. Differential inhibitory effects of cholera toxoids and ganglioside on the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):1009–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R. C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):378–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Appleman M. M. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. A., Zenser T. V. Separation of cyclic 3',5'-nucleoside monophosphates from other nucleotides on aluminum oxide columns. Application to the assay of adenyl cyclase and guanyl cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):372–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenser T. V., DeRubertis F. R., Curnow R. T. Effects of prostaglandins on hepatic adenylate cyclase activity and cyclic adenosine 3',5',-monophosphate content. Endocrinology. 1974 May;94(5):1404–1410. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-5-1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



