Abstract
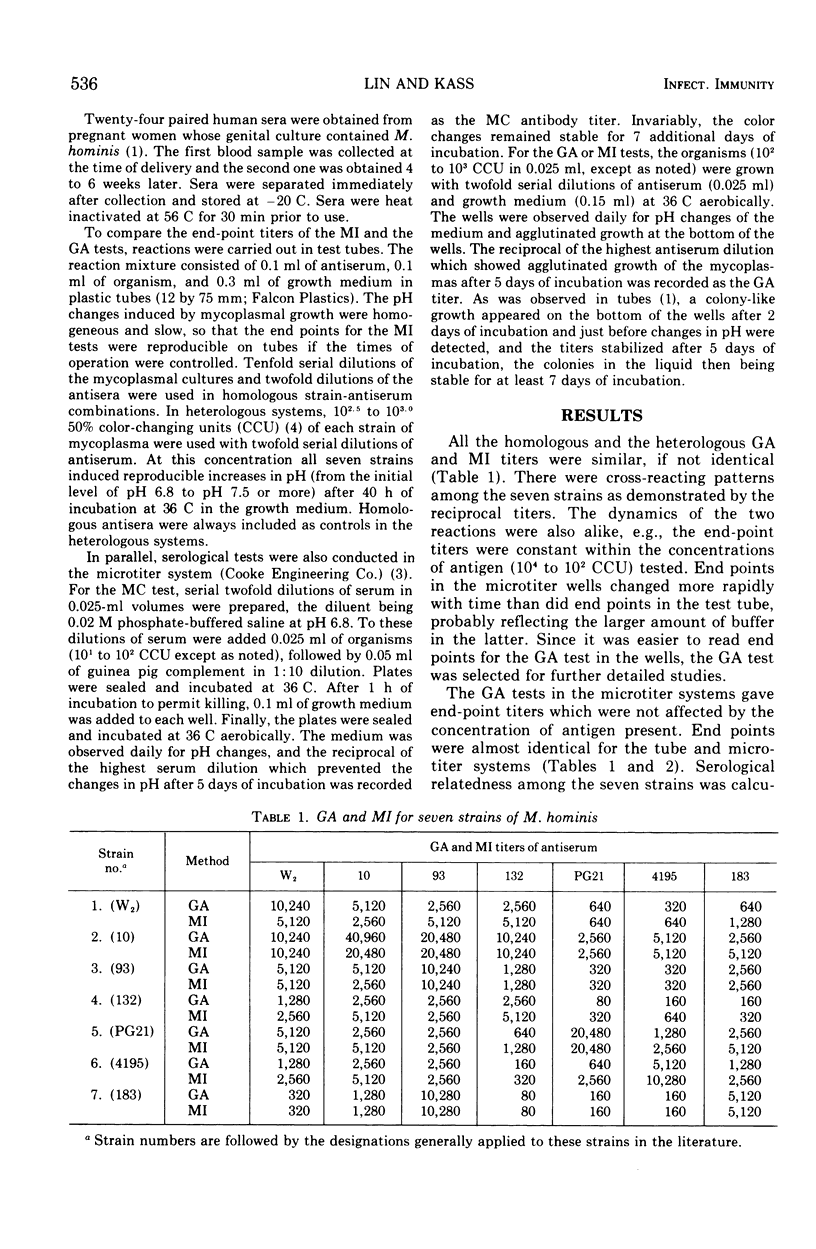
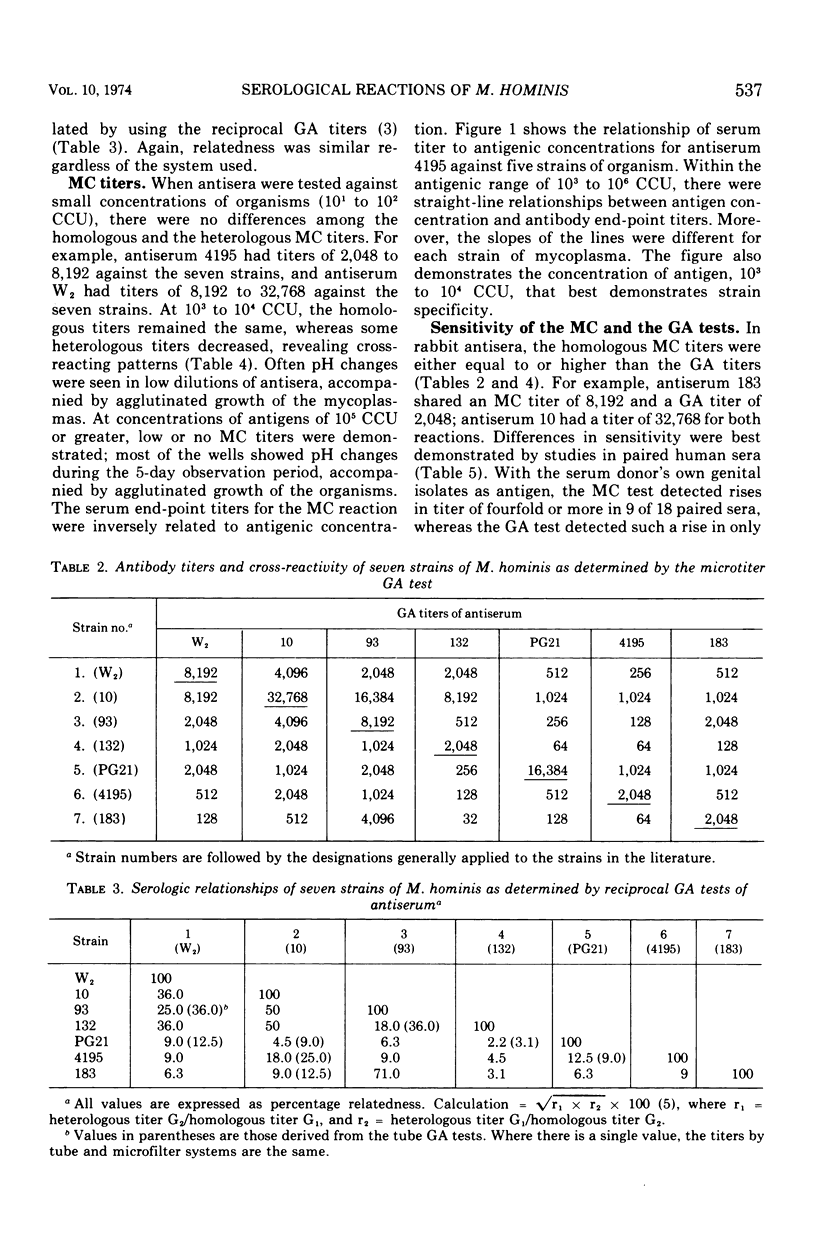
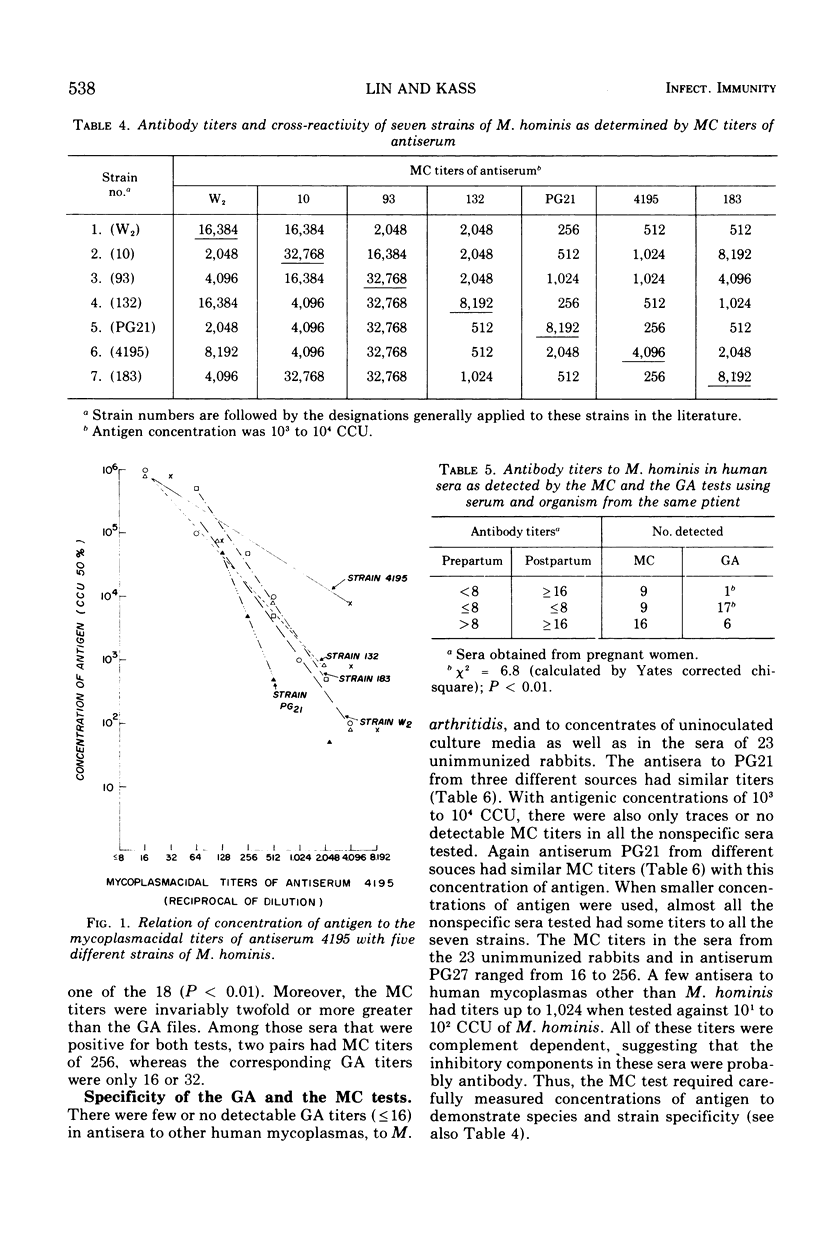
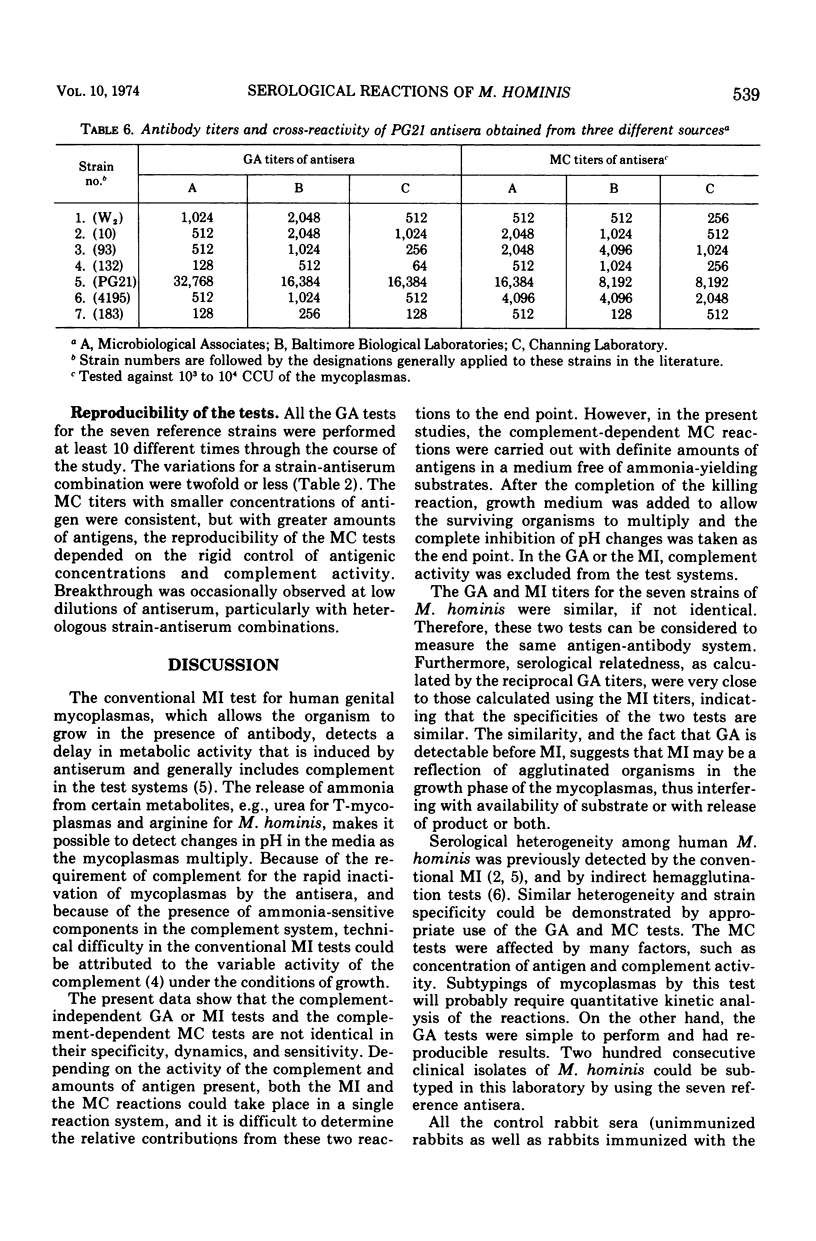
Seven strains of Mycoplasma hominis from human genital tracts were selected to produce antisera. The complement-dependent mycoplasmacidal (MC) activity and two complement-independent activities, metabolic inhibition (MI) and agglutination during growth (GA), of these sera were compared. The GA and MI tests were equivalent in titer and generally not affected by concentration of antigen; they revealed specific cross-reacting patterns among the seven strains. There was little if any cross-reactivity with antisera to other human mycoplasmas or to Mycoplasma arthritidis. Control sera from unimmunized rabbits and sera against concentrated uninoculated culture media were also nonreactive. On the other hand, the sensitivity and specificity of the MC test were affected by the concentration of antigen: at about 102 color-changing units (CCU) of antigen, all strains were equivalently cross-reactive against the seven antisera, but at 102 to 104 CCU the individual strain specificity appeared, whereas at about 105 CCU little or no antibody was detectable by MC. The MC tests with the lowest concentrations of antigen gave the highest titers of antibody, but at such low concentrations of antigen there was not only loss of individual strain specificity but also some cross-reactivity against other human mycoplasmas, M. arthritidis, or control rabbit sera. Studies with paired human sera also indicate that the MC test with small amounts of antigen is more sensitive than GA-MI.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun P., Lee Y. H., Klein J. O., Marcy S. M., Klein T. A., Charles D., Levy P., Kass E. H. Birth weight and genital mycoplasmas in pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jan 28;284(4):167–171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197101282840401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. Antigenic differences within the species Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):469–477. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Kass E. H. Immune inactivation of T-strain mycoplasmas. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jul-Aug;122(1):93–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.1-2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Kendrick M. I., Kass E. H. Serologic typing of human genital T-mycoplasmas by a complement-dependent mycoplasmacidal test. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., LUDWIG W. M., PURCELL R. H., MUFSON M. A., CHANOCK R. M. SIGNIFICANCE OF ANTIBODY TO MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS TYPE 1 AS MEASURED BY INDIRECT HEMAGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Apr;118:1073–1083. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-30049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


